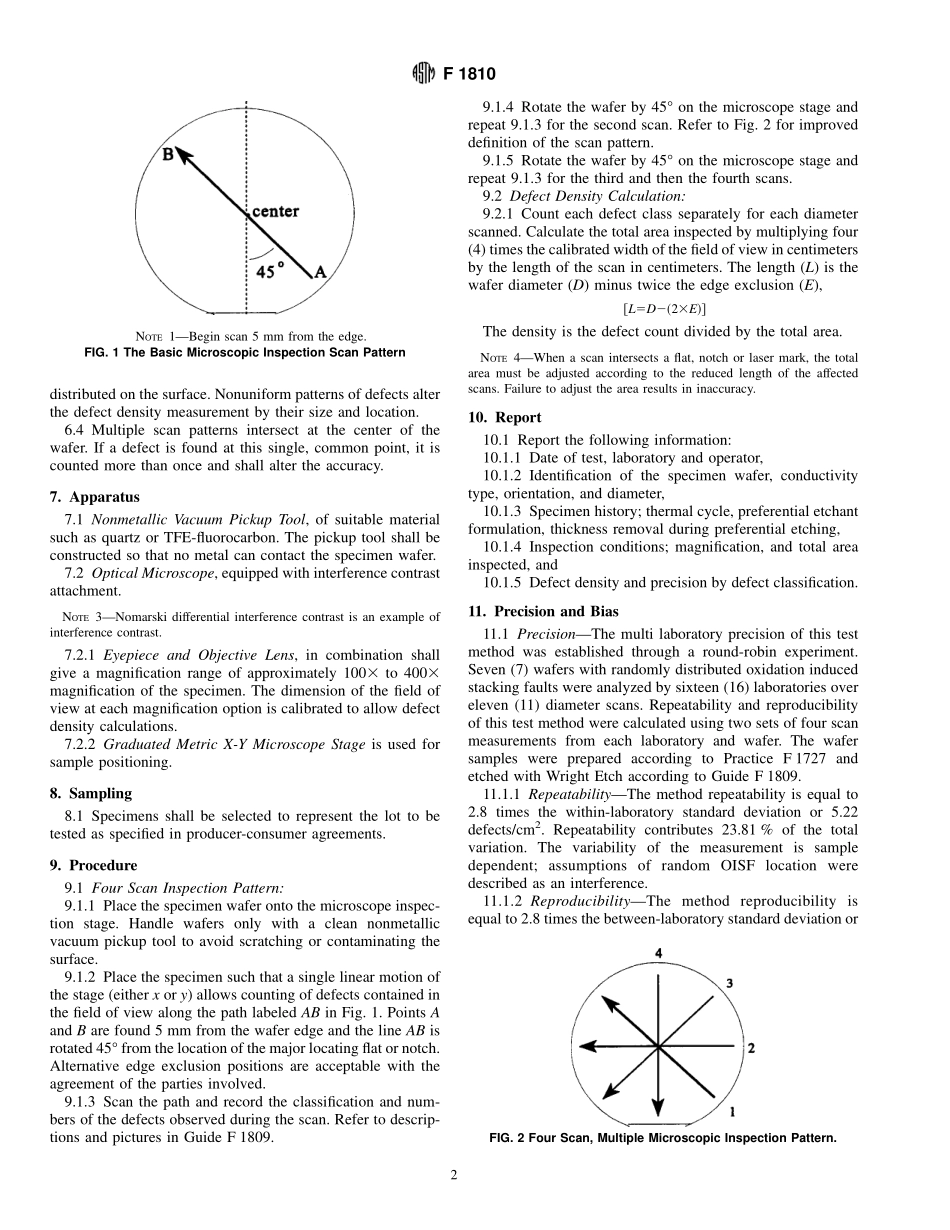
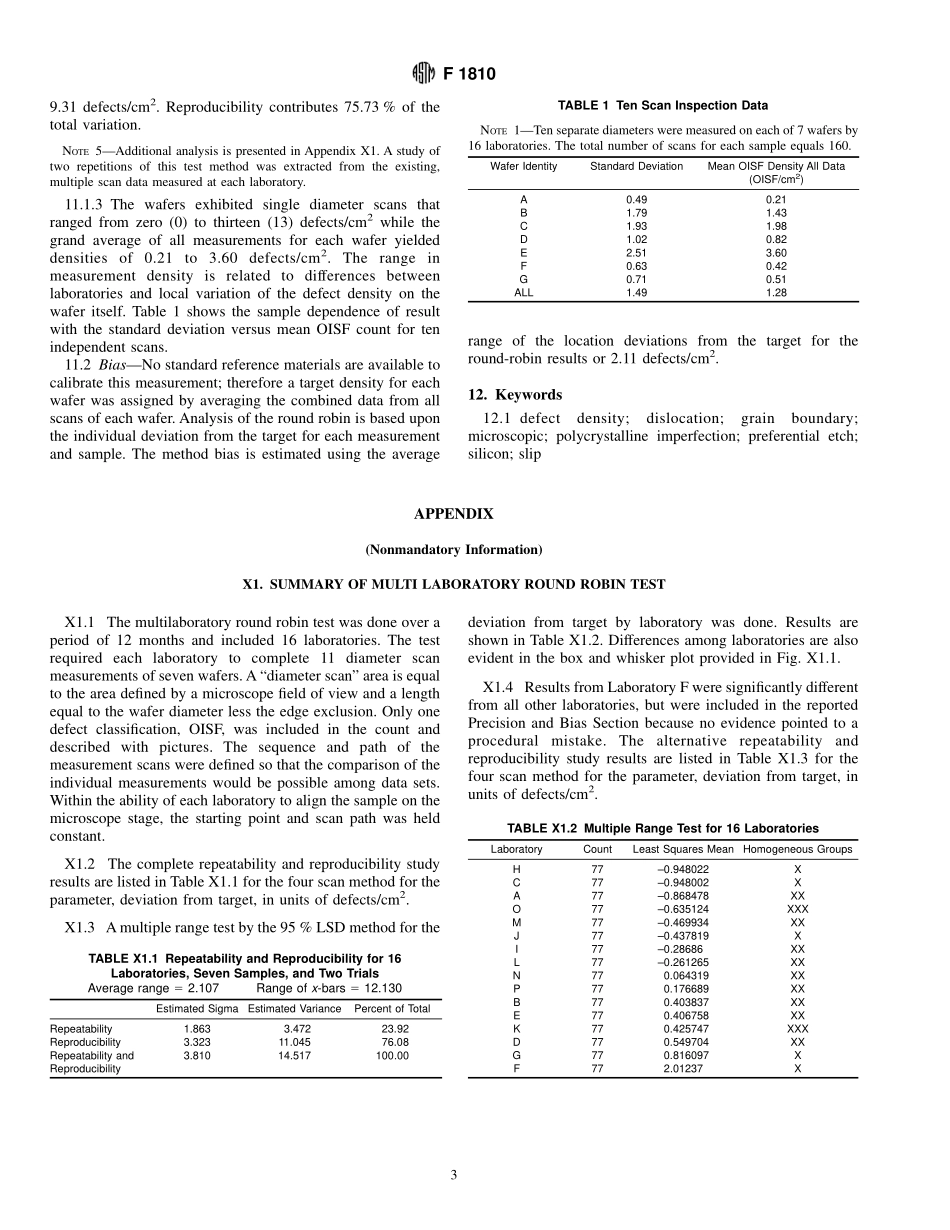
Designation:F1810–97StandardTestMethodforCountingPreferentiallyEtchedorDecoratedSurfaceDefectsinSiliconWafers1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF1810;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethoddescribesthetechniquetocountthedensityofsurfacedefectsinsiliconwafersbymicroscopicanalysis.NOTE1—Practicaluseofadefectcountingmethodrequiresanassump-tionbemadethatdefectsarerandomlydistributedonthesurface.Ifthisassumptionisnotmet,theaccuracyandprecisionofthistestmethodwillbediminished.1.2Applicationofthistestmethodislimitedtospecimensthathavediscrete,identifiableartifactsonthesurfaceofthesiliconsample.TypicalsampleshavebeenpreferentiallyetchedaccordingtoGuideF1809orepitaxiallydeposited,formingdefectsinasiliconlayerstructure.1.3Waferthicknessanddiameterforthistestmethodislimitedonlybytherangeofmicroscopestagemotionsavail-able.1.4Thistestmethodisapplicabletosiliconwaferswithdefectdensitybetween0.01and10000defectspercm2.NOTE2—Thecommerciallysignificantdefectdensityrangeisbetween0.01to10defectspercm2,butthistestmethodextendstohigherdefectlevelsdueandimprovedstatisticalsamplingobtainedwithhighercounts.1.5Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:F1241TerminologyofSiliconTechnology2F1725PracticeforAnalysisofCrystallographicPerfectionofSiliconIngots2F1726PracticeforAnalysisofCrystallographicPerfectionofSiliconWafers2F1727PracticeforDetectionofOxidationInducedDefectsinPolishedSiliconWafers2F1809GuideforSelectionandUseofEtchingSolutionstoDelineateStructuralDefectsinSilicon23.Terminology3.1Definitionsofterms...