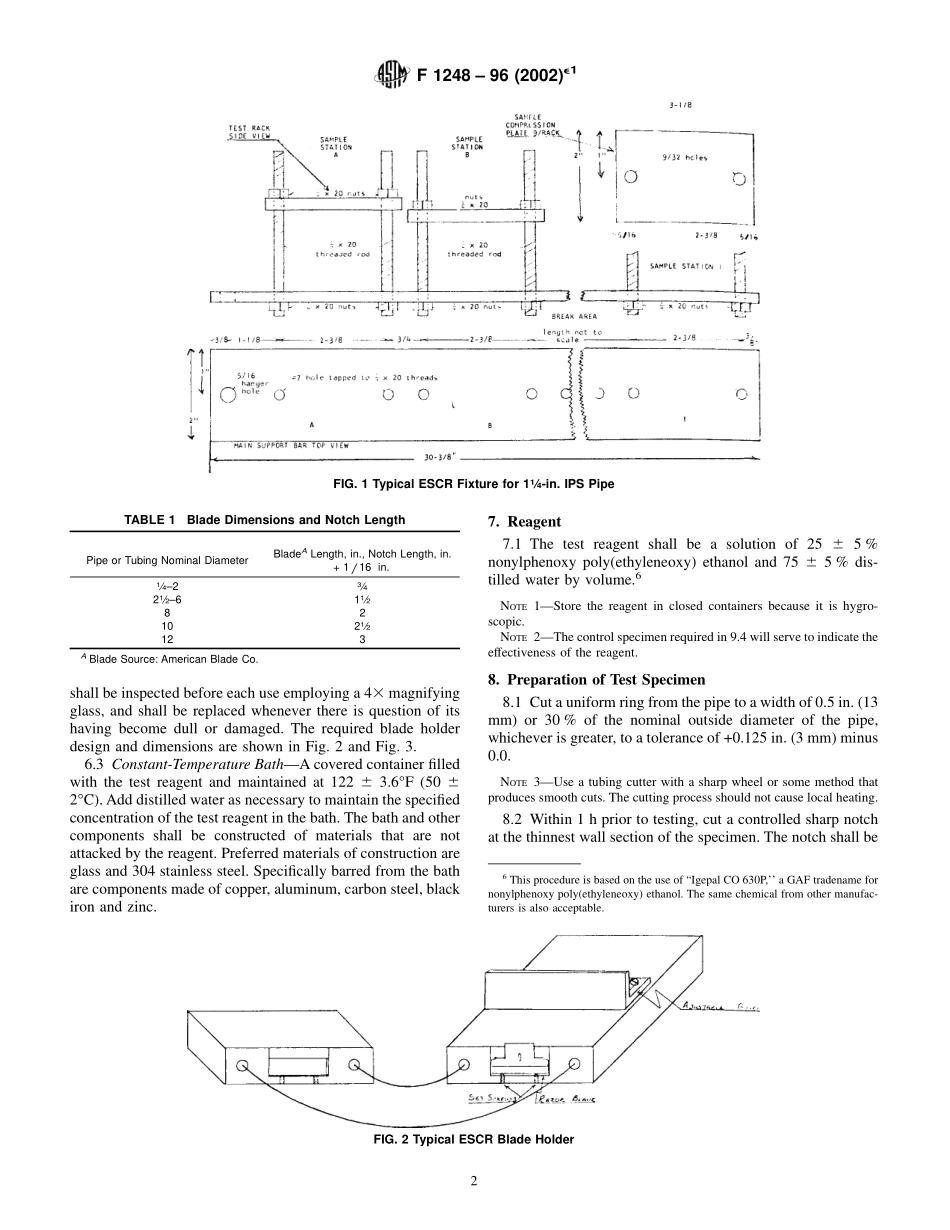
Designation:F1248–96(Reapproved2002)e1AnAmericanNationalStandardStandardTestMethodforDeterminationofEnvironmentalStressCrackResistance(ESCR)ofPolyethylenePipe1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF1248;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.e1NOTE—Section3.2.2andTables1-3wereeditoriallyrevisedinNovember2002.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofapolyeth-ylenepipespecimen’sresistancetostresscrackingwhensubjectedtocompressiondeformationinthepresenceofasurfaceactiveagentatelevatedtemperature.1.2Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.ThevaluesgiveninparenthesesmathematicalconversionstoSIunits,whichareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlastics2D1693TestMethodforEnvironmentalStressCrackingofEthylenePlastics3F412TerminologyRelatingtoPlasticPipingSystems43.Terminology3.1Definitions—DefinitionsoftermsareinaccordancewithTerminologyF412andabbreviationsareinaccordancewithTerminologyD1600,unlessotherwiseindicated.3.2DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:3.2.1environmentalstresscrackresistance(ESCR)—anumberinunitsofhours-to-failureindicatingtheresistanceofPEpipetocrackingatstressesbelowtheshort-termmechani-calstressvaluesofthepipewhileimmersedinasurface-activeliquidatelevatedtemperature.3.2.2failure,n—acrackinthesurfaceofthepipespecimen,visiblewiththeunaidedeye.3.2.2.1Discussion—Extensionofthecontrollednotchisnotafailure.Appearanceofmorethanonecrackinaspecimenshallbeclassifieda...