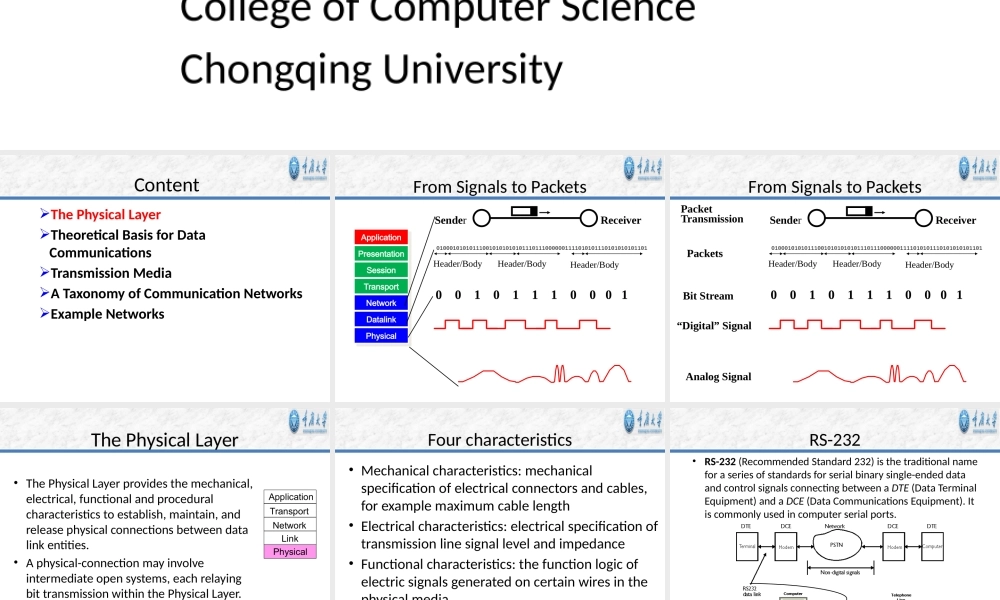
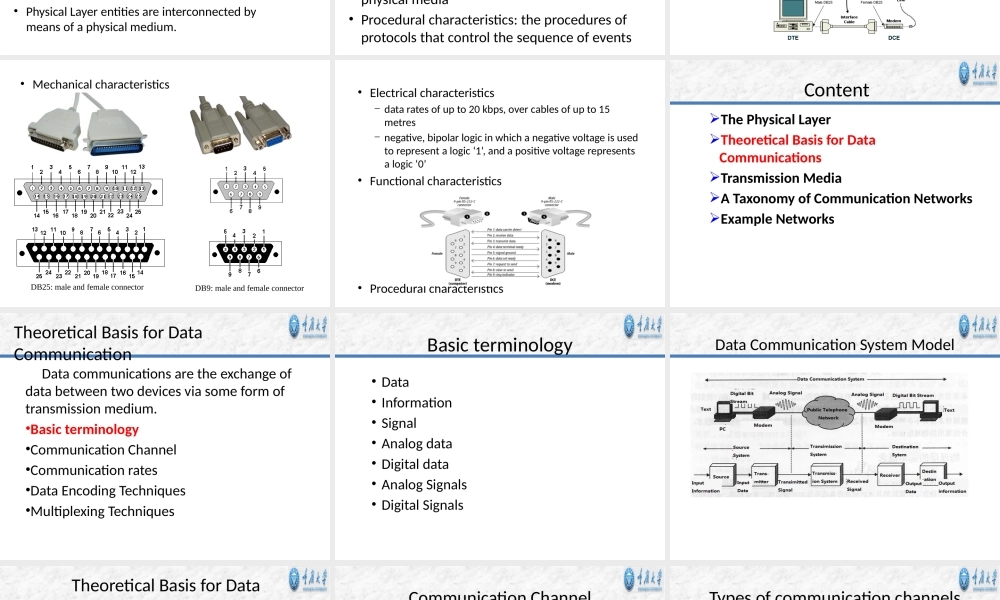
Chapter2ThePhysicalLayerCollegeofComputerScienceChongqingUniversityContentThePhysicalLayerTheoreticalBasisforDataCommunicationsTransmissionMediaATaxonomyofCommunicationNetworksExampleNetworksFromSignalstoPackets001011100010100010101011100101010101011101110000001111010101110101010101101Header/BodyHeader/BodyHeader/BodyReceiverSenderApplicationApplicationPresentationPresentationSessionSessionTransportTransportNetworkNetworkDatalinkDatalinkPhysicalPhysicalFromSignalstoPacketsAnalogSignal“Digital”SignalBitStream00101110001Packets0100010101011100101010101011101110000001111010101110101010101101Header/BodyHeader/BodyHeader/BodyReceiverSenderPacketTransmissionThePhysicalLayerPhysicalLinkNetworkTransportApplication•ThePhysicalLayerprovidesthemechanical,electrical,functionalandproceduralcharacteristicstoestablish,maintain,andreleasephysicalconnectionsbetweendatalinkentities.•Aphysical-connectionmayinvolveintermediateopensystems,eachrelayingbittransmissionwithinthePhysicalLayer.•PhysicalLayerentitiesareinterconnectedbymeansofaphysicalmedium.Fourcharacteristics•Mechanicalcharacteristics:mechanicalspecificationofelectricalconnectorsandcables,forexamplemaximumcablelength•Electricalcharacteristics:electricalspecificationoftransmissionlinesignallevelandimpedance•Functionalcharacteristics:thefunctionlogicofelectricsignalsgeneratedoncertainwiresinthephysicalmedia•Proceduralcharacteristics:theproceduresofprotocolsthatcontrolthesequenceofeventsRS-232•RS-232(RecommendedStandard232)isthetraditionalnameforaseriesofstandardsforserialbinarysingle-endeddataandcontrolsignalsconnectingbetweenaDTE(DataTerminalEquipment)andaDCE(DataCommunicationsEquipment).Itiscommonlyusedincomputerserialports.•MechanicalcharacteristicsDB25:maleandfemaleconnectorDB9:maleandfemaleconnector•Electricalcharacteristics−dataratesofupto20kbps,overcablesofupto15metres−negative,bipolarlogicinwhichanegativevoltageisusedtorepresentalogic‘1’,andapositivevoltagerepresentsalogic‘0’•Functionalch...