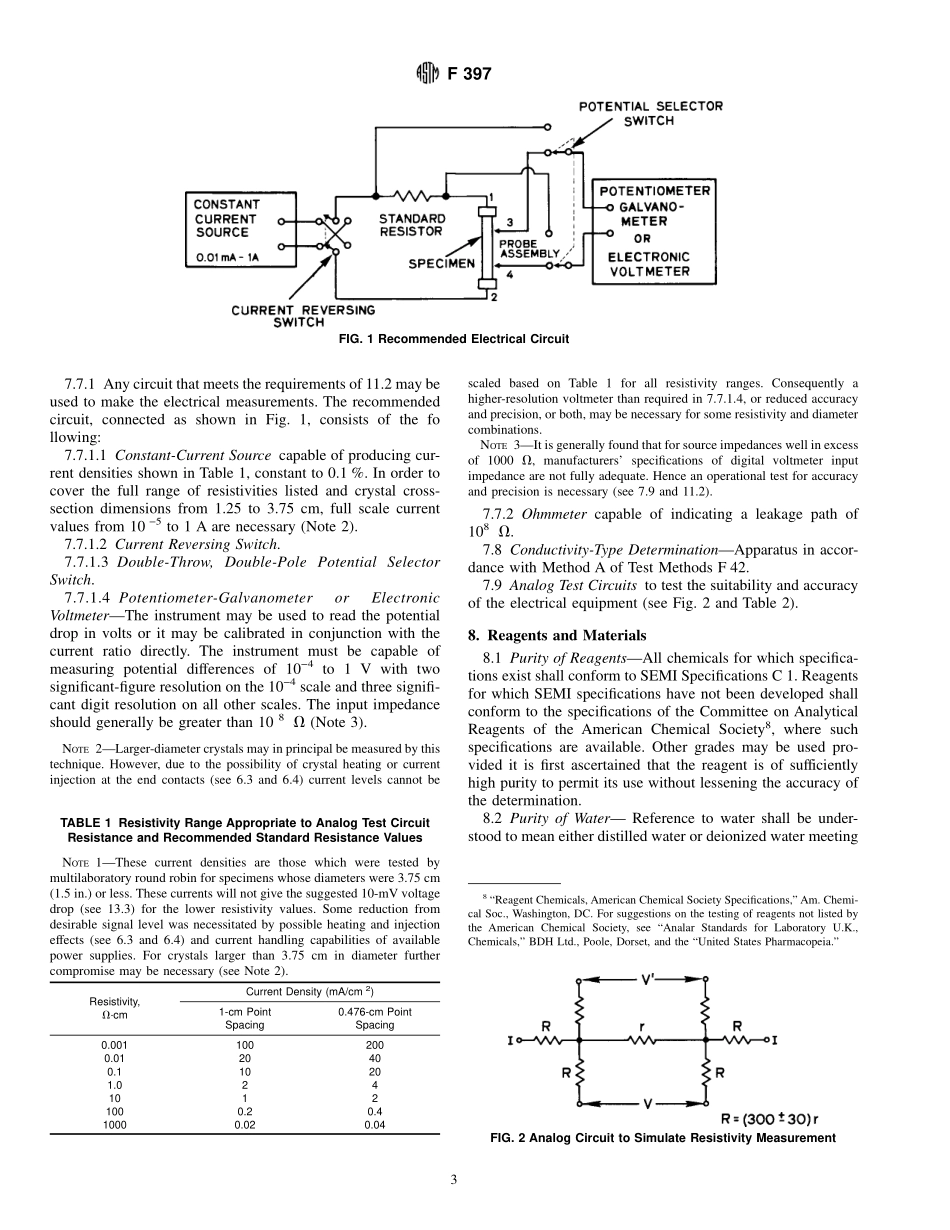
Designation:F397–93(Reapproved1999)DIN50430StandardTestMethodforResistivityofSiliconBarsUsingaTwo-PointProbe1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF397;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethod2coversthemeasurementoftheresis-tivityofsingle-crystalbarshavingcrosssectionsthatareuniforminareaandsquare,rectangularorroundinshape,andhavingresistivitybetween0.0009and3000V·cm.Theresis-tivityofasiliconcrystalisanimportantacceptancerequire-ment.1.2Thistestmethodisintendedforuseonsinglecrystalsofsiliconofeithern-orp-typeforwhichtheuniformityofthecrystalcrosssectionissuchthattheareacanbeaccuratelycalculated.Thespecimencross-sectionalareashallbeconstanttowithin61%oftheaverageareaasdeterminedbymeasure-mentsalongthecrystalaxis(see12.2).1.3Theratioofthelengthtothemaximumdimensionofthecrosssectionofthespecimenshallnotbelessthan3:1(see12.1).Thelargestdiametertestedbyroundrobinwas3.75cm(1.5in.),andthisisthelargestdiameterthatcanbemeasuredbythismethod.Thespecimenshallnormallyhaveasurfacefinishof0.4µm(16µin.)rmsorless(seeANSIB46).Othersurfacefinishesmaybeusedifmutuallyacceptable;however,themultilaboratoryprecisionfiguresofthistest(see16.1)thenmaynolongerapply.1.4Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.SpecifichazardstatementsaregiveninSection9.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:D1193SpecificationforReagentWater3E1SpecificationforASTMThermometers4F42TestMethodsforConductivityTypeofExtrinsicSemiconductingMaterials52.2OtherStandard:ANSIB46SurfaceTexture62.3SEMIStandard:C1SpecificationsforReagents73.Terminology3.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThis...