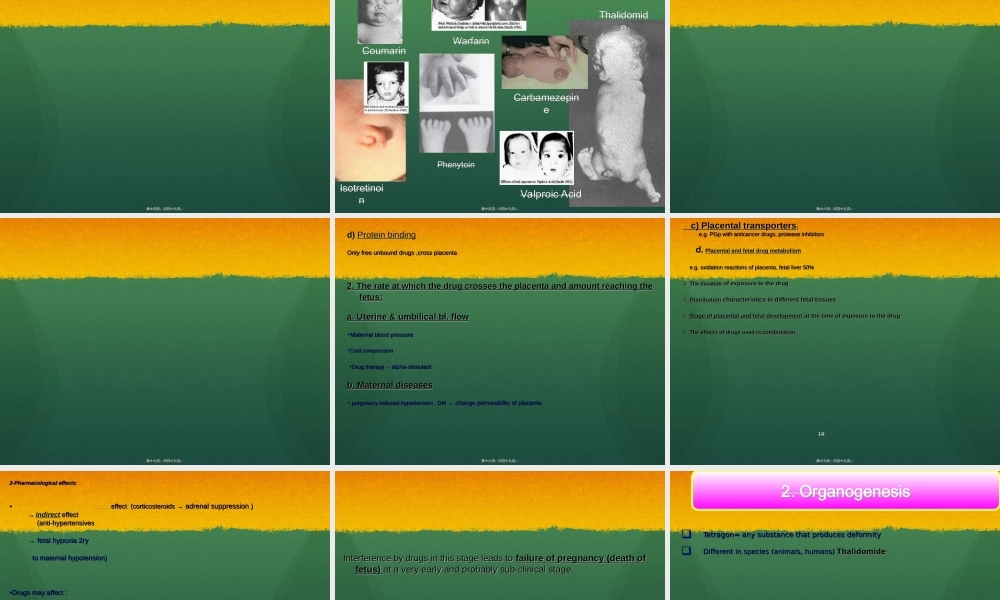
ByByDrAttiaMJabrDrAttiaMJabrDrAmalHassanainDrAmalHassanainFacultyofMedicineFacultyofMedicineQassimUniversityQassimUniversity11第一页,共四十九页。第一页,共四十九页。TherearetwomajorconsiderationsregardingdruguseinTherearetwomajorconsiderationsregardingdruguseinpregnantwomen:pregnantwomen:EffectofpregnancyonEffectofpregnancyon::drugs(pharmacokinetics)drugs(pharmacokinetics)EffectofdrugsonEffectofdrugson::pregnancy(fetus)pregnancy(fetus)第二页,共四十九页。第二页,共四十九页。第三页,共四十九页。第三页,共四十九页。1.1.About40%About40%ofpregnantwomentakedrugs(atleast1drug)ofpregnantwomentakedrugs(atleast1drug)6%6%takedrugsduring1takedrugsduring1ststtrimester(excludefolic,iron,vitamins)trimester(excludefolic,iron,vitamins)3.3.ThemostcommondrugsareThemostcommondrugsareanalgesics,antibacterial,antacids.analgesics,antibacterial,antacids.Whataboutnewdrugs?Whataboutnewdrugs?44第四页,共四十九页。第四页,共四十九页。A.A.AbsorptionAbsorption::TherateTheratemaybemaybereducedreducedbecauseofdelayedgastricemptyingbecauseofdelayedgastricemptyingTheextentTheextentmaynotbeabsorbedmaynotbeabsorbedVomitingVomitingiscommon.Effect?iscommon.Effect?55第五页,共四十九页。第五页,共四十九页。B)Distribution:B)Distribution:11..MaternalMaternalplasmavolumeplasmavolume&ECF&ECF▲50%(3▲50%(3rdrdtrimester)trimester)2.2.TotalbodywaterTotalbodywater▲20%&totalbodyfat▲20%&totalbodyfat3.3.WhatistheeffectonVd&steadystateconcentration?WhatistheeffectonVd&steadystateconcentration?4.4.SerumalbuminSerumalbumin▼▼byabout20%(inpre-eclampsia35%)byabout20%(inpre-eclampsia35%)5.5.Alpha1-acidglycoproteinAlpha1-acidglycoprotein▲▲Byabout40%(inpre-eclampsia100%)Byabout40%(inpre-eclampsia100%)6.Thefreefractionof6.Thefreefractionofacidicdrugsacidicdrugs▲▲7.Thefreefractionof7.Thefreefractionofbasicdrugsbasicdrugs▼▼8.E.G.Diazepam,phenytoin,valproate.What?8.E.G.Diazepam,phenytoin,valproate.What?Whatistheeffectont½ofthedrug?E.g.phenytoinWhatistheeffectont½ofthedrug?E.g.phenytoin66第六页,共四十九页...