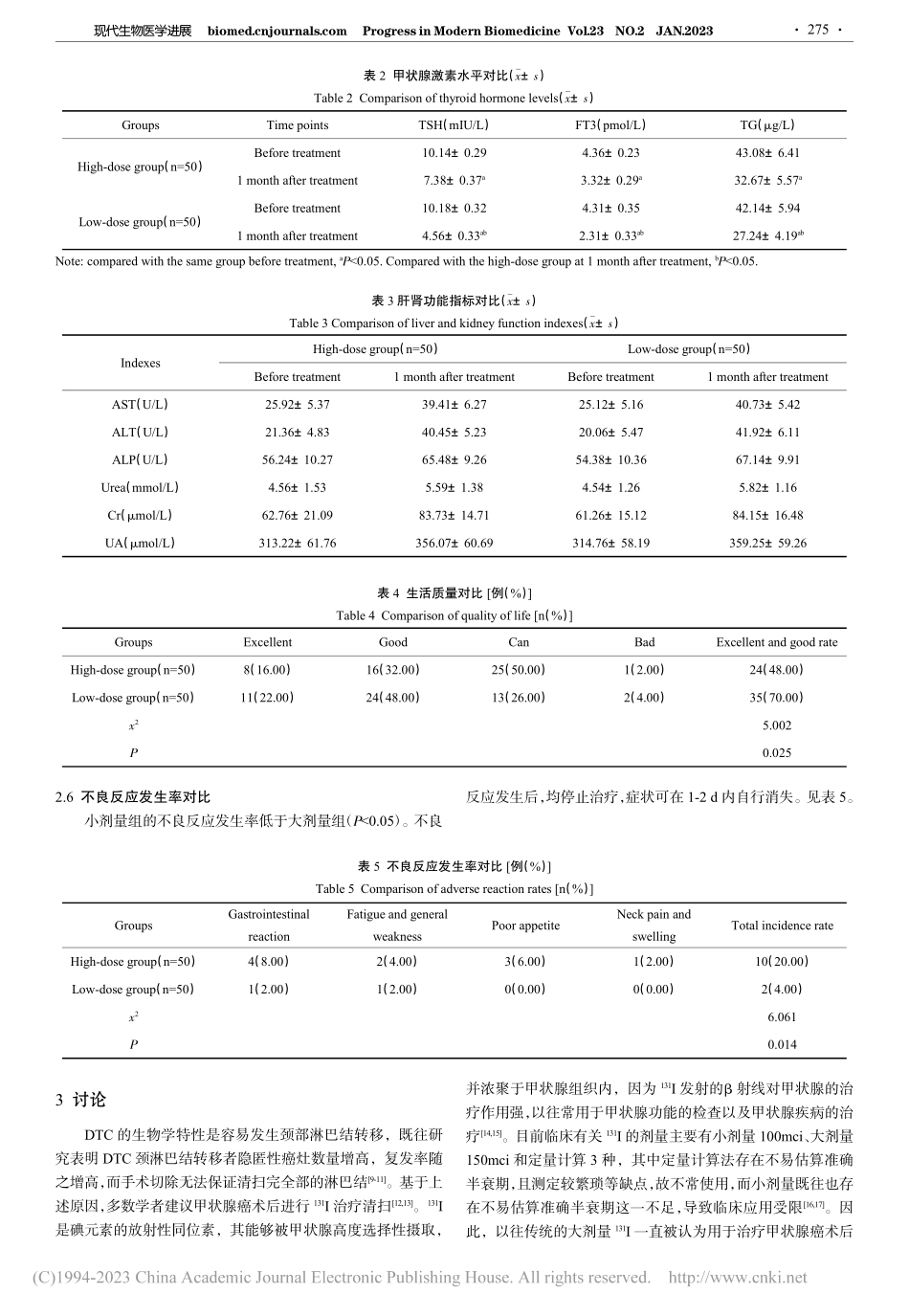
现代生物医学进展biomed.cnjournals.comProgressinModernBiomedicineVol.23NO.2JAN.2023doi:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.02.013不同剂量131I对分化型甲状腺癌患者摄碘率、甲状腺激素水平及生活质量的影响*高晓洁季梅丽张乐乐姚晓晨吴琪(南京医科大学附属南京医院(南京市第一医院)核医学科江苏南京210006)摘要目的:探讨不同剂量131I对分化型甲状腺癌(DTC)患者摄碘率、甲状腺激素水平及生活质量的影响。方法:选取2018年6月~2020年6月我院收治的DTC患者100例,均接受131I清甲治疗,根据放射剂量的不同分为小剂量组(100mci)和大剂量组(150mci),例数均为50例。比较两组患者摄碘率、甲状腺激素水平、肝肾功能、生活质量和不良反应发生率。结果:小剂量组2h、6h、24h的摄碘率高于大剂量组(P<0.05)。小剂量组的清甲率高于大剂量组(P<0.05)。两组治疗1个月后促甲状腺激素(TSH)、游离三碘甲状腺原氨酸(FT3)、甲状腺球蛋白(TG)水平下降(P<0.05);小剂量组治疗1个月后TSH、FT3、TG水平低于大剂量组(P<0.05)。两组治疗前、治疗1个月后的组间、组内门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、血清尿素(Urea)、肌酐(Cr)、尿酸(UA)水平对比,差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。小剂量组的生活质量优良率高于大剂量组(P<0.05)。小剂量组的不良反应发生率低于大剂量组(P<0.05)。结论:不同剂量131I清甲治疗对DTC患者肝肾功能无明显影响,但选用100mci剂量可提高DTC患者摄碘率,减轻对甲状腺功能的损害,同时还可提高患者的生活质量,减少不良反应发生率。关键词:不同剂量;131I;分化型甲状腺癌;摄碘率;甲状腺激素;生活质量;肝肾功能中图分类号:R736.1文献标识码:A文章编号:1673-6273(2023)02-273-04EffectsofDifferentDosesof131IonIodineUptakeRate,ThyroidHormoneLevelandQualityofLifeinPatientswithDifferentiatedThyroidCancer*GAOXiao-jie,JIMei-li,ZHANGLe-le,YAOXiao-chen,WUQi(DepartmentofNuclearMedicine,NanjingHospitalAffiliatedtoNanjingMedicalUniversity(NanjingFirstHospital),Nanjing,Jiangsu,210006,China)ABSTRACTObjective:Toinvestigatetheeffectsofdifferentdosesof131Ioniodineintakerate,thyroidhormonelevelandqualityoflifeinpatientswithdifferentiatedthyroidcarcinoma(DTC).Methods:100patientswithDTCwhowereadmittedtoourhospitalfromJune2018toJune202...