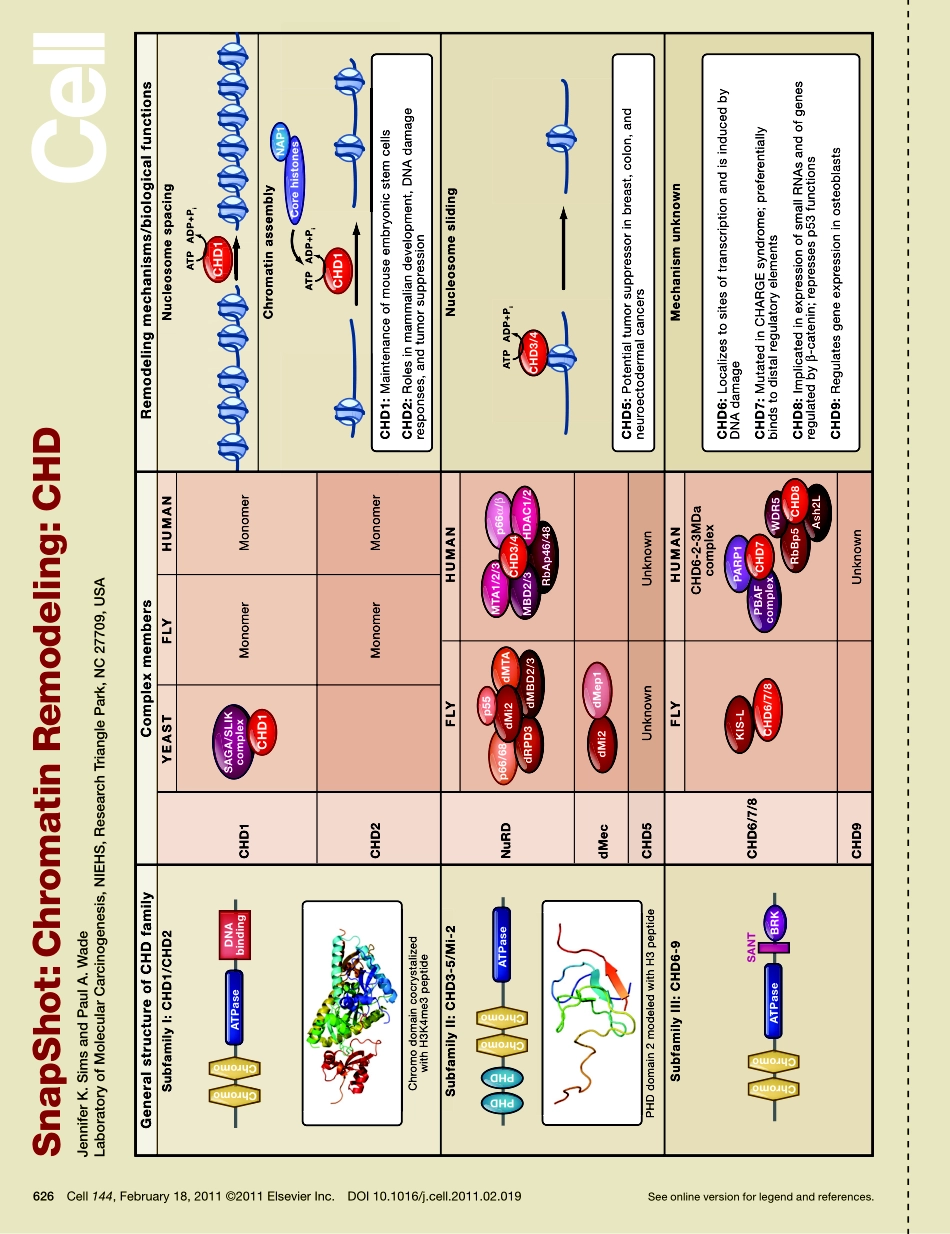
SnapShot:ChromatinRemodeling:CHDJenniferK.SimsandPaulA.WadeLaboratoryofMolecularCarcinogenesis,NIEHS,ResearchTrianglePark,NC27709,USASeeonlineversionforlegendandreferences.626Cell144,February18,2011©2011ElsevierInc.DOI10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.019RbAp46/48RbBp5SubfamilyI:CHD1/CHD2ChromodomaincocrystalizedwithH3K4me3peptideYEASTCHD1MonomerMonomerMonomerMonomerCHD2FLYHUMANNuRDUnknownUnknownUnknownCHD6-2-3MDacomplexCHD5CHD9CHD6/7/8dMecFLYHUMANFLYHUMANNucleosomespacingNucleosomeslidingMechanismunknownChromatinassemblySubfamilyII:CHD3-5/Mi-2SubfamilyIII:CHD6-9CHD3/4dMi2PARP1WDR5Ash2LPBAFcomplexMTA1/2/3p66α/βMBD2/3HDAC1/2p66/68dRPD3dMBD2/3dMep1SAGA/SLIKcomplexCHD1HDAC1/2MBD2/3HDAC1/2CHD3/4complexCHD7CHD8KIS-LCHD6/7/8PHDdomain2modeledwithH3peptideATPaseChromoChromoDNAbindingATPaseChromoChromoATPaseChromoChromoPHDPHDBRKSANTGeneralstructureofCHDfamilyComplexmembersRemodelingmechanisms/biologicalfunctionsATPADP+PiCHD1CHD1ATPADP+PiATPADP+PidMTAdMi2p55CorehistonesCHD1:MaintenanceofmouseembryonicstemcellsCHD2:Rolesinmammaliandevelopment,DNAdamageresponses,andtumorsuppressionCHD5:Potentialtumorsuppressorinbreast,colon,andneuroectodermalcancersCHD6:LocalizestositesoftranscriptionandisinducedbyDNAdamageCHD7:MutatedinCHARGEsyndrome;preferentiallybindstodistalregulatoryelementsCHD8:ImplicatedinexpressionofsmallRNAsandofgenesregulatedbyβ-catenin;repressesp53functionsCHD9:RegulatesgeneexpressioninosteoblastsCHD1CHD1CHD1CHD1CHD1NAP1ChromodomaincocrystalizedwithH3K4me3peptideSubfamilyII:CHD3-5/Mi-2ChromoChromoPHDdomain2modeledwithH3peptide626.e1Cell144,February18,2011©2011ElsevierInc.DOI10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.019SnapShot:ChromatinRemodeling:CHDJenniferK.SimsandPaulA.WadeLaboratoryofMolecularCarcinogenesis,NIEHS,ResearchTrianglePark,NC27709,USATheCHDfamilyofchromatin-remodelingcomplexesisdefinedbythepresence(fromaminotocarboxytermini)ofdualchromodomains,aDNA-dependentATPasedomainoftheSNF2superfamily,and,insomecases,aDNA-bindingdomain.Thefamilyissubdividedintothreesubfamiliesbasedonth...