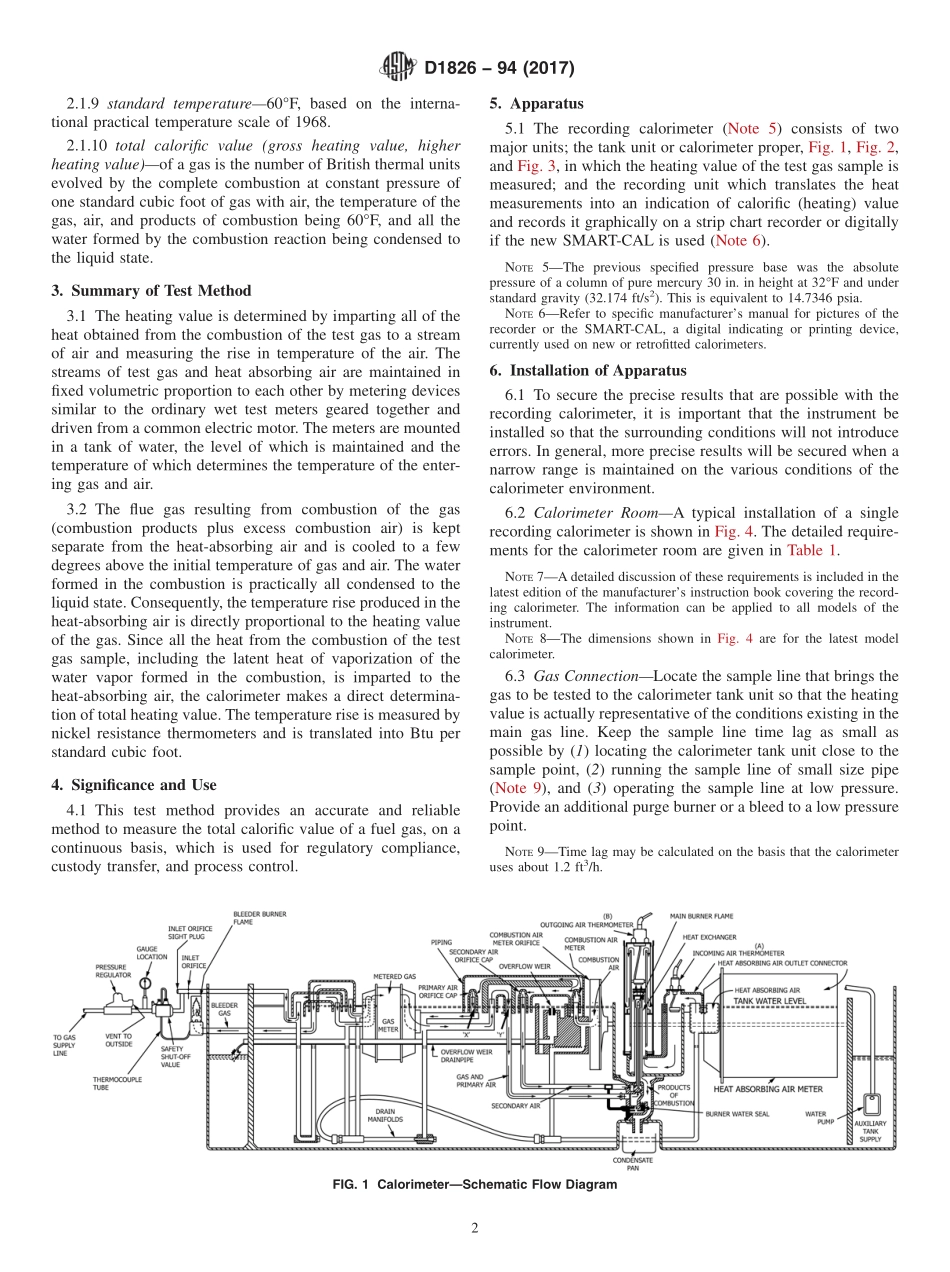
Designation:D1826−94(Reapproved2017)StandardTestMethodforCalorific(Heating)ValueofGasesinNaturalGasRangebyContinuousRecordingCalorimeter1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD1826;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationwiththecontinuousrecordingcalorimeter(Note1)ofthetotalcalorific(heating)valueoffuelgasproducedorsoldinthenaturalgasrangefrom900to1200Btu/standardft3.NOTE1—AnextensiveinvestigationoftheaccuracyoftheCutler-Hammerrecordinggascalorimeter,whenusedwithgasesofhighheatingvalue,wasmadebytheNationalBureauofStandardsin1957underaresearchprojectsponsoredbytheAmericanGasAssociation.1.2Thesubjectscoveredinthistestmethodappearinthefollowingsections:SectionsAir-GasRatioTest11Apparatus5BasisofMeasurement14ColdBalanceTest10CompensationofComplicatingFactors13ConditionofGasSample7Definitions2InstallationofApparatus6MaintenanceAppendixX1OperatingPrecautionsAppendixX2OperationandCheckingofApparatus9Precision15Scope1SignificanceandUse4StandardizationofCalorimeter12Standardization,Preliminary,ofCalorimeterbyHydrogen8SummaryofTestMethod31.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.4Thisinternationalstandardwasdevelopedinaccor-dancewithinternationallyrecognizedprinciplesonstandard-izationestablishedintheDecisiononPrinciplesfortheDevelopmentofInternationalStandards,GuidesandRecom-mendationsissuedbytheWorldTradeOrganizationTechnicalBarrierstoTrade(TBT)Committee.2.Terminology2.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:2.1.1Themostimportanttermsusedinconnectionwiththedeterminationofthecalorificvalueofgaseousfuelsinr...