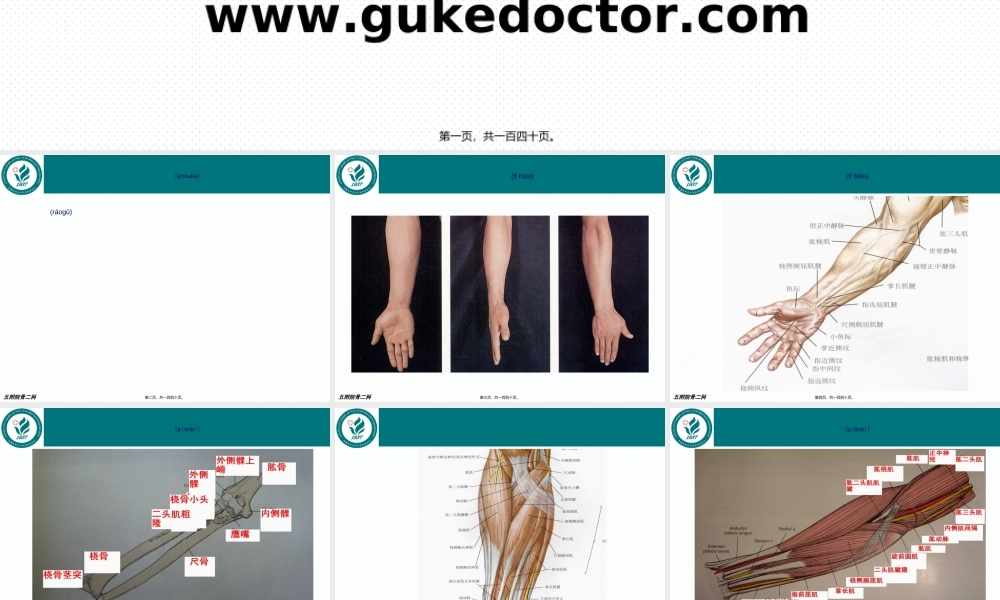
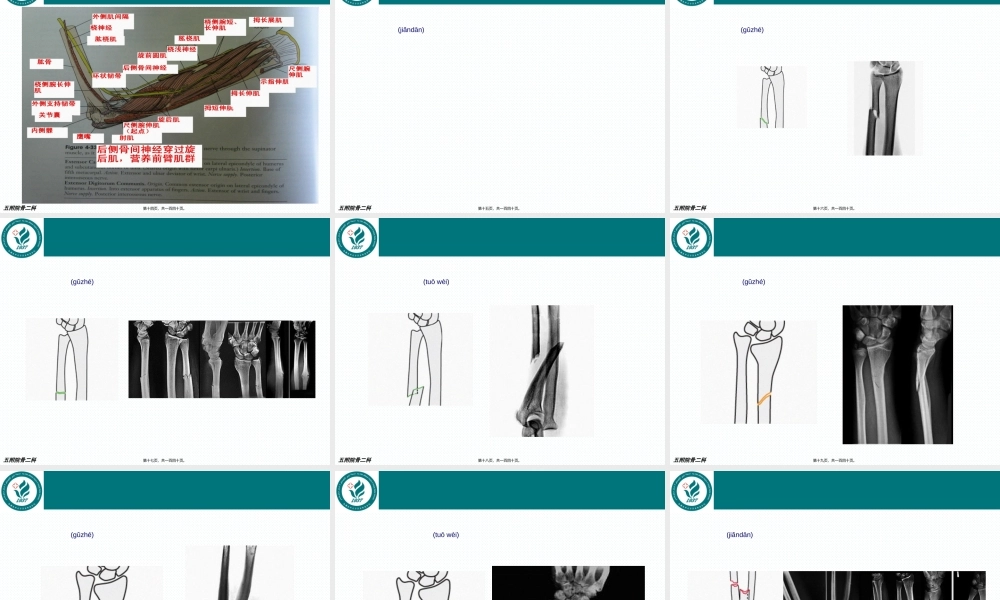
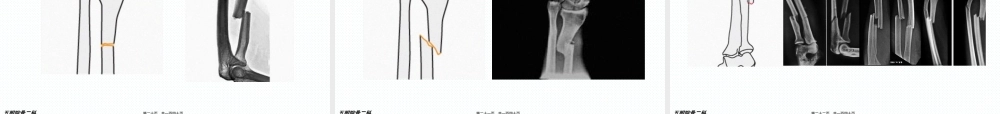
www.gukedoctor.com前臂(qiánbì)骨折五附院骨二科第一页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科尺桡骨(ráogǔ)双骨折尺骨单骨折桡骨单骨折前臂远端骨折(shòukè)第二页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(tǐbiǎo)第三页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(tǐbiǎo)第四页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第五页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科第六页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第七页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第八页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第九页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科桡神经深支和后侧骨间神经:桡神经在肘窝外侧,肱骨外上髁前方,分浅、深两支桡神经深支发出肌支至桡侧腕长、短伸肌和旋后肌,然后(ránhòu)穿入旋后肌,在桡骨头下方5~7CM出穿出该肌,称为后侧骨间神经,走行与前臂肌后群浅、深两层之间分短支与长支(qiánbì)第十页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第十一页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第十二页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第十三页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科(qiánbì)第十四页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A型简单(jiǎndān)骨折(A1,A2,A3)B型锲型骨折(B1,B2,B3)C型复杂骨折(C1,C2,C3)(qiánbì)第十五页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A1.1斜型骨折(gǔzhé)第十六页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A1.2横型骨折(gǔzhé)第十七页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A1.3伴有桡骨头脱位(tuōwèi)(孟氏骨折)第十八页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A2.1斜型骨折(gǔzhé)第十九页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A2.2横型骨折(gǔzhé)第二十页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A2.3伴头下尺桡关节脱位(tuōwèi)(盖氏骨折)第二十一页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科A3简单(jiǎndān)的双骨折第二十二页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B1.1完整(wánzhěng)锲型第二十三页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B1.2带有碎片(suìpiàn)的锲型骨折第二十四页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B1.3伴有桡骨头脱位(tuōwèi)(孟氏骨折)第二十五页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B2.1完整(wánzhěng)锲型第二十六页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B2.2碎片(suìpiàn)锲型第二十七页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B2.3伴有下尺桡关节(guānjié)脱位(盖氏骨折)第二十八页,共一百四十页。五附院骨二科B3.1尺骨锲型,桡骨简单(jiǎndān)骨折第二十九页,共一百四十页。五附院...