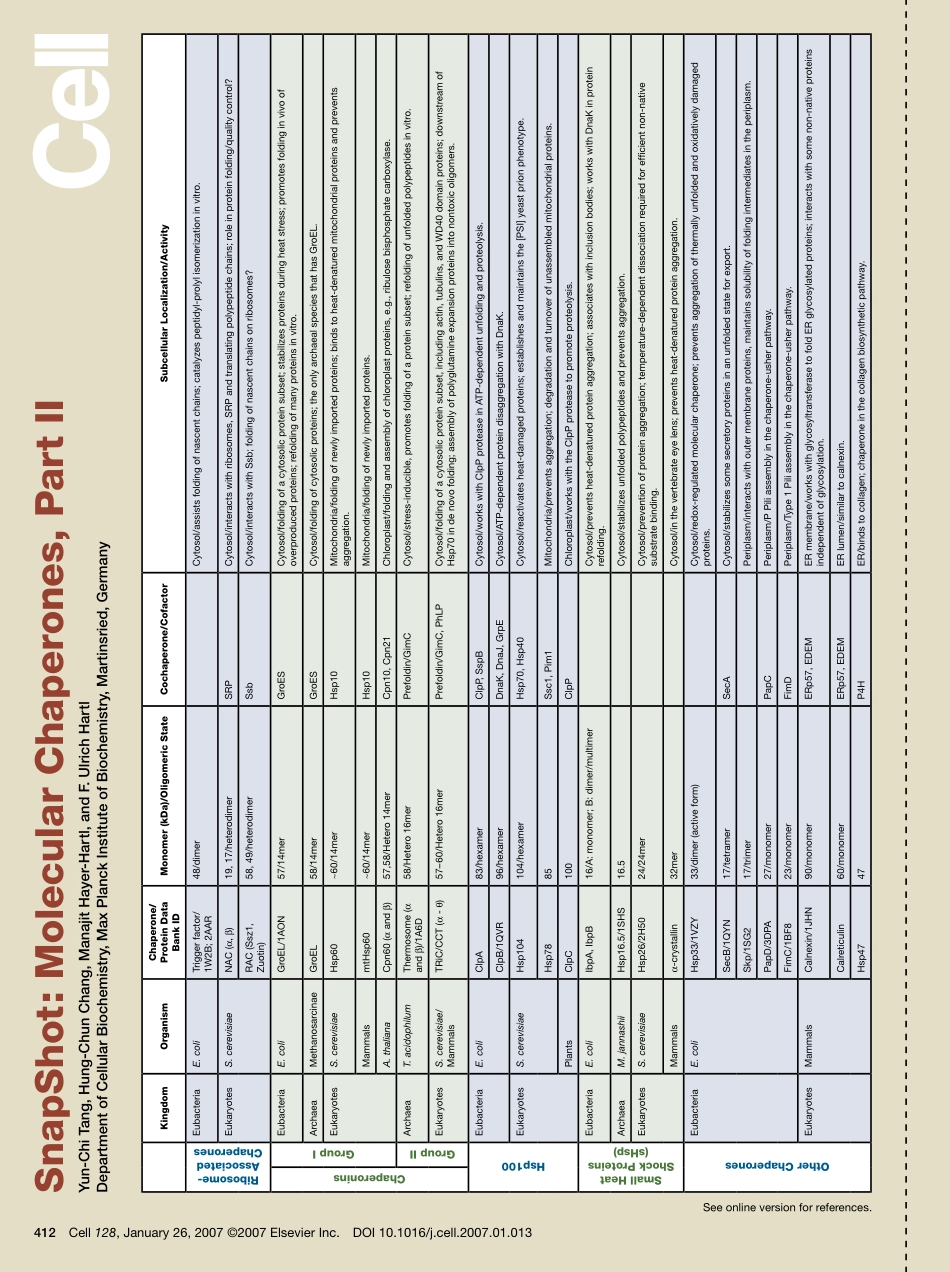
Seeonlineversionforreferences.SnapShot:MolecularChaperones,PartIIYun-ChiTang,Hung-ChunChang,ManajitHayer-Hartl,andF.UlrichHartlDepartmentofCellularBiochemistry,MaxPlanckInstituteofBiochemistry,Martinsried,Germany412Cell128,January26,2007©2007ElsevierInc.DOI10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.013KingdomOrganismChaperone/ProteinDataBankIDMonomer(kDa)/OligomericStateCochaperone/CofactorSubcellularLocalization/ActivityRibosome-AssociatedChaperonesEubacteriaE.coliTriggerfactor/1W2B;2AAR48/dimerCytosol/assistsfoldingofnascentchains;catalyzespeptidyl-prolylisomerizationinvitro.EukaryotesS.cerevisiaeNAC(α,β)19,17/heterodimerSRPCytosol/interactswithribosomes,SRPandtranslatingpolypeptidechains;roleinproteinfolding/qualitycontrol?RAC(Ssz1,Zuotin)58,49/heterodimerSsbCytosol/interactswithSsb;foldingofnascentchainsonribosomes?ChaperoninsGroupIEubacteriaE.coliGroEL/1AON57/14merGroESCytosol/foldingofacytosolicproteinsubset;stabilizesproteinsduringheatstress;promotesfoldinginvivoofoverproducedproteins;refoldingofmanyproteinsinvitro.ArchaeaMethanosarcinaeGroEL58/14merGroESCytosol/foldingofcytosolicproteins;theonlyarchaealspeciesthathasGroEL.EukaryotesS.cerevisiaeHsp60~60/14merHsp10Mitochondria/foldingofnewlyimportedproteins;bindstoheat-denaturedmitochondrialproteinsandpreventsaggregation.MammalsmtHsp60~60/14merHsp10Mitochondria/foldingofnewlyimportedproteins.A.thalianaCpn60(αandβ)57,58/Hetero14merCpn10,Cpn21Chloroplast/foldingandassemblyofchloroplastproteins,e.g.,ribulosebisphosphatecarboxylase.GroupIIArchaeaT.acidophilumThermosome(αandβ)/1A6D58/Hetero16merPrefoldin/GimCCytosol/stress-inducible,promotesfoldingofaproteinsubset;refoldingofunfoldedpolypeptidesinvitro.EukaryotesS.cerevisiae/MammalsTRiC/CCT(α-θ)57–60/Hetero16merPrefoldin/GimC,PhLPCytosol/foldingofacytosolicproteinsubset,includingactin,tubulins,andWD40domainproteins;downstreamofHsp70indenovofolding;assemblyofpolyglutamineexpansionproteinsintonontoxicoligomers.Hsp100EubacteriaE.coliClpA83/hexamerClpP,SspBCytosol/workswithCl...