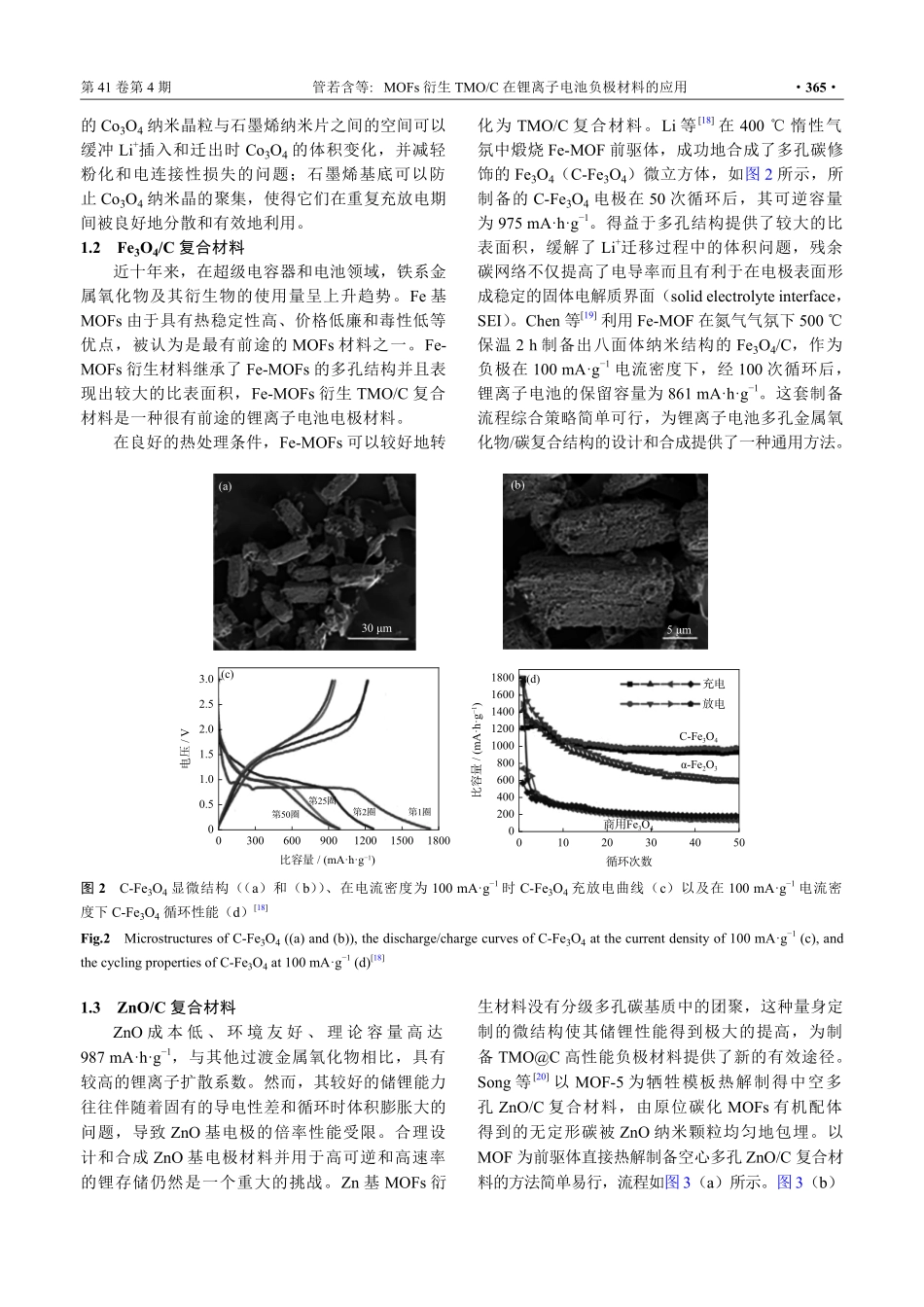
MOFs衍生TMO/C在锂离子电池负极材料的应用管若含,董桂霞✉,杨双娟华北理工大学材料科学与工程学院,唐山063000✉通信作者,E-mail:dongguixia199@163.com摘要锂离子电池商用负极材料石墨比容量低,难以满足市场需求,金属有机骨架材料(metal-organicframeworkmaterials,MOFs)具有可调控的结构、较大的表面积和可调节的孔径,可用作下一代电化学储能器件,引起广泛研究。本文综述了金属(Fe、Co、Zn、Mn、Cu)基金属有机骨架及其衍生物的合成,重点介绍了以金属有机骨架材料为前驱体制备过渡金属氧化物(transitionmetaloxide,TMO)/C作为锂离子电池负极材料的研究进展,并对其发展方向进行了展望。关键词锂离子电池;负极材料;金属有机骨架材料;过渡金属氧化物分类号TM912.9ApplicationofMOFs-derivedTMO/Cinanodematerialsforlithium-ionbatteriesGUANRuohan,DONGGuixia✉,YANGShuangjuanCollegeofMaterialsScienceandEngineering,NorthChinaUniversityofTechnology,Tangshan063000,China✉Correspondingauthor,E-mail:dongguixia199@163.comABSTRACTThegraphiteasthecommercialanodematerialforlithium-ionbatteriesshowsthelowspecificcapacity,whichisdifficulttomeetthemarketdemand.Themetal-organicframeworkmaterials(MOFs)havethetunablestructure,largesurfacearea,andadjustableporesize,whichcanbeusedasthenextgenerationofelectrochemicalenergystoragedevices,causingtheextensiveresearch.Thesynthesisofthemetal(Fe,Co,Zn,Mn,Cu)-basedmetalorganicframeworksandthederivativeswereintroducedinthispaper,theresearchprogressonthepreparationoftransitionmetaloxide(TMO)/Castheanodematerialsforlithium-ionbatterieswasfocused,usingMOFsastheprecursors,andthedevelopmentdirectionwasprospected.KEYWORDSlithium-ionbatteries;anodematerials;metal-organicframeworkmaterials;transitionmetaloxide传统锂离子电池(lithiumionbatteries,LIBs)由石墨负极和锂化过渡金属氧化物(transitionmetaloxide,TMO)正极构成,已达到其性能极限。新电极材料和新存储机制有助于开发出具有高容量和循环稳定性的先进锂离子电池,但由于电化学过程可能发生的相变和副反应,产生了许多具有挑战性的问题,如不可逆性和不稳定性[1−3]。近年来,金属有机骨架材料(metal-organicframe-收稿日期:2021−05−12DOI:10.19591/j.cnki.cn...