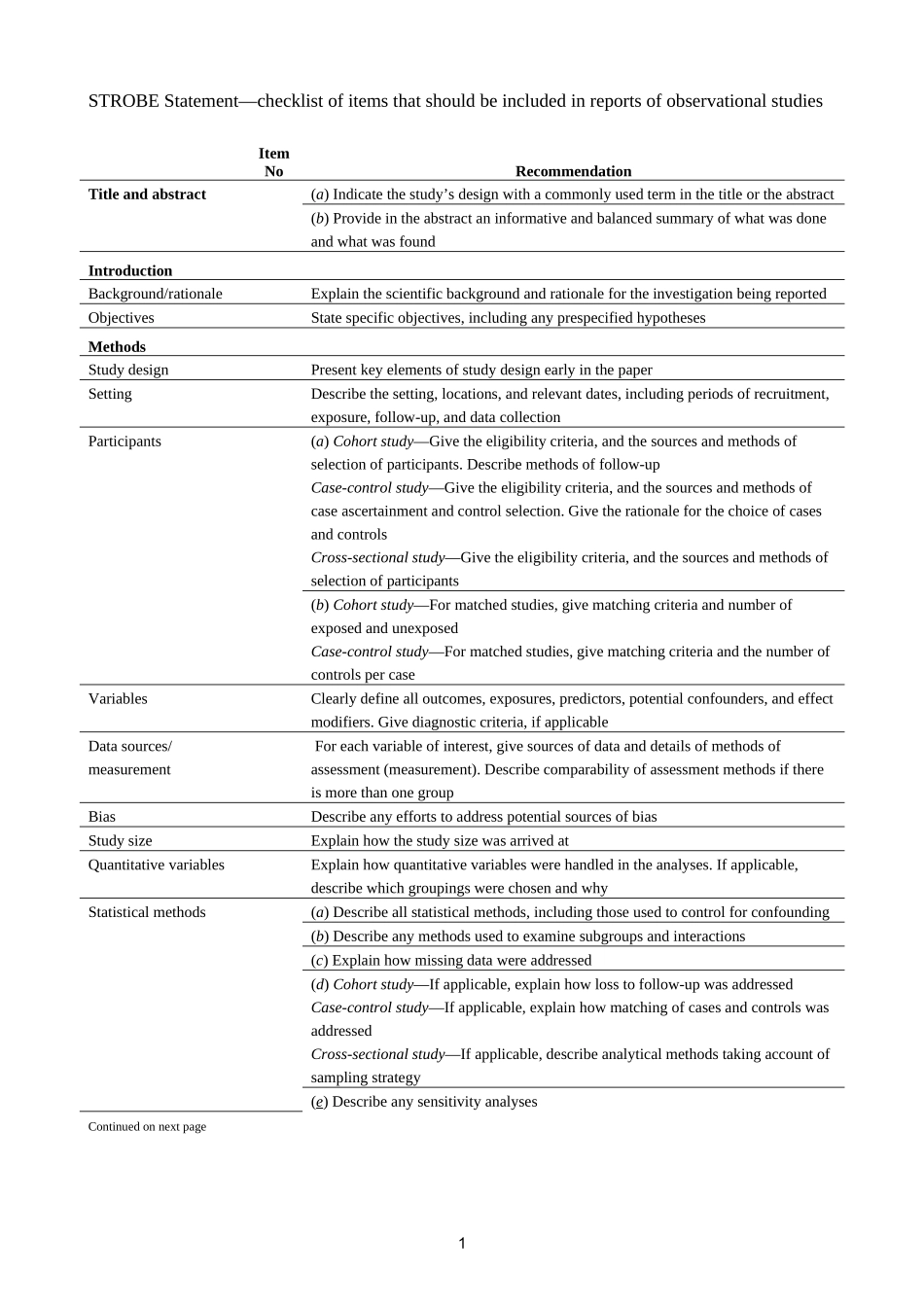
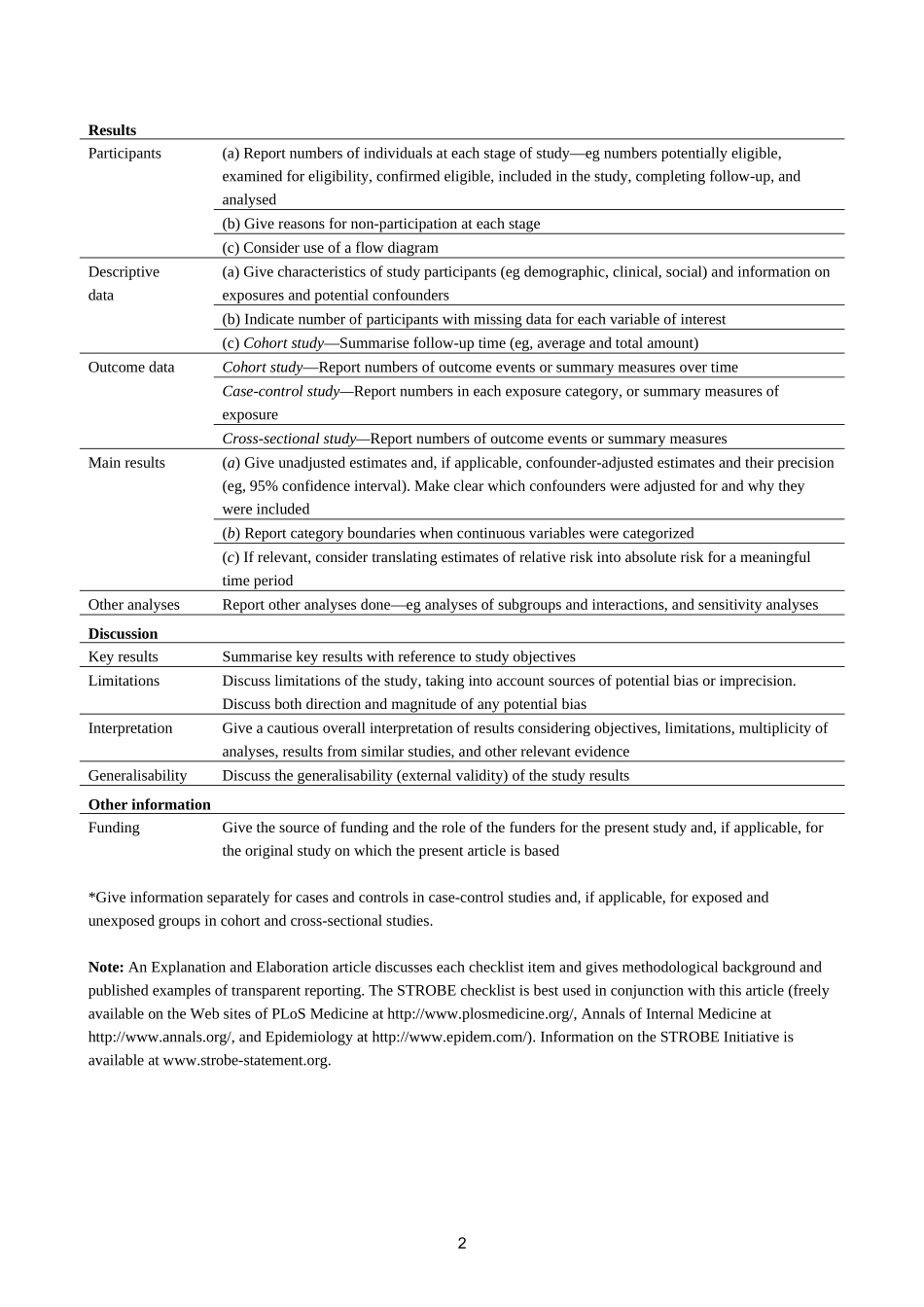
STROBEStatement—checklistofitemsthatshouldbeincludedinreportsofobservationalstudiesItemNoRecommendationTitleandabstract(a)Indicatethestudy’sdesignwithacommonlyusedterminthetitleortheabstract(b)ProvideintheabstractaninformativeandbalancedsummaryofwhatwasdoneandwhatwasfoundIntroductionBackground/rationaleExplainthescientificbackgroundandrationalefortheinvestigationbeingreportedObjectivesStatespecificobjectives,includinganyprespecifiedhypothesesMethodsStudydesignPresentkeyelementsofstudydesignearlyinthepaperSettingDescribethesetting,locations,andrelevantdates,includingperiodsofrecruitment,exposure,follow-up,anddatacollectionParticipants(a)Cohortstudy—Givetheeligibilitycriteria,andthesourcesandmethodsofselectionofparticipants.Describemethodsoffollow-upCase-controlstudy—Givetheeligibilitycriteria,andthesourcesandmethodsofcaseascertainmentandcontrolselection.GivetherationaleforthechoiceofcasesandcontrolsCross-sectionalstudy—Givetheeligibilitycriteria,andthesourcesandmethodsofselectionofparticipants(b)Cohortstudy—Formatchedstudies,givematchingcriteriaandnumberofexposedandunexposedCase-controlstudy—Formatchedstudies,givematchingcriteriaandthenumberofcontrolspercaseVariablesClearlydefinealloutcomes,exposures,predictors,potentialconfounders,andeffectmodifiers.Givediagnosticcriteria,ifapplicableDatasources/measurementForeachvariableofinterest,givesourcesofdataanddetailsofmethodsofassessment(measurement).DescribecomparabilityofassessmentmethodsifthereismorethanonegroupBiasDescribeanyeffortstoaddresspotentialsourcesofbiasStudysizeExplainhowthestudysizewasarrivedatQuantitativevariablesExplainhowquantitativevariableswerehandledintheanalyses.Ifapplicable,describewhichgroupingswerechosenandwhyStatisticalmethods(a)Describeallstatisticalmethods,includingthoseusedtocontrolforconfounding(b)Describeanymethodsusedtoexaminesubgroupsandinteractions(c)Explainhowmissingdatawereaddressed(d)Cohortstudy—Ifapplicable,explainhowlosstofollow-upwasaddressedCase-controlstudy—Ifapplicable,...