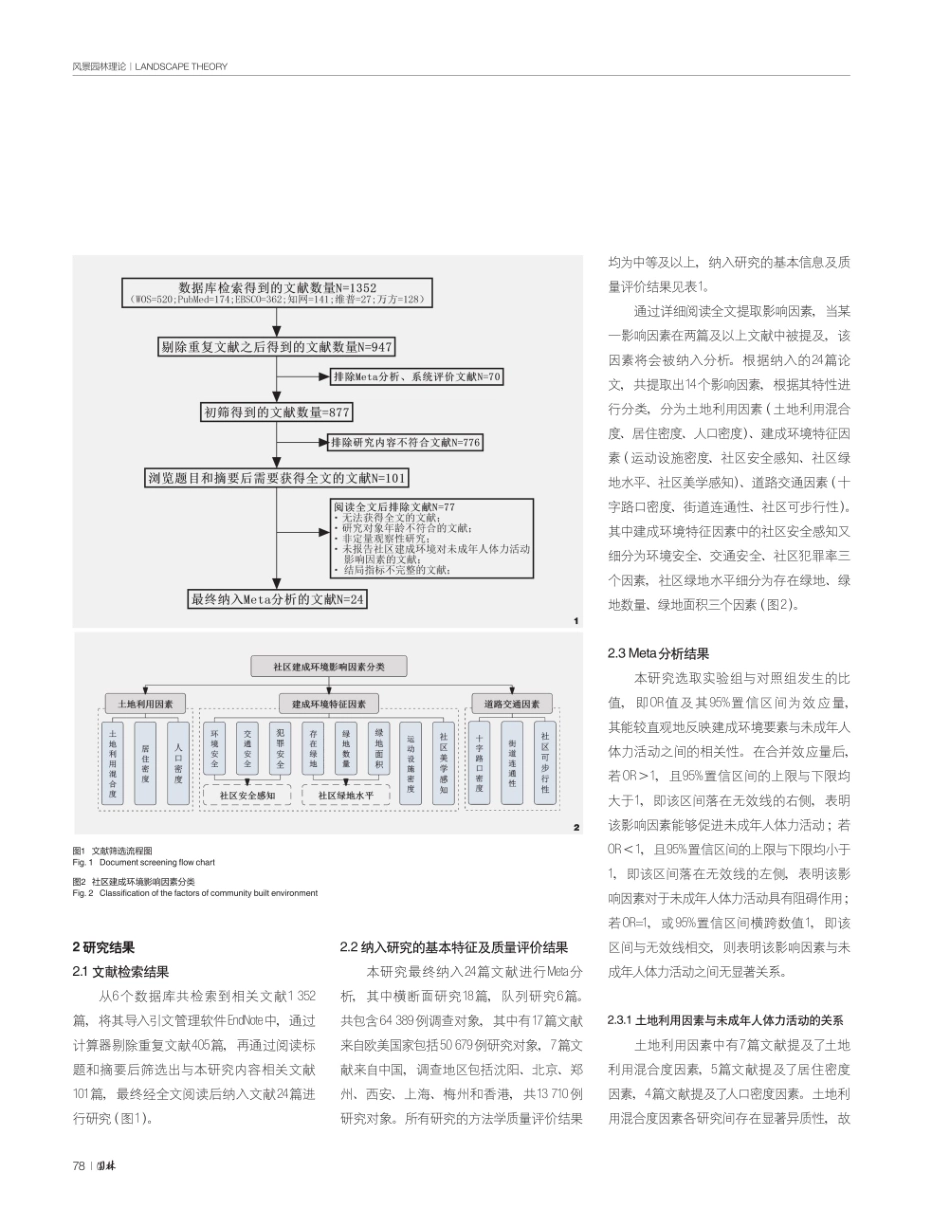
园林,2024,41(01):76-84.未成年人体力活动社区建成环境影响因素的Meta分析AMeta-analysisonCommunityBuiltEnvironmentalFactorsonthePhysicalActivityofMinors刘佳欣,吴晨虹李房英邱淇钰”LIUJiaxin'WUChenhong'LIFangying"”QIUQiyu?(1.福建农林大学风景园林与艺术学院,福州350100;2.香港理工大学设计学院,香港999077)(1.CollegeofLandscapeArchitectureandArt,FujianAgricultureofForestryUniversity,Fuzhou,Fujian,China,350100;2.SchoolofDesign,HongKongPolytechnicUniversity,HongKong,China,999077)文章编号:1000-0283(2024)01-0076-09DOl:10.12193/j.laing.2024.01.0076.009中图分类号:TU986文献标志码:A收稿日期:2023-09-08修回日期:2023-10-30摘要已有研究证明了社区建成环境与未成年人体力活动之间的关系,为更加科学系统地评价社区建成环境因素对未成年人体力活动的影响,通过检索CNKI及WebofScience等国内外主流数据库相关文献,共纳人24篇文献进行Meta分析。结果显示:社区建成环境中的诸多因素对未成年人体力活动均能起到促进作用。归纳出14项影响因素,根据影响程度从大到小依次为:土地利用混合度、绿地数量、街道连通性、社区存在绿地、绿地面积、居住密度、环境安全感知、交通安全感知、社区可步行性。而在本研究中,设施密度、社区美学感知、十字路口密度三个因素对未成年人体力活动影响不显著。通过比较分析了建成环境因素对未成年人体力活动的影响程度与机制,提供了更加科学的量化数据,旨在为未来社区规划建设以及该领域相关研究者提供科学参考。关键词风景园林;建成环境;未成年人;体力活动;影响因素;社区规划AbstractPreviousstudieshaveprovedtherelationshipbetweencommunitybuiltenvironmentandthephysicalactivityofminors.Inordertosystematicallyevaluatetheimpactofcommunitybuiltenvironmentfactorsonminors'physicalactivitymorescientifically,mainstreamdatabasesathomeandabroad,suchasWebofScienceandCNKI,andincludedatotalof24literaturesformeta-anal-ysis.Theresultsshowthatmanyfactorsinthecommunitybuiltenvironmentcanpromotethephysicalactivityofminors.Atotalof14influencingfactorsweresummarizedinthisstudy.Inorderofinfluencedegree,theywere:landusemixingdegree,amountofgreenspace,streetconnectivity,presenceofgreenspaceinthecommunity,areaofgreenspace,residential...