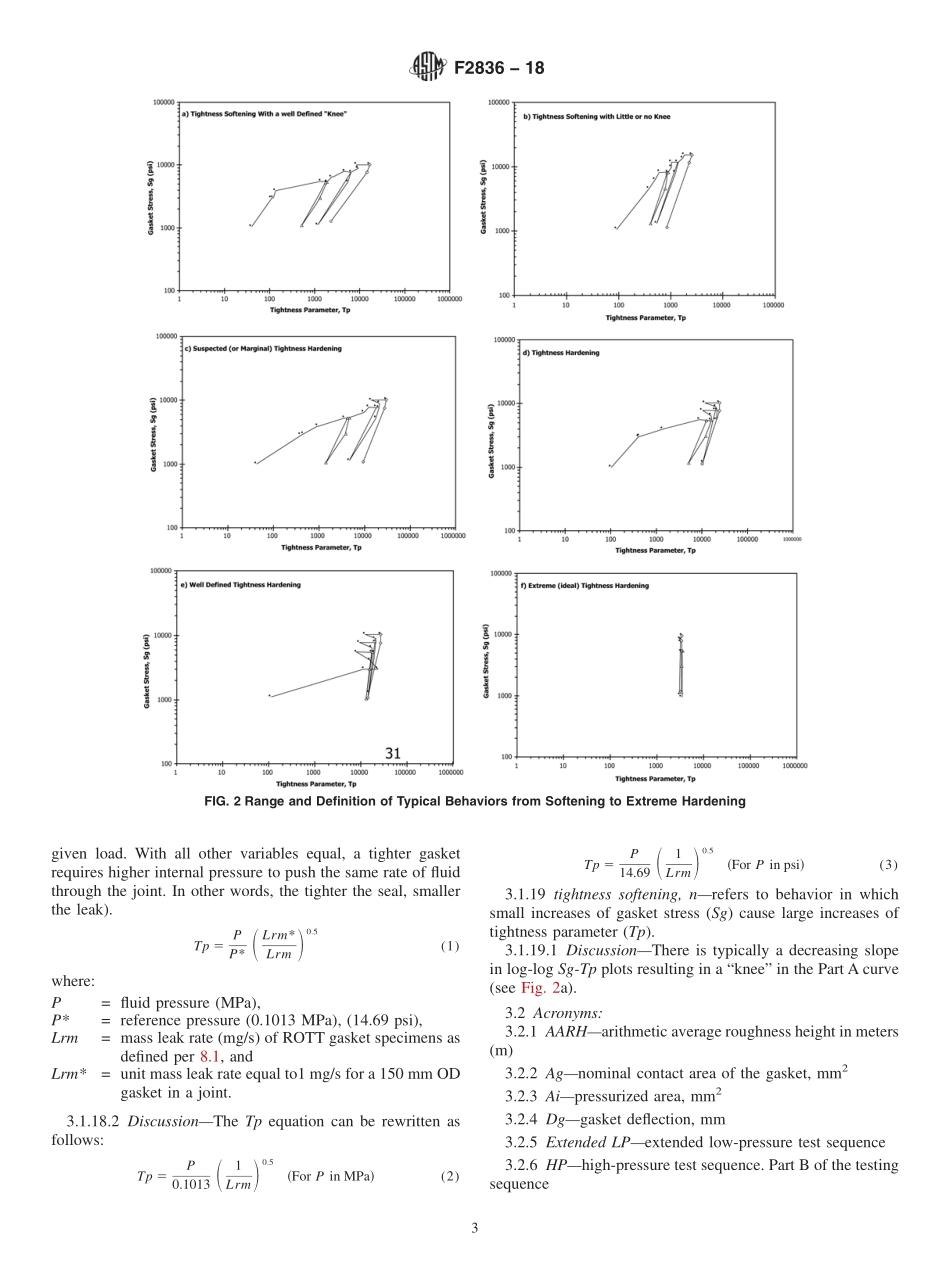
Designation:F2836−18StandardPracticeforGasketConstantsforBoltedJointDesign1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF2836;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thispracticedeterminesroomtemperaturegaskettight-nessdesignconstantsforpressurizedboltedflangedconnec-tionssuchasthosedesignedinaccordancewiththeASMEBoilerandPressureVesselCode.1.2Thispracticeappliesmainlytoalltypesofcirculargasketproductsandfacingstypicallyusedinprocessorpowerplantpressurevessels,heatexchangers,andpipingincludingsolidmetal,jacketed,spiralwound,andsheet-typegaskets.Asanoptionalextensionofthispractice,themaximumassemblystressforthosegasketsmayalsobedeterminedbythisprocedure.1.3Units—ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard,butotherunitsmaybeincluded.1.4Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafety,health,andenvironmentalpracticesanddeter-minetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.5Thisinternationalstandardwasdevelopedinaccor-dancewithinternationallyrecognizedprinciplesonstandard-izationestablishedintheDecisiononPrinciplesfortheDevelopmentofInternationalStandards,GuidesandRecom-mendationsissuedbytheWorldTradeOrganizationTechnicalBarrierstoTrade(TBT)Committee.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASMEStandards:2ASMEB16.5SteelPipeFlangesandFlangedFittingsASMEB16.20MetallicGasketsforPipeFlanges—Ring-Joint,Spiral-Wound,andJacketedASMEB16.21NonmetallicFlatGasketsforPipeFlangesASMEBoilerandPressureVesselCodeSectionVIIIDivi-sion1,Appendix23.Terminology3.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:3.1.1ASMEClass150,n—referstothedimensionsandpressureratingofClass150ofstandardflangesinASMEStandardB16.5.3.1.2flangerotation,n—rotationoftheflangefacesu...