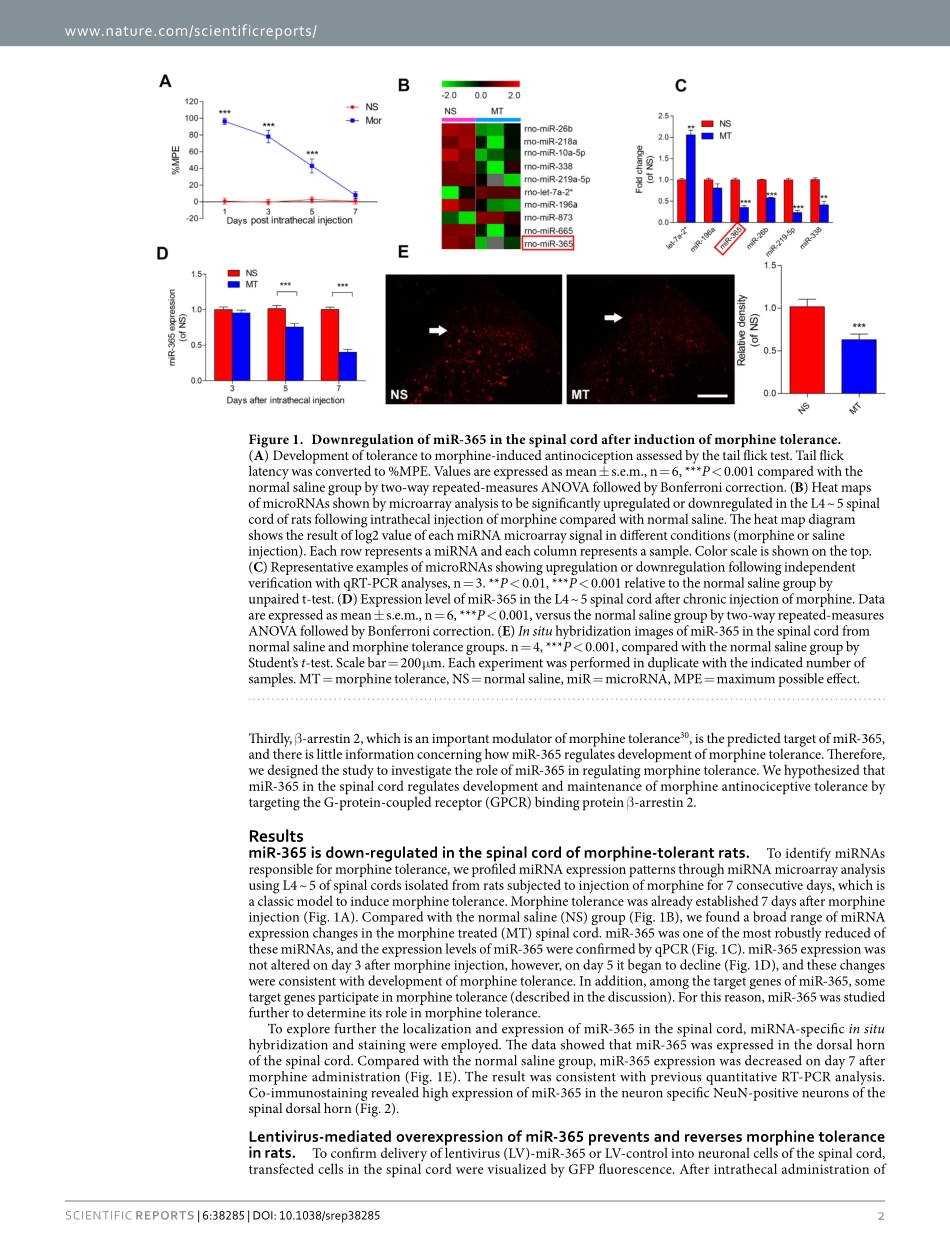
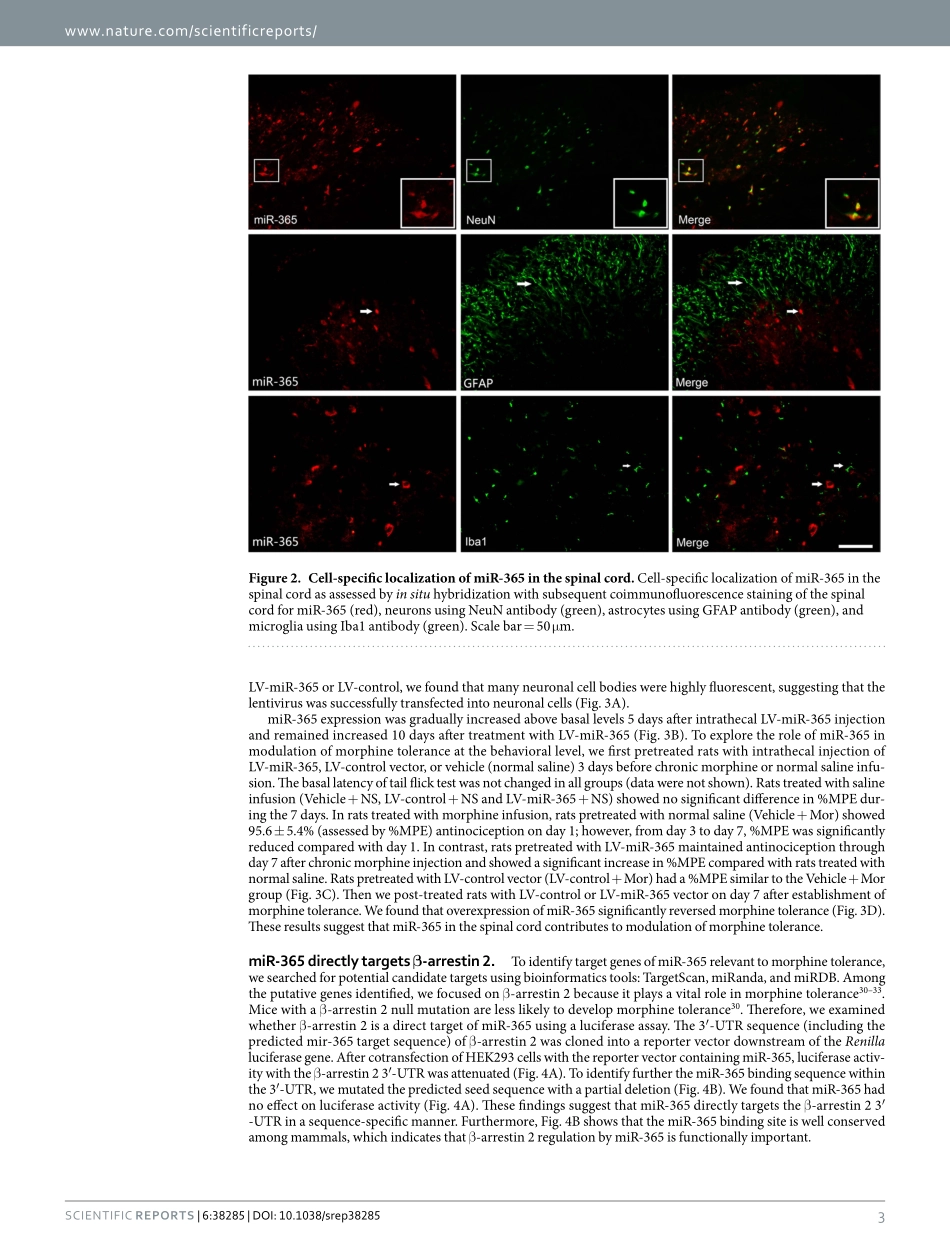
1ScientificRepoRts|6:38285|DOI:10.1038/srep38285www.nature.com/scientificreportsmiR-365targetsβ-arrestin2toreversemorphinetoleranceinratsJianWang1,WeiXu1,TaoZhong1,ZongbinSong1,YuZou1,ZhuofengDing1,QulianGuo1,XinzhongDong2,3&WangyuanZou1Morphinetoleranceisachallengingclinicalproblemthatlimitsitsclinicalapplicationinpaintreatment.Non-codingmicroRNAs(miRNAs)modulategeneexpressioninaposttranscriptionalmanner,andtheirdysregulationcausesvariousdiseases.However,thesignificanceofmiRNAsinmorphinetoleranceisstillpoorlyunderstood.Inthepresentstudy,wehypothesizedthatmicroRNA-365(miR-365)isakeyfunctionalsmallRNAthatreversesmorphinetolerancethroughregulationofβ-arrestin2inrats.Here,microarrayanalysisandquantitativereal-timePCRshowedthatmiR-365wasrobustlydecreasedinthespinalcordafterchronicmorphineadministration.InsituhybridizationandimmunochemistrydoublestainingshowedthatmiR-365wasexpressedinneuronsofthespinalcord.Weidentifiedβ-arrestin2asthetargetgeneofmiR-365bybioinformaticsanalysisandluciferasereporterassay.ThedatashowedthatoverexpressionofmiR-365preventedandreversedestablishedmorphinetolerance,andincreasedexpressionofmiR-365causedadecreaseinexpressionofβ-arrestin2protein.miR-365downregulationisinvolvedinthedevelopmentandmaintenanceofmorphinetolerancethroughregulationofβ-arrestin2,andmiR-365upregulationprovidesapromisingandnovelapproachfortreatmentofmorphinetolerance.Morphineiscommonlyusedinclinicalmanagementtoalleviatemoderatetoseverepain.However,prolongedandrepeateduseofmorphineleadstotolerance1.Insomepatients,eventhemaximumtolerateddoseofmor-phinecannotachieveasufficientanalgesiceffect2,3.Morphinetoleranceisdefinedasagraduallossofdrugpotencyorefficacyandreduceddurationofaction.Whenmorphinetoleranceoccurs,doseescalationbecomesnecessarytomaintainthesameanalgesiceffect,whichresultsinanincreasedlikelihoodofsideeffects.Thusfar,themechanismsunderlyingmorphinetolerancearepoorlyunderstood.Multiplefactorsmaybeinvolvedinthesecomplexprocesses,suchasopioidreceptordesensitizati...