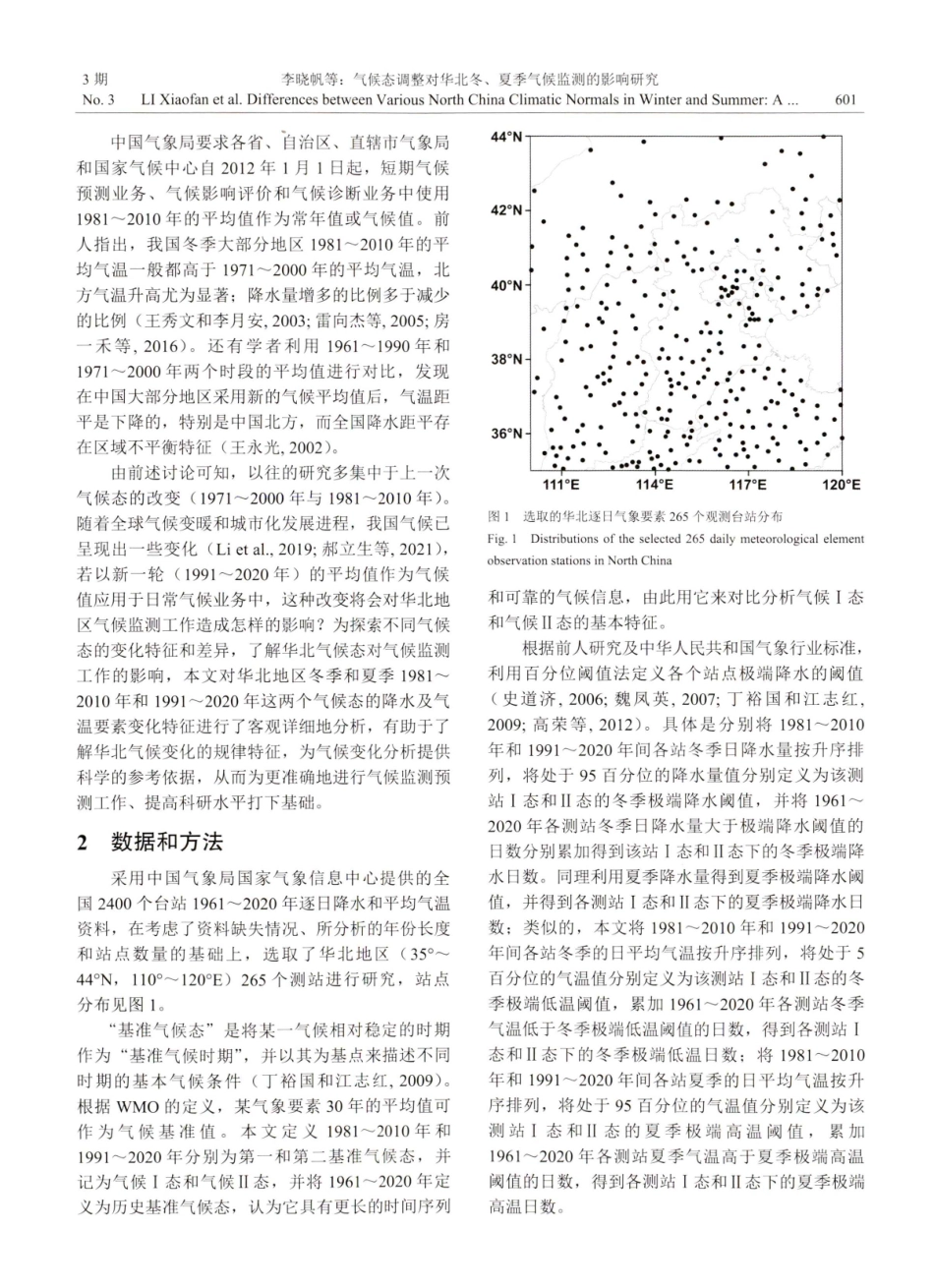
Monitoring[J].ChineseJournalofAtmosphericSciences(inChinese),47(3):599-615.doi:10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2202.21200GONGZhiqiangetal.2023.DifferencesbetweenVariousNorthChinaClimaticNormalsinWinterandSummer:AStudyofItsImpactonClimateLIXiaofan,YUChangwen,李晓帆,于长文,龚志强,等.2023.气候态调整对华北冬、夏季气候监测的影响研究[J].大气科学,47(3:599-615.May20232023年5月ChinessciencesVol.47No.3第47卷第3期学科气候态调整对华北冬、夏季气候监测的影响研究李晓帆1,2于长文1,2龚志强3,4封国林3车少静1,2李天宇25,61河北省气象与生态环境重点实验室/河北省气候中心,石家庄0500212中国气象局雄安大气边界层重点开放实验室,雄安新区0718003中国气象局国家气候中心开放实验室,北京1000814常熟理工学院电子与信息工程学院,苏州2150005牡丹江市气象局,牡丹江1570106吉林省气候中心,长春130062摘要本研究对比分析了不同气候态下,华北冬、夏季降水及气温的差异,分析了气候平均值的改变对历史极端事件监测的可能影响。研究结果发现,19912020年(简称气候I态)的冬季和夏季的平均降水量均略多于1981~2010年(简称气候1态),但接近或略少于1961~2020年的平均降水量,平均降水量逐年变化幅度冬季I态小于I态,夏季反之。气候I态冬季降水空间分布不均,夏季较I态呈“中部减少,东西增加”的分布型。冬季和夏季极端降水阈值II态(0.86mm和22.0mm)较1态(0.83mm和21.6mm)均略有提高,造成近60年华北大部基于II态阈值的冬、夏季极端降水日数较I态略减少。此外,气候I态的华北冬、夏季平均气温均明显高于态,也高于1961~2020年平均值。II态气温较I态基本呈全区增加特征,但空间分布不均匀。冬季极端低温和夏季极端高温阈值I态(-9.8℃℃和27.9℃)较态(-10.2℃℃和27.5℃)均有所有所提高,造成华北大部分地区基于II态阈值的近60年冬季极端低温日数较I态有所增加,夏季极端高温日数较I态存在不同程度的减少。因此,新气候态下华北气温和降水均值,华北大部极端降水阈值和极端气温阈值均有所提高,造成气候监测中更容易出现气温偏低,降水偏少,历史极端事件监测中极端事件略减少的情况,在未来10年的气候监测预测业务中要充分考虑新气候态可能造成的影响。关键词华北冬季夏季气候态差异文章编号1006-9895(2023)03-0599-17中图分类号P466文献标识码Adoi:10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2202.21200DifferencesbetweenVariousNorth...