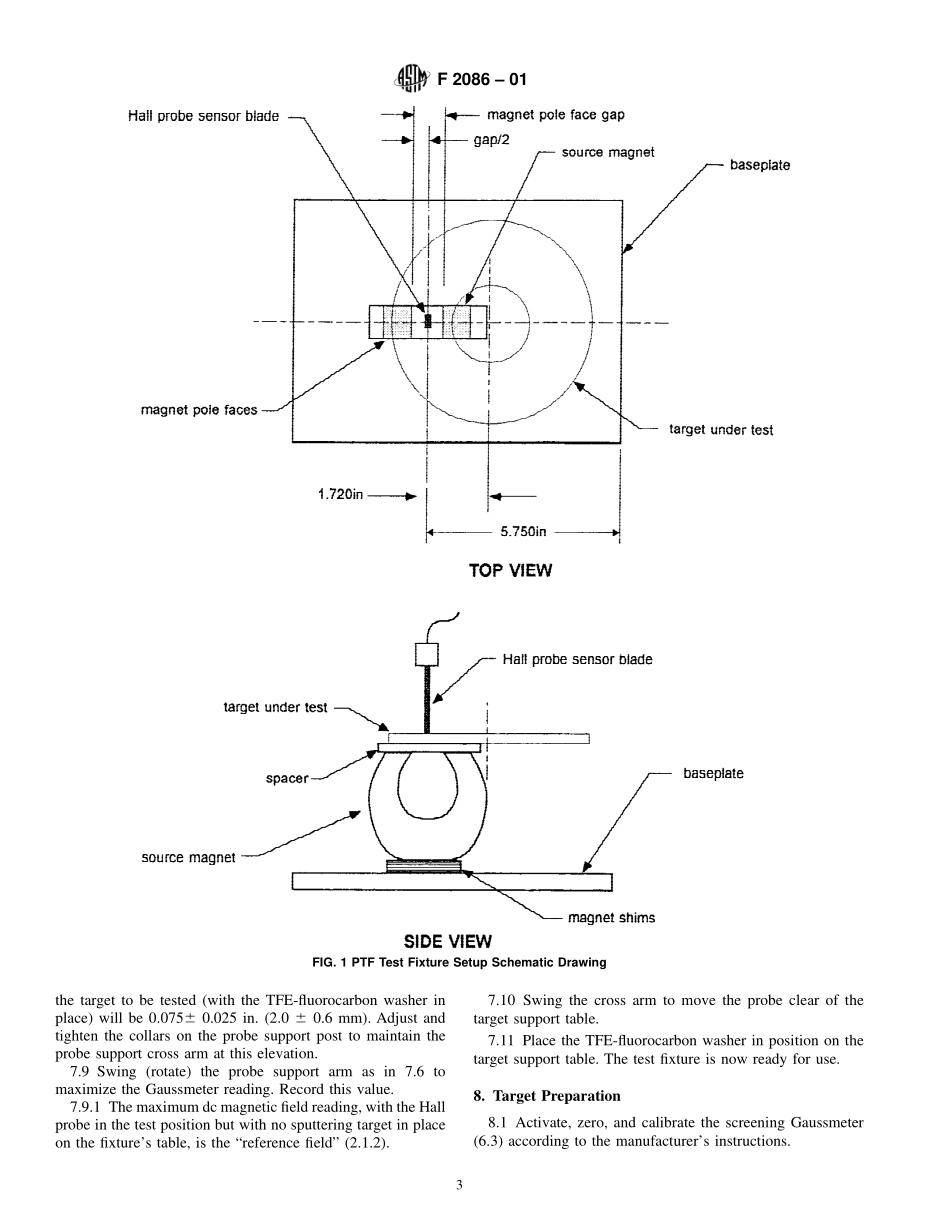
Designation:F2086–01StandardTestMethodforPassThroughFluxofCircularMagneticSputteringTargets,Method21ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF2086;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversmeasuringthedcmagneticfieldtransmittedthrougharoundferromagneticsputteringtarget(“passthroughflux”or“PTF”).Inthistestmethodthesourcemagneticfieldisinthetesttarget’sradialdirection.1.2Planardisk-shapedtargetsinthediameterrange5to8in.inclusive(125to205mminclusive)andofthickness0.1to0.5in.inclusive(2.5to13mm)maybecharacterizedbythisprocedure.1.3Thistestmethodisalsoapplicabletotargetshavinganopencenter,forexample,totargets5-in.outsidediameterby2.5-in.insidediameterby0.25-in.thick(127-mmoutsidediameterby63.5-mminsidediameterby6.35-mmthick).1.4Targetsofvariousdiametersandthicknessesareaccom-modatedbysuitablefixturingtoalignthepieceundertestwiththesourcemagnetmountedinthetestfixture.Tooling,cover-ingseveralpopulartargetdesignsisspecifiedinthisprocedure.Additionaltargetconfigurationsmaybetestedbyprovidingspecialtooling.Whenspecialfixturingisusedallpartiesconcernedwiththetestingmustagreetothetestsetup.1.5Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.Terminology2.1Definitions:2.1.1passthroughflux(PTF),n—forpurposesofthisstandard,the“passthroughflux”isthedcmagneticfieldtransmittedthroughaferromagneticsputteringtarget,fromonefacetotheoppositeface.2.1.1.1Discussion—PTFisalsofrequentlycalled“leakageflux.”2.1.2referencefield,n—forpurpo...