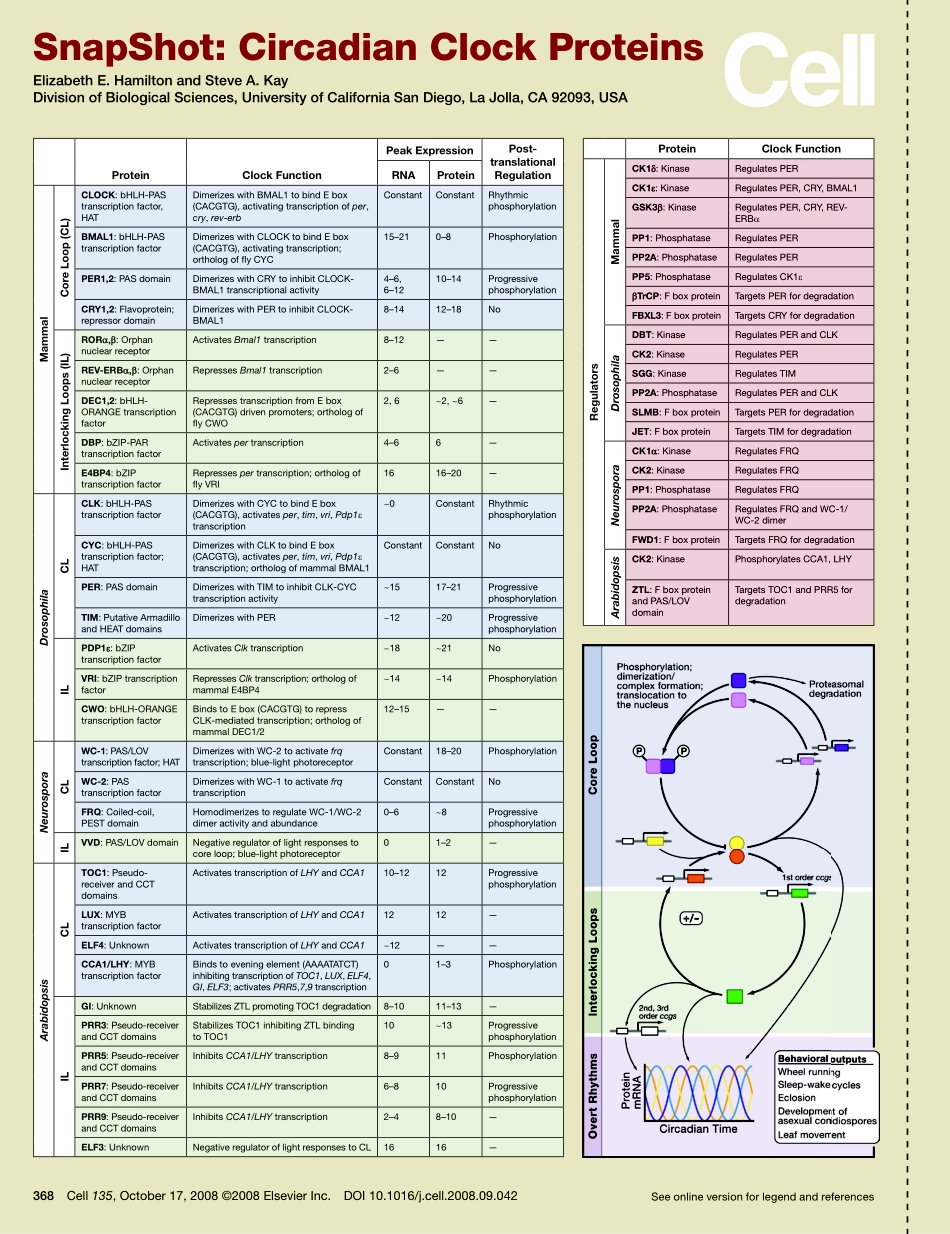
Seeonlineversionforlegendandreferences368Cell135,October17,2008©2008ElsevierInc.DOI10.1016/j.cell.2008.09.042SnapShot:CircadianClockProteinsElizabethE.HamiltonandSteveA.KayDivisionofBiologicalSciences,UniversityofCaliforniaSanDiego,LaJolla,CA92093,USAProteinclockFunctionPeakexpressionPost-translationalRegulationRnAProteinMammalcoreLoop(cL)cLOcK:bHLH-PAStranscriptionfactor,HATDimerizeswithBMAL1tobindEbox(CACGTG),activatingtranscriptionofper,cry,rev-erbConstantConstantRhythmicphosphorylationBMAL1:bHLH-PAStranscriptionfactorDimerizeswithCLOCKtobindEbox(CACGTG),activatingtranscription;orthologofflyCYC15–210–8PhosphorylationPeR1,2:PASdomainDimerizeswithCRYtoinhibitCLOCK-BMAL1transcriptionalactivity4–6,6–1210–14ProgressivephosphorylationcRY1,2:Flavoprotein;repressordomainDimerizeswithPERtoinhibitCLOCK-BMAL18–1412–18NoInterlockingLoops(IL)RORα,β:OrphannuclearreceptorActivatesBmal1transcription8–12——ReV-eRBα,β:OrphannuclearreceptorRepressesBmal1transcription2–6——Dec1,2:bHLH-ORANGEtranscriptionfactorRepressestranscriptionfromEbox(CACGTG)drivenpromoters;orthologofflyCWO2,6~2,~6—DBP:bZIP-PARtranscriptionfactorActivatespertranscription4–66—e4BP4:bZIPtranscriptionfactorRepressespertranscription;orthologofflyVRI1616–20—DrosophilacLcLK:bHLH-PAStranscriptionfactorDimerizeswithCYCtobindEbox(CACGTG),activatesper,tim,vri,Pdp1εtranscription~0ConstantRhythmicphosphorylationcYc:bHLH-PAStranscriptionfactor;HATDimerizeswithCLKtobindEbox(CACGTG),activatesper,tim,vri,Pdp1εtranscription;orthologofmammalBMAL1ConstantConstantNoPeR:PASdomainDimerizeswithTIMtoinhibitCLK-CYCtranscriptionactivity~1517–21ProgressivephosphorylationTIM:PutativeArmadilloandHEATdomainsDimerizeswithPER~12~20ProgressivephosphorylationILPDP1ε:bZIPtranscriptionfactorActivatesClktranscription~18~21NoVRI:bZIPtranscriptionfactorRepressesClktranscription;orthologofmammalE4BP4~14~14PhosphorylationcWO:bHLH-ORANGEtranscriptionfactorBindstoEbox(CACGTG)torepressCLK-mediatedtranscription;orthologofmammal...