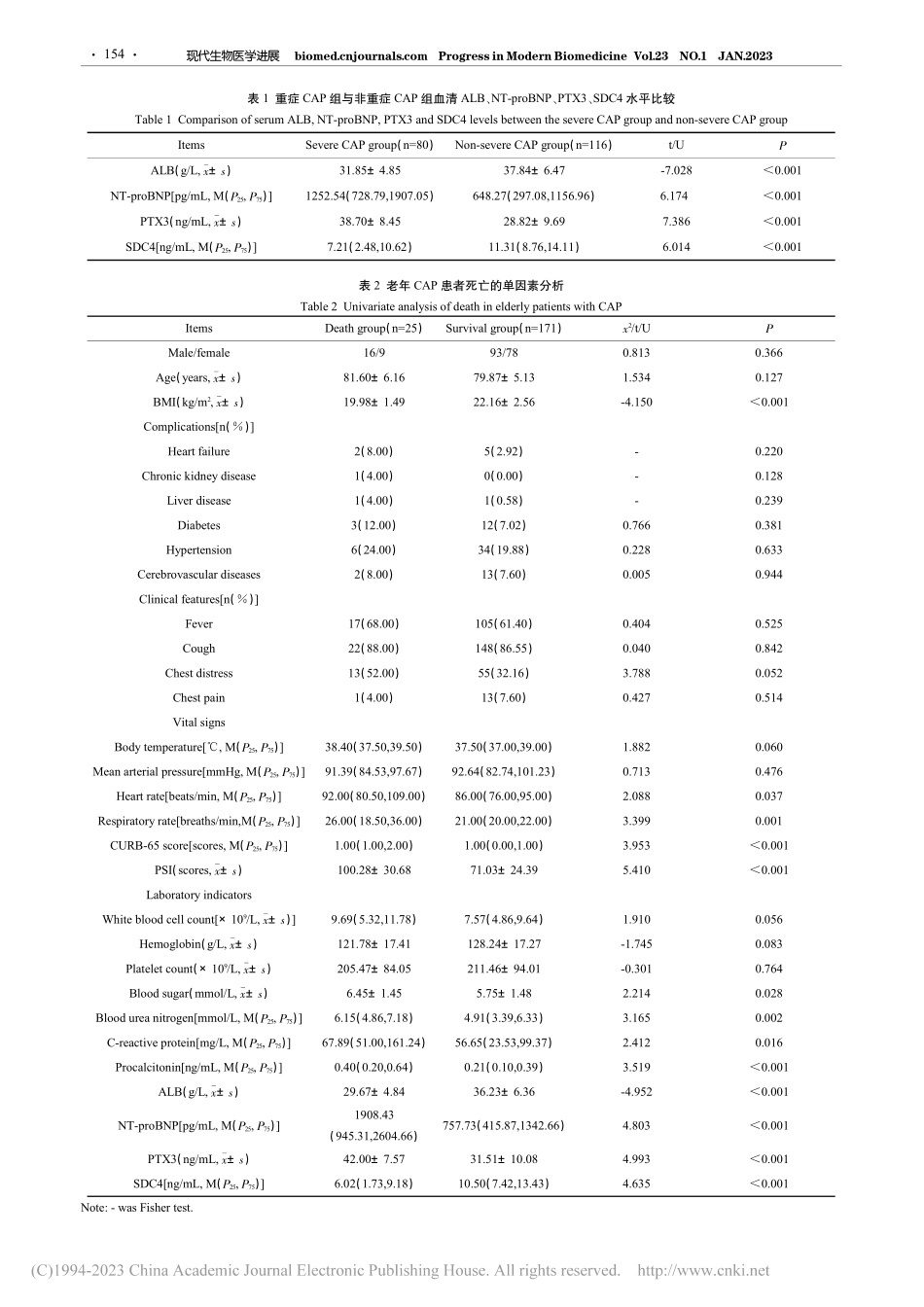
现代生物医学进展biomed.cnjournals.comProgressinModernBiomedicineVol.23NO.1JAN.2023doi:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2023.01.030不同病情老年社区获得性肺炎患者血清ALB、NT-proBNP、PTX3、SDC4的变化及对预后的影响分析*冯凯范贤明欧阳晓莉赵会君陈菊屏△(西南医科大学附属医院呼吸与危重症医学科四川泸州646000)摘要目的:分析不同病情老年社区获得性肺炎(CAP)患者血清白蛋白(ALB)、N末端脑钠肽前体(NT-proBNP)、正五聚蛋白3(PTX3)、多配体蛋白聚糖4(SDC4)的变化并探讨其对患者预后的影响。方法:选取2019年1月~2020年1月西南医科大学附属医院收治的196例老年CAP患者,根据病情严重程度分为重症CAP组80例和非重症CAP组116例,根据入院后28d存活情况分为死亡组25例和存活组171例。收集患者临床资料,检测血清ALB、NT-proBNP、PTX3、SDC4水平。通过多因素Logistic回归分析老年CAP患者死亡的影响因素,受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析血清ALB、NT-proBNP、PTX3、SDC4水平对老年CAP患者死亡风险的预测价值。结果:与非重症CAP组比较,重症CAP组血清ALB、SDC4水平降低,NT-proBNP、PTX3水平升高(P<0.05)。多因素Logistic回归分析显示,ALB升高、SDC4升高为老年CAP患者死亡的保护因素,呼吸频率加快、CURB-65评分增加、肺炎严重指数(PSI)增加、NT-proBNP升高、PTX3升高为老年CAP患者死亡的危险因素(P<0.05)。ROC曲线分析显示,血清ALB、NT-proBNP、PTX3、SDC4水平联合预测老年CAP患者死亡的曲线下面积(AUC)大于各指标单独预测。结论:老年CAP患者体内血清ALB、SDC4水平降低,NT-proBNP、PTX3水平升高,血清ALB、NT-proBNP、PTX3、SDC4与患者病情加重和预后有关,具有作为老年CAP患者预后评估指标的潜能。关键词:老年;社区获得性肺炎;ALB;NT-proBNP;PTX3;SDC4;预后中图分类号:R563.1文献标识码:A文章编号:1673-6273(2023)01-152-06ChangesinSerumALB,NT-proBNP,PTX3andSDC4inElderlyPatientswithCommunity-AcquiredPneumoniawithDifferentConditionsandAnalysisoftheImpactonPrognosis*FENGKai,FANXian-ming,OUYANGXiao-li,ZHAOHui-jun,CHENJu-ping△(DepartmentofRespiratoryandCriticalCareMedicine,AffiliatedHospitalofSouthwestMedicalUniversity,Luzhou,Sichuan,646000,China)ABSTRACTObjective:Toanalyzethechangesinserumalbumin(ALB),N-terminalpro-brainnatriureticpeptide(NT-proBNP),pentraxin3(PTX3)andsyn...