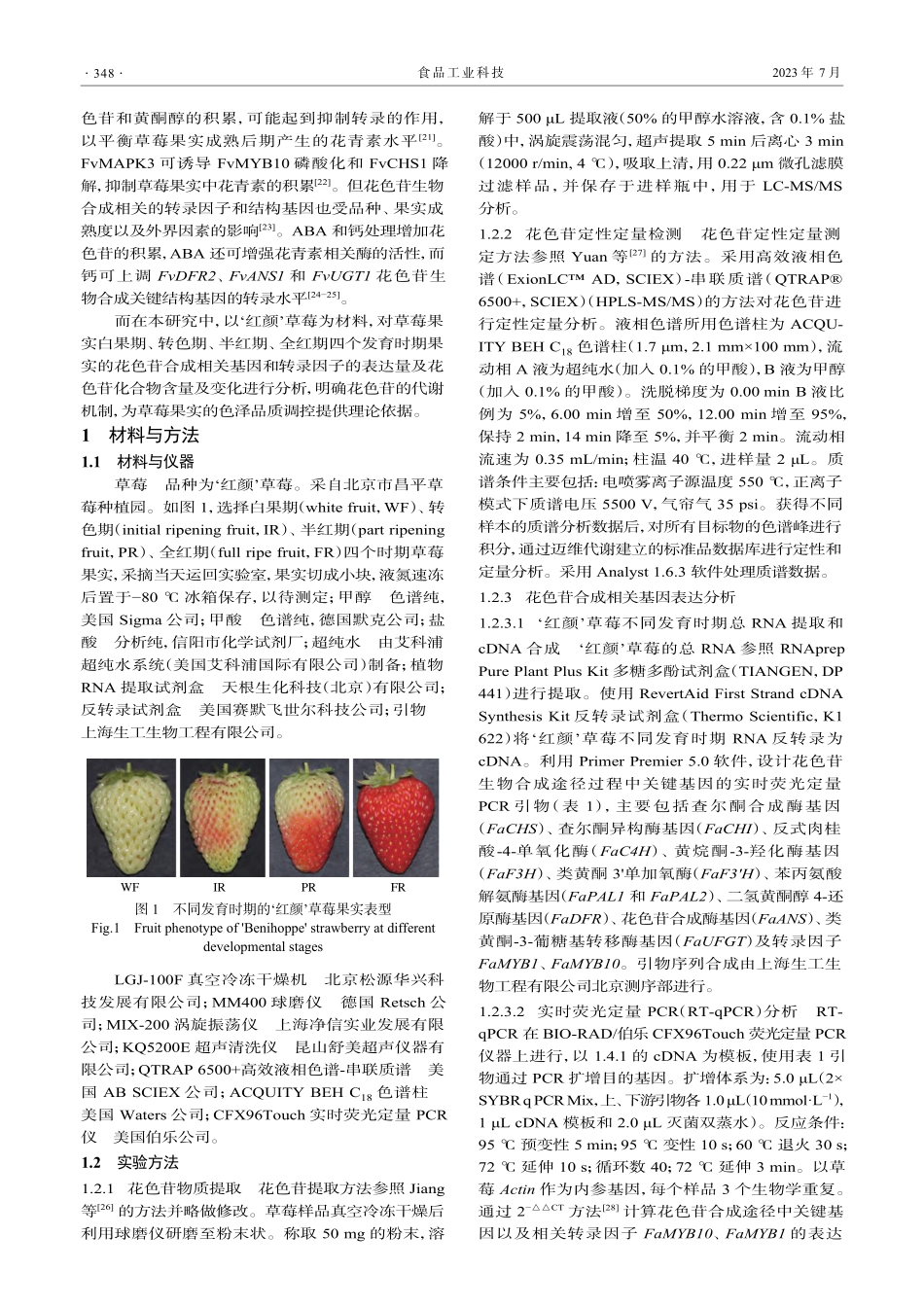
彭贞贞,钟传飞,王宝刚,等.‘红颜’草莓果实成熟过程中花色苷积累及合成途径基因表达的分析[J].食品工业科技,2023,44(14):346−354.doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022090106PENGZhenzhen,ZHONGChuanfei,WANGBaogang,etal.AnalysisofAnthocyaninAccumulationandGeneExpressionofAnthocyaninSynthesisPathwayduringFruitRipeningof'Benihoppe'Strawberry[J].ScienceandTechnologyofFoodIndustry,2023,44(14):346−354.(inChinesewithEnglishabstract).doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022090106·贮运保鲜·‘红颜’草莓果实成熟过程中花色苷积累及合成途径基因表达的分析彭贞贞1,2,钟传飞3,王宝刚1,4,5,李文生1,4,5,周家华1,4,5,傅达奇2,常虹1,4,5,王云香1,4,5,*(1.北京市农林科学院农产品加工与食品营养研究所,北京100097;2.中国农业大学食品科学与营养工程学院,北京100083;3.北京市农林科学院林业果树研究所,北京100093;4.果蔬农产品保鲜与加工北京市重点实验室,北京100097;5.农业农村部蔬菜产后处理重点实验室,北京100097)摘要:为探究‘红颜’草莓果实成熟过程中花色苷积累和合成相关基因表达规律,以‘红颜’草莓白果期(whitefruit,WF)、转色期(initialripeningfruit,IR)、半红期(partripeningfruit,PR)、全红期(fullripefruit,FR)四个发育时期果实为研究对象,采用高效液相色谱-串联质谱方法对其花色苷物质进行定性和定量分析,并测定不同发育过程中的花色苷生物合成途径中结构基因表达水平,以期为草莓果实花色苷代谢以及色泽品质调控提供理论依据。结果表明:‘红颜’草莓中有24种花色苷化合物和4种原花青素,随着果实成熟,总花色苷含量逐渐增加,原花青素含量逐渐降低。各发育时期的差异代谢物质主要是天竺葵素和矢车菊素。其中天竺葵素-3-O-葡萄糖苷、天竺葵素-3-O-芸香糖苷和矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷是花色苷中的主要物质,在‘红颜’草莓全熟期时,分别占花色苷总量的79.7%,14.1%和3.56%。实时定量PCR分析表明,花色苷合成途径基因FaPAL1、FaC4H、FaF3H、FaANS、FaUFGT和转录因子FaMYB10表达水平随果实发育逐渐升高。综上所述,‘红颜’草莓果实的花色苷含量随果实成熟逐渐积累,花色苷差异代谢的物质包含天竺葵素和矢车菊素,花色苷合成途径相关结构基因FaPAL1、FaC4H、FaF3H、FaANS、FaUFGT表达水平影响果实花色苷的积累。关键词:‘红颜’草莓,花色苷,代谢物质,基因本文网刊:中图分类号:TS...