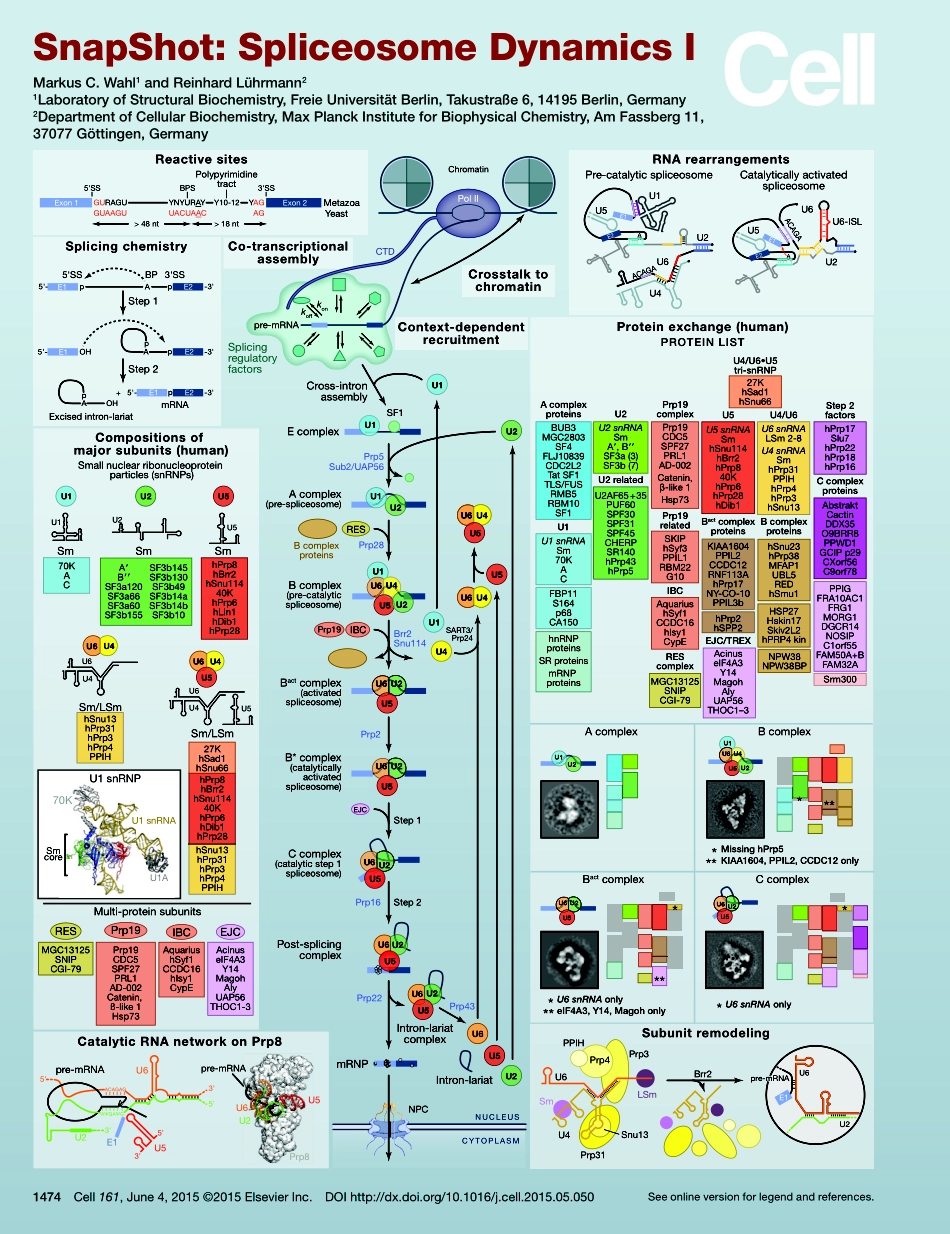
SubunitremodelingPrp3Prp4PPIHLSmSmSnu13Prp31U4U6Brr2U2E1pre-mRNAU6Proteinexchange(human)AcomplexPROTEINLISTU2U1U1U5U4U6U2BcomplexBactcomplexU2U5U6U2U5U6CcomplexReactivesitesExon1Exon2GURAGUYNYURAYY10-12YAGUACUAACAGGUAAGU>48nt>18nt5'SS3'SSBPSPolypyrimidinetractMetazoaYeastSplicingchemistry-3'5'-5'SS3'SSBPApE1E2p-3'5'-AOHE1E2ppStep1Step2-3'5'-E1E2pApOH+mRNAExcisedintron-lariatRNArearrangementsPre-catalyticspliceosomeCatalyticallyactivatedspliceosomeU2AACAGAACAGAU1U4U6E1E2U5U2U6-ISLU6E2E1AU5CatalyticRNAnetworkonPrp8ACAGAGAAΨGAΨG5'3'U2pre-mRNAU6U53'5'3'5'E1U6U2U5pre-mRNAPrp8Acomplex(pre-spliceosome)U2U1Bactcomplex(activatedspliceosome)U2U5U6U5U6U2Ccomplex(catalyticstep1spliceosome)Step1U1U5U4U6U2Bcomplex(pre-catalyticspliceosome)Brr2Snu114Step2Prp16Prp28Prp5Sub2/UAP56B*complex(catalyticallyactivatedspliceosome)U2U5Prp2IBCRESEJCU1SF1EcomplexBcomplexproteinsCross-intronassemblyPrp19NPCNUCLEUSCYTOPLASMU2U6U5Post-splicingcomplexmRNPPrp22Intron-lariatcomplexU2U5U6Intron-lariatU5U6Prp43CrosstalktochromatinCo-transcriptionalassemblypre-mRNAkonkoffPolIICTDChromatinSplicingregulatoryfactorsU5U4U6U4U6U1U4U5U2U1SART3/Prp24Compositionsofmajorsubunits(human)Prp19Prp19CDC5SPF27PRL1AD-002Catenin,ß-like1Hsp73IBCAquariushSyf1CCDC16hIsy1CypERESMGC13125SNIPCGI-79AcinuseIF4A3Y14MagohAlyUAP56THOC1-3EJCU1snRNA70KU1ASmcoreU1snRNPSm/LSmSmSmSmhSnu13hPrp31hPrp3hPrp4PPIHU6U4U6U4U6U4U5Sm/LSmhPrp8hBrr2hSnu11440KhPrp6hDib1hPrp2827KhSad1hSnu66hSnu13hPrp31hPrp3hPrp4PPIHU5U6U470KACU1U1A′B′′SF3a120SF3a66SF3a60SF3b155U2U2hPrp8hBrr2hSnu11440KhPrp6hLin1hDib1hPrp28U5U5Smallnuclearribonucleoproteinparticles(snRNPs)Multi-proteinsubunitsContext-dependentrecruitmentSF3b145SF3b130SF3b49SF3b14aSF3b14bSF3b10U6U2U1AcomplexproteinsBUB3MGC2803SF4FLJ10839CDC2L2TatSF1TLS/FUSRMB5RBM10SF1U2U1snRNASm70KACU2snRNASmA′,B′′SF3a(3)SF3b(7)U2relatedU2AF65+35PUF60SPF30SPF31SPF45CHERPSR140hPrp43hPrp5hnRNPproteinsSRproteinsmRNPproteinsFBP11S164p68CA150Prp19complexU4/U6•U5tri-snRNPREScomplexMissinghPrp5KIAA1604,PPIL2,CC...