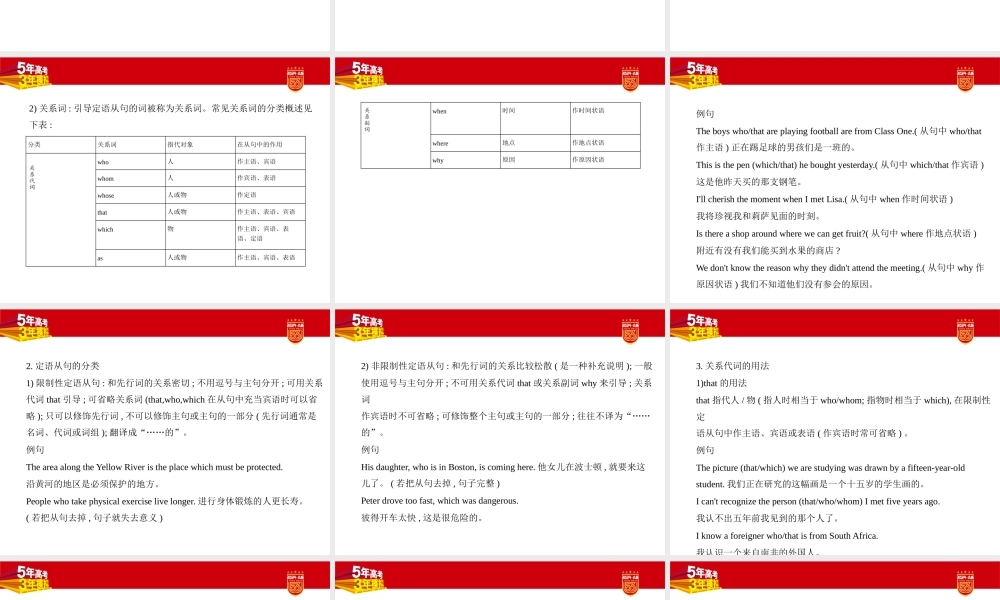
高考英语新高考专用第三部分句法专题九并列复合句和主从复合句知识清单·并列复合句和主从复合句专讲考点一并列复合句由并列连词把两个或两个以上的简单句连在一起的句子叫并列复合句。常见的并列连词1.表并列关系:and,notonly...but(also)...等。例句Shedanceswellandhesingswell.她舞跳得好,他歌唱得好。2.表转折关系:but,yet等。例句Honeyissweet,butthebeestings.蜂蜜是甜的,但蜜蜂会蜇人。It'sasmallcar,yetit'ssurprisinglyspacious.这辆轿车小,然而宽敞得出奇。3.表因果关系:for,so等。例句Hedidn'tattendthemeeting,forhewasill.他由于病了,没有参会。ItwasstillpainfulsoIwenttoseeadoctor.那地方还疼,因此我去看了医生。4.表选择关系:or,either...or...等。例句EitheryoucometomyhouseorIgotoyours.或者你到我家来,或者我到你家去。5.when可用作并列连词,意为“正在这时/那时;一……就;刚……就”,相当于andatthis/thattime。例句Wewerehavingameetingwhensomeonebrokein.我们正在开会,这时突然有人闯了进来。Iwasabouttogooutwhenthetelephonerang.我刚要出去电话就响了。6.while作为并列连词,意为“而,却”,表示对比。例句HelikespopmusicwhileIamfondofclassicalmusic.他喜欢流行音乐,而我喜欢古典音乐。注意并列连词用于连接并列的单词、短语、从句或分句,既可用于简单句,也可用于复合句。考点二主从复合句一、定语从句1.基本概念在主从复合句中作定语,修饰名词、代词等的从句叫定语从句。定语从句的作用相当于形容词。例句I'llforevercherishthedayswhenIstudiedabroad.我将永远珍视我在国外学习的日子。1)先行词:被定语从句修饰的名词、代词等称为先行词,一般出现在定语从句之前。有时先行词是整个主句。例句Thisisthemuseumwhichwasbuiltlastyear.这就是去年建成的那个博物馆。Theysentmychildtotheschooleverymorning,whichIconsideredagreathelptome.他们每天早晨送我的孩子去学校,我认为这对我是极大的帮助。分类关系词指代对象在从句中的作用who人作主语、宾语whom人作宾语、表语whose人或物作定语that人或物作主语、表语、宾语which物作主语、宾语、表语、定语as人或物作主语、宾语、表语2)关系词:引导定语从句的词被称为关系词。常见关系词的分类概述见下表:when时间作时间状语where地点作地点状语why原因作原因状语例句Theboyswho/thatareplayingfootballarefromClassOne.(从句中who/that作主语)正在踢足球的男孩们是一班...