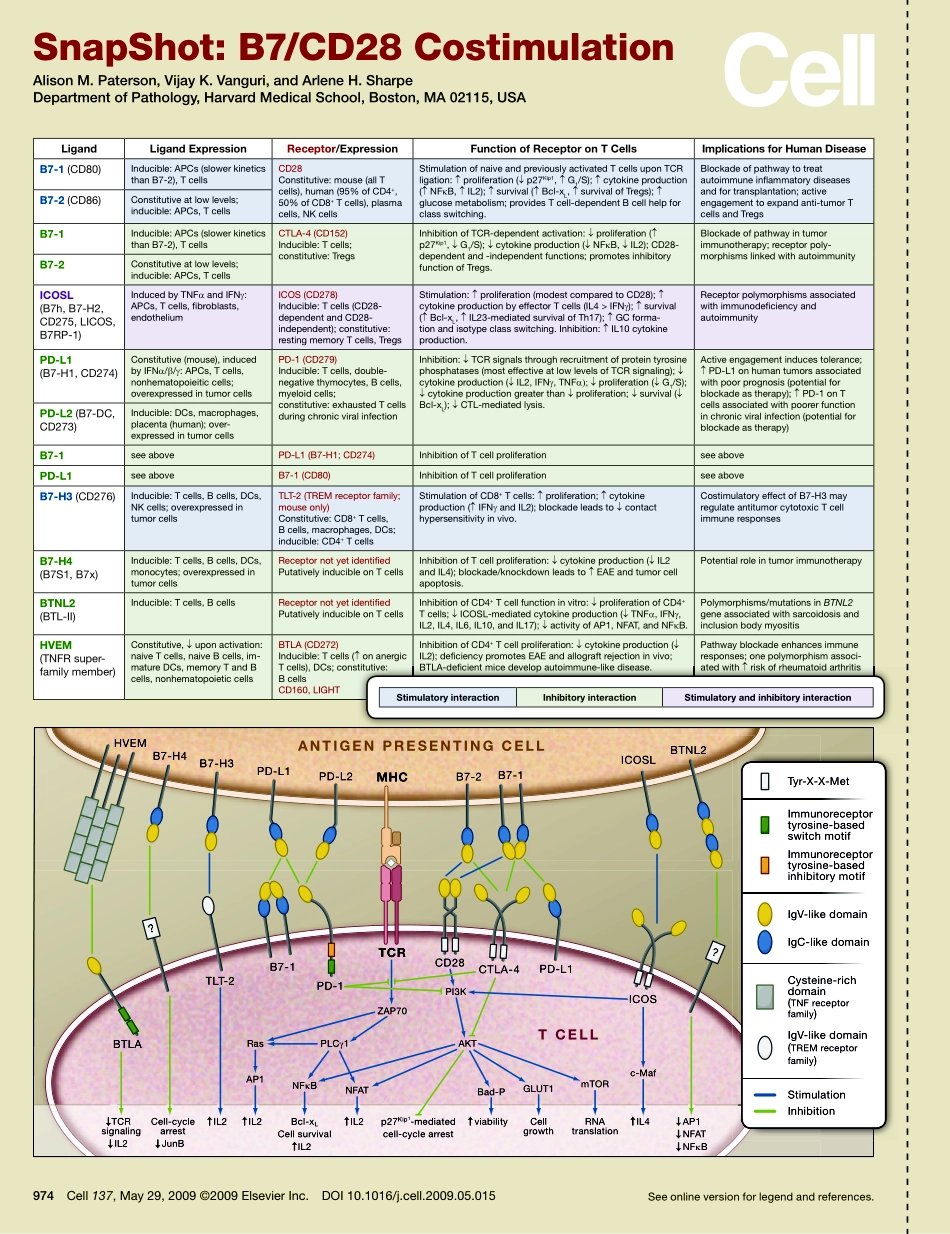
Seeonlineversionforlegendandreferences.974Cell137,May29,2009©2009ElsevierInc.DOI10.1016/j.cell.2009.05.015SnapShot:B7/CD28CostimulationAlisonM.Paterson,VijayK.Vanguri,andArleneH.SharpeDepartmentofPathology,HarvardMedicalSchool,Boston,MA02115,USAligandligandexpressionReceptor/expressionfunctionofReceptorontcellsImplicationsforHumandiseaseB7-1(CD80)Inducible:APCs(slowerkineticsthanB7-2),TcellsCD28Constitutive:mouse(allTcells),human(95%ofCD4+,50%ofCD8+Tcells),plasmacells,NKcellsStimulationofnaiveandpreviouslyactivatedTcellsuponTCRligation:↑proliferation(↓p27Kip1,↑G1/S);↑cytokineproduction(↑NFκB,↑IL2);↑survival(↑Bcl-xL,↑survivalofTregs);↑glucosemetabolism;providesTcell-dependentBcellhelpforclassswitching.Blockadeofpathwaytotreatautoimmuneinflammatorydiseasesandfortransplantation;activeengagementtoexpandanti-tumorTcellsandTregsB7-2(CD86)Constitutiveatlowlevels;inducible:APCs,TcellsB7-1Inducible:APCs(slowerkineticsthanB7-2),TcellsCTLA-4(CD152)Inducible:Tcells;constitutive:TregsInhibitionofTCR-dependentactivation:↓proliferation(↑p27Kip1,↓G1/S);↓cytokineproduction(↓NFκB,↓IL2);CD28-dependentand-independentfunctions;promotesinhibitoryfunctionofTregs.Blockadeofpathwayintumorimmunotherapy;receptorpoly-morphismslinkedwithautoimmunityB7-2Constitutiveatlowlevels;inducible:APCs,TcellsIcosl(B7h,B7-H2,CD275,LICOS,B7RP-1)InducedbyTNFαandIFNγ:APCs,Tcells,fibroblasts,endotheliumICOS(CD278)Inducible:Tcells(CD28-dependentandCD28-independent);constitutive:restingmemoryTcells,TregsStimulation:↑proliferation(modestcomparedtoCD28);↑cytokineproductionbyeffectorTcells(IL4>IFNγ);↑survival(↑Bcl-xL,↑IL23-mediatedsurvivalofTh17);↑GCforma-tionandisotypeclassswitching.Inhibition:↑IL10cytokineproduction.ReceptorpolymorphismsassociatedwithimmunodeficiencyandautoimmunityPd-l1(B7-H1,CD274)Constitutive(mouse),inducedbyIFNα/β/γ:APCs,Tcells,nonhematopoieiticcells;overexpressedintumorcellsPD-1(CD279)Inducible:Tcells,double-negativethymocytes,Bcells,myeloidcells;constitutive...