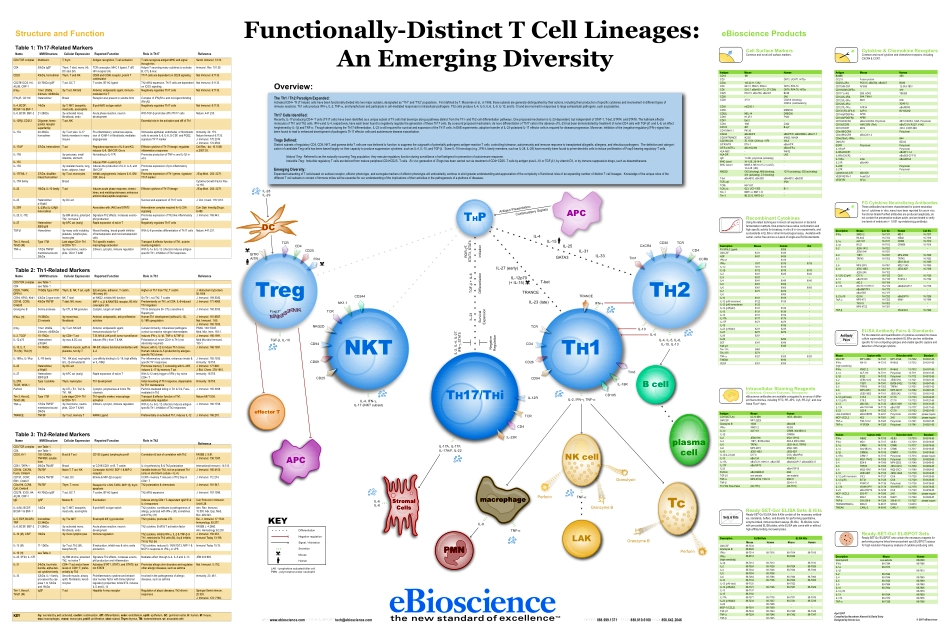
LAKGranzymeBPerforinStromalCellsNKcellPerforinGranzymeBGranulysinTcBcellplasmacellmacrophagePMNeffectorTAPCTregFoxp3+/-TH2IL-4,IL-5,IL-6,IL-10,IL-13NKTTH17/THiTH1IL-2,IFN-�,TNF-�IL-4IL-10IFN-�THPAPCDCGITR/AITRTCRCD4CD25CD25CD69CD94NKG2DTCRNK1.1CD244IL-12RTCRCD4IL-23RCD94CD26CD4TCRCD195IL-18RTim3TRANCETim1CXCR4CD30TCRCD4CCR8FR4CostimulatorySignalsAntigenPresentationIL-17A,IL-17F,IL-17A/F,IL-22TGF-�,IL-10IL-4,IFN-�,IL-17(iNKTsubset)TNF-�IL-8IL-23SurvivalExpansionTGF-�+IL-6DifferentiationIL-4IL-15IL-25IL-31IL-33IL-6IL-8TNF-�IL-28IL-29IL-27(early)IL-12p70(+IL-15)TRANCEIL-23(late)T-betGATA3ROR-�T,STAT3,STAT4InitiationIL-2,IL-4,IL-27,IFN-�,STAT5NegativeRegulationNegativeregulationSignal/ActivationDifferentiationSecretionLAK-lymphokineactivatedkillercellPMN-polymorphonuclearneutrophilKEYMouseHumanApril2007CompiledbyNoosheenAlaverdi&DavidSehyDesignedbyStevenLee©2007eBioscienceFunctionally-DistinctTCellLineages:AnEmergingDiversityWEBwww.ebioscience.com▪TECHSUPPORTtech@ebioscience.comORDER888.999.1371▪TECH888.810.6168▪FAX858.642.2046Overview:TheTh1/Th2ParadigmExpanded:ActivatedCD4+Th(Thelper)cellshavebeenfunctionallydividedintotwomajorsubsets,designatedas“Th1”and“Th2”populations.FirstdefinedbyT.Mossmanetal.,in1986,thesesubsetsaregenerallydistinguishedbytheiractions,includingtheirproductionofspecificcytokinesandinvolvementindifferenttypesofimmunereactions.Th1cellsproduceIFN-�,IL-2,TNF-�,andlymphotoxinandparticipateincell-mediatedresponsestointracellularpathogens.Th2cellsproduceIL-4,IL-5,IL-6,IL-9,IL-10,andIL-13andareinvolvedinresponsestolargeextracellularpathogens,suchasparasites.Th17CellsIdentified:Recently,IL-17-producingCD4+Tcells(Th17cells)havebeenidentifiedasauniquesubsetofThcellsthatdevelopsalongapathwaydistinctfromtheTh1-andTh2-celldifferentiationpathways.OneproposedmechanismisIL-23-dependent,butindependentofSTAT-1,T-bet,STAT4,andSTAT6.ThehallmarkeffectormoleculesofTh1andTh2cells,IFN-�andIL-4,respectively,haveeachbeenfoundtonegativelyregulatetheg...