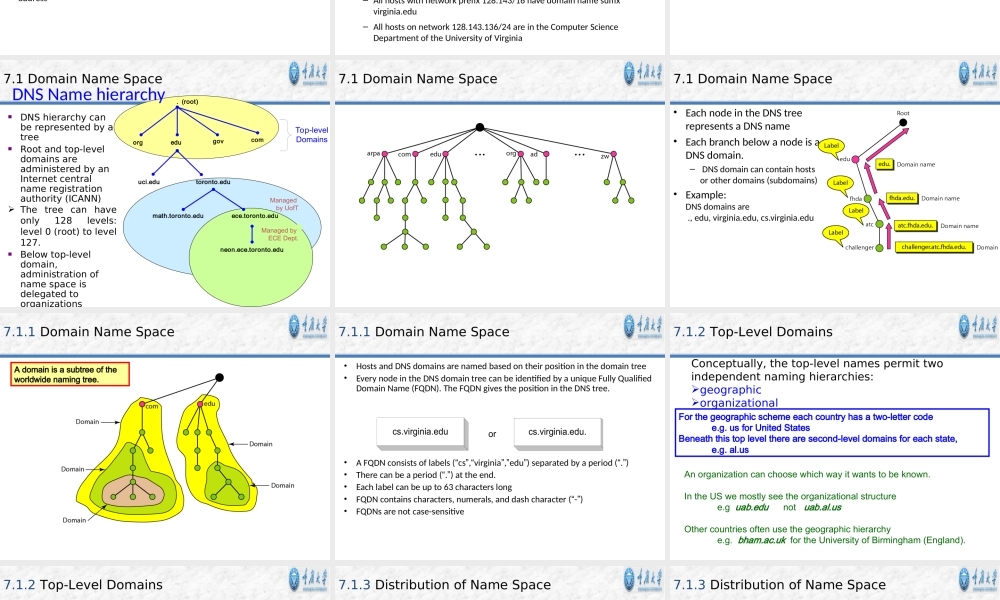
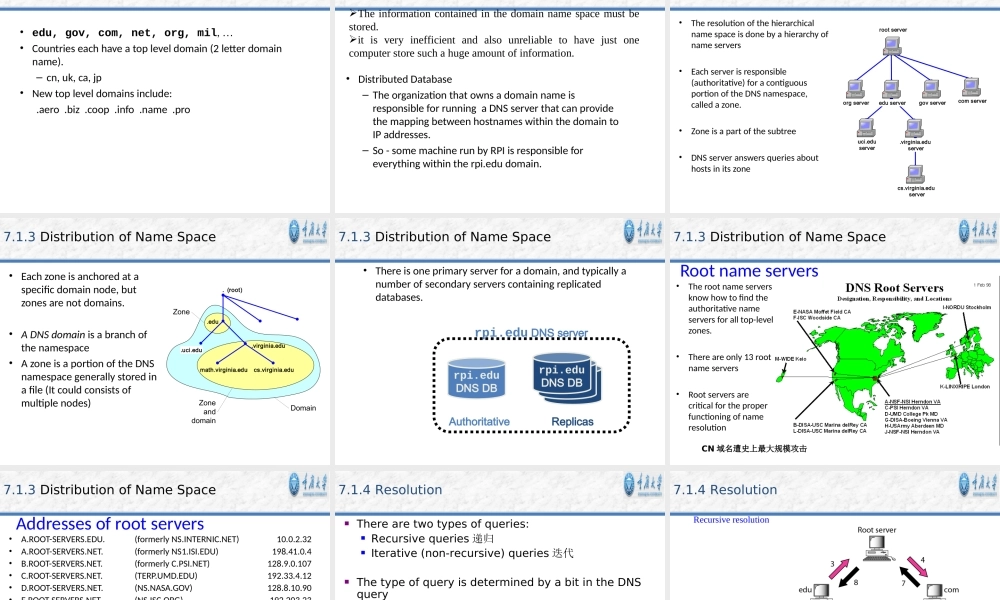
Chapter7TheApplicationLayerCollegeofComputerScienceChongqingUniversityContents•7.1DNS•7.2E-Mail•7.3FTP•7.4theWorldWideWeb•7.5Multimedia7.1DNS-TheDomainNameSystem•IPAddressesaregreatforcomputers–IPaddressincludesinformationusedforrouting.•IPaddressesaretoughforhumanstoremember.•IPaddressesareimpossibletoguess.–everguessedatthenameofaWWWsite?WhyHostnamesserverBeforetherewasDNS….….therewastheHOSTSfileBeforeDNS(until1985),thename-to-IPaddresswasdonebydownloadingasinglefile(hosts.txt)fromacentralserverwithFTP.–Namesinhosts.txtarenotstructured.–Thehosts.txtfilestillworksonmostoperatingsystems.Itcanbeusedtodefinelocalnames.12306hostC:\WINDOWS\system32\drivers\etc\hostsResolverandnameserver•AnapplicationprogramonahostaccessesthedomainsystemthroughaDNSclient,calledtheresolver•ResolvercontactsDNSserver,callednameserver•DNSserverreturnsIPaddresstoresolverwhichpassestheIPaddresstoapplication•Reverselookupsarealsopossible,i.e.,findthehostnamegivenanIPaddressHTTPResolverHostname(neon.tcpip-lab.edu)IPaddress(128.143.71.21)NameserverHostname(neon.tcpip-lab.edu)IPaddress(128.143.71.21)DesignprincipleofDNS•ThenamingsystemonwhichDNSisbasedisahierarchicalandlogicaltreestructurecalledthedomainnamespace.•Anorganizationobtainsauthorityforpartsofthenamespace,andcanaddadditionallayersofthehierarchy•Namesofhostscanbeassignedwithoutregardoflocationonalinklayernetwork,IPnetworkorautonomoussystem•Inpractice,allocationofthedomainnamesgenerallyfollowstheallocationofIPaddress,e.g.,–Allhostswithnetworkprefix128.143/16havedomainnamesuffixvirginia.edu–Allhostsonnetwork128.143.136/24areintheComputerScienceDepartmentoftheUniversityofVirginia7.1DomainNameSpaceCQUDNSIP•www.cqu.edu.cn202.202.1.3(202.202.0.35)•mail.cqu.edu.cn202.202.0.36(202.202.0.26)•jwc.cqu.edu.cn202.202.1.41(202.202.1.42)•www.cs.cqu.edu.cn202.202.5.138•bysj.cqu.edu.cn202.202.5.145(222.198.128.35)ManagedbyUofTDNShierarchycanberepresentedbyatreeRootandtop-leveldomainsareadministeredbyanInternetc...