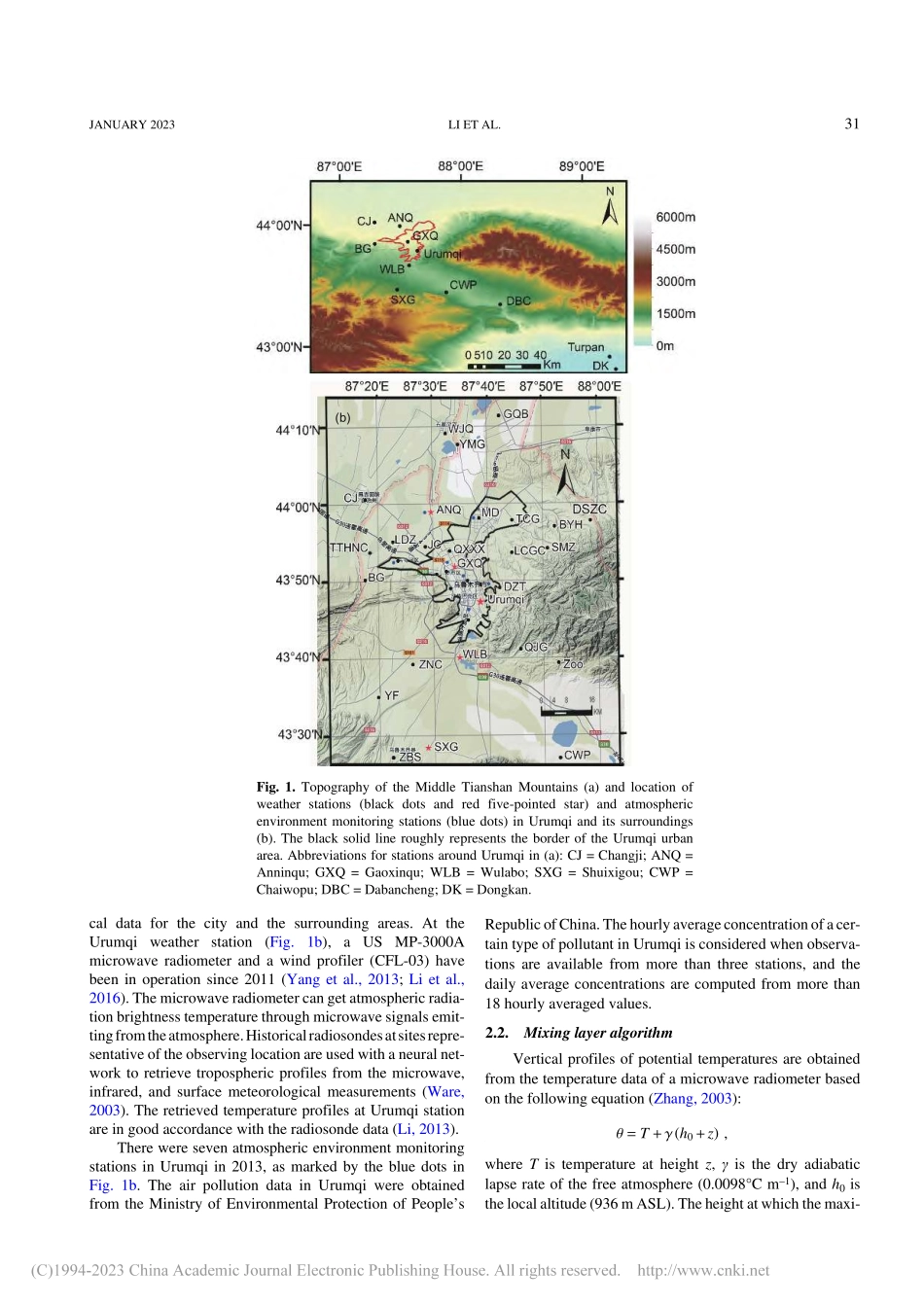
EvolutionofMeteorologicalConditionsduringaHeavyAirPollutionEventundertheInfluenceofShallowFoehninUrumqi,ChinaXiaLI*1,KemingZHAO2,ShiyuanZHONG3,XiaojingYU4,ZhiminFENG5,YutingZHONG1,AyitkenMAULEN1,andShutingLI11InstituteofDesertMeteorology,ChinaMeteorologicalAdministration,Urumqi830002,China2XinjiangMeteorologicalObservatory,Urumqi830002,China3DepartmentofGeography,EnvironmentandSpatialSciences,MichiganStateUniversity,EastLansing48823-5243,USA4LASG,InstituteofAtmosphericPhysics,ChineseAcademyofSciences,Beijing100029,China5UrumqiMeteorologicalSatelliteGroundStation,Urumqi830011,China(Received10November2021;revised6April2022;accepted11April2022)ABSTRACTTheairpollutioninUrumqiwhichislocatedonthenorthernslopeoftheTianshanMountainsinnorthwesternChina,isveryseriousinwinter.Ofparticularimportanceistheinfluenceofterrain-inducedshallowfoehn,knownlocallyaselevatedsoutheasterlygale(ESEG).Itusuallymodulatesatmosphericboundarylayerstructureandwindfieldpatternsandproducesfavorablemeteorologicalconditionsconducivetohazardousairpollution.During2013–17,Urumqihadanaverageof50dyr–1ofheavypollution(dailyaveragePM2.5concentration>150μgm–3),ofwhich41dayswereinwinter.Themajority(71.4%)ofheavypollutionprocesseswereassociatedwiththeshallowfoehn.Basedonmicrowaveradiometer,windprofiler,andsurfaceobservations,thesurfacemeteorologicalfieldsandboundarylayerevolutionduringtheworstpollutionepisodeinUrumqiduring16–23February2013areinvestigated.Theresultsillustratethesignificantroleofshallowfoehninthebuilding,strengthening,andcollapsingoftemperatureinversions.Therewerefourwindfieldpatternscorrespondingtofourdifferentphasesduringthewholepollutionevent.ThemostseriouspollutionphasefeaturedshallowfoehnactivityinthesouthofUrumqicityandtheappearanceofanintenseinversionlayerbelow600m.Intenseconvergencecausedbyfoehnandmountain–valleywindswassustainedduringmostofthephase,resultinginpollutantssinkingdownwardtothelowerboundarylayerandaccumulatingaroundurbanarea.Thekeyindicatorsofsucheventsidentifiedinth...