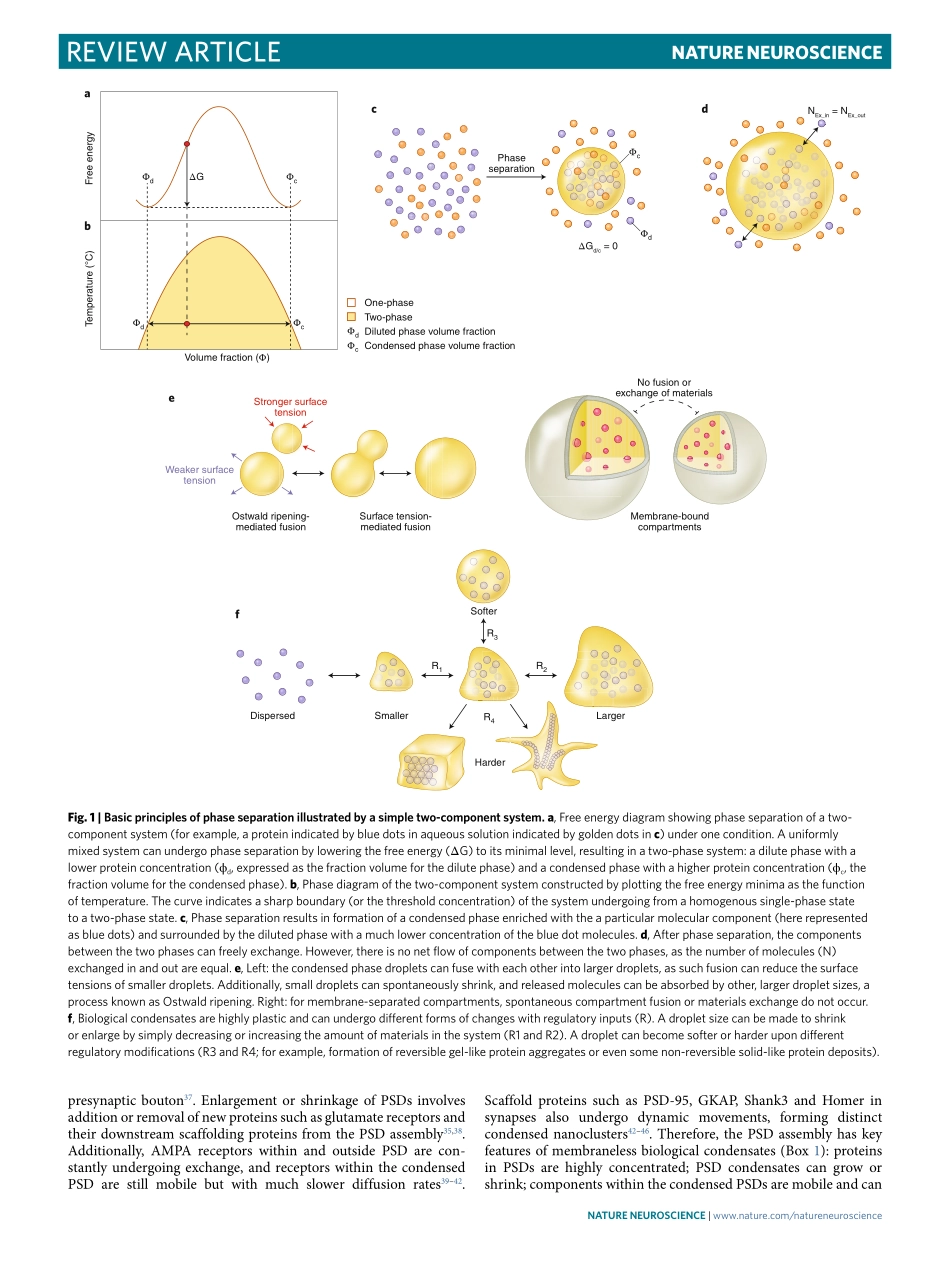
ReviewARticlehttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-019-0579-91DivisionofLifeScience,StateKeyLaboratoryofMolecularNeuroscience,HongKongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,HongKong,China.2CenterofSystemsBiologyandHumanHealth,HongKongUniversityofScienceandTechnology,HongKong,China.*e-mail:mzhang@ust.hkEukaryoticcellsorchestratenumerousbiochemicalreactionsspatiotemporallybysegregatingeachcellintostructurallyandfunctionallydistinctcompartments.Inadditiontoclassicalmembrane-enclosedcellularcompartments,increasingrecentevi-dencerevealsadiverseclassofcellularcompartmentsthateitherlackmembranesorarenotenclosedbymembranes,formedbyaphysicalprocessknownasliquid–liquidphaseseparationandfre-quentlyreferredtoasmembranelesscompartmentsorbiologicalcondensates(Fig.1andBox1).Observationofmembranelesscondensatesmaydatebacktomorethan100yearsagowhenRamonyCajalobserveddensespotsinthenucleiofsilver-stainedneurons1.ThesearenowknownasCajalbodies,mRNAprocessingmachinerieslocalizedwithinthenucleusandenrichedinproteinsandRNAs.Somewell-recognizedexamplesofmembranelesscondensatesincludevariousnuclearbodies,Pgranules,stressgranulesandprocessingbodies2–5.Neuronstakecellularcompartmentalizationtoextremesduetotheirelaboratemorphologiesandhighdegreeofpolarity.Inaddi-tiontomembrane-enclosedorganellesandmembranelessconden-satescommontoothercelltypes,neuronscontainauniquetypeofmembrane-semi-enclosedcompartmentsknownassynapses,whicharemolecularapparatusesdictatingsignalprocessingandtransmis-sionsinallnervoussystems(Fig.2).Neitherpre-norpostsynapticcompartmentsareenclosedbymembranebilayers.Underneaththepostsynapticplasmamembranesofeachsynapseisacondensedprotein-richsub-compartmentknownasthepostsynapticdensity(PSD),astructureresponsibleforreceiving,amplifyingandstoringsignalsinitiatedbypresynapticcells.PSDsarecomposedofdenselypackedproteinsformingmega-assembliesafewhundrednanome-tersinwidthand~30–50nmthick6–8(Fig.2b).Inthepresynap-ticcompartments,alayerofelectron-densematerialbeneaththeplasmamembranes,knownast...