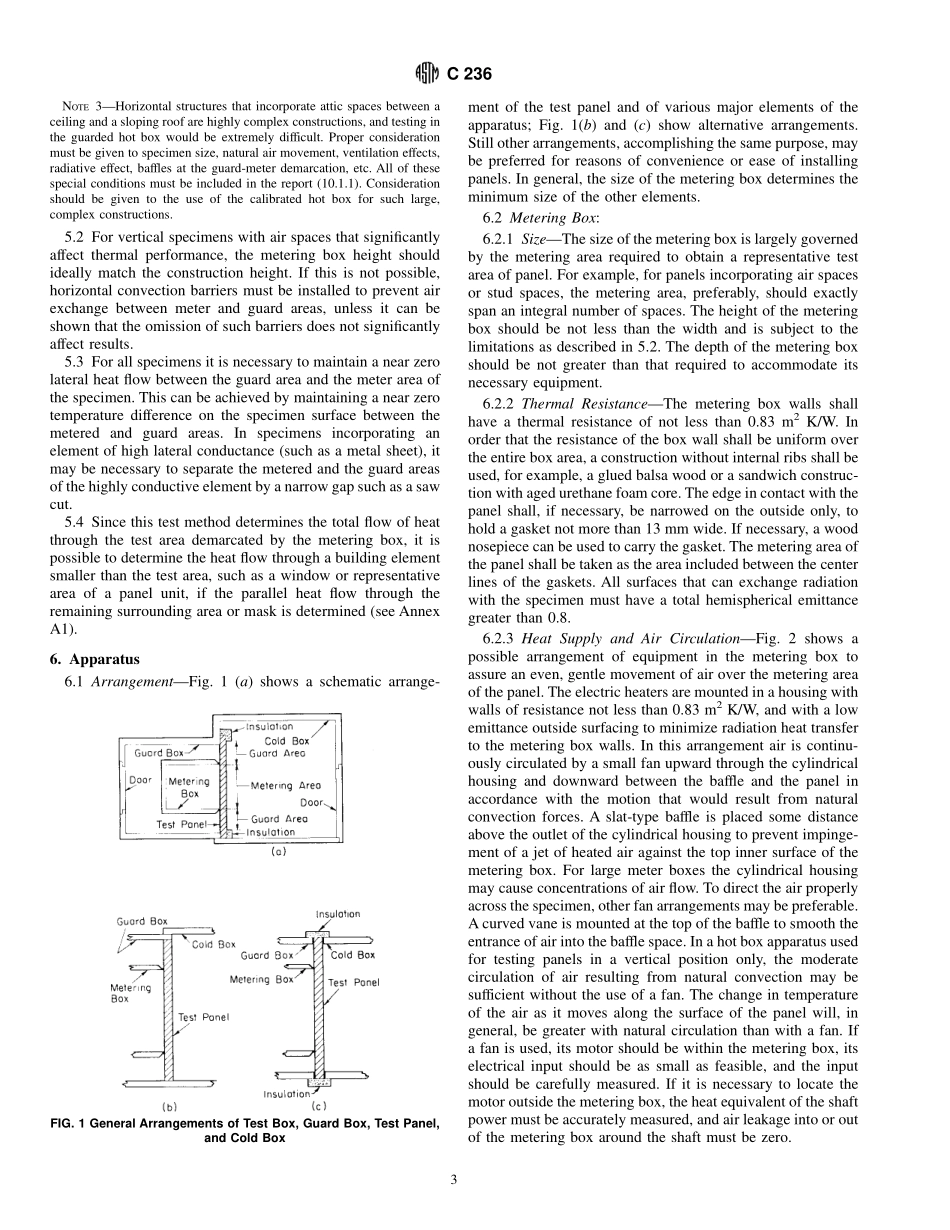
Designation:C236–89(Reapproved1993)e1StandardTestMethodforSteady-StateThermalPerformanceofBuildingAssembliesbyMeansofaGuardedHotBox1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationC236;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.ThisstandardhasbeenapprovedforusebyagenciesoftheDepartmentofDefense.e1NOTE—Section12wasaddededitoriallyinSeptember1993.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethod,knownastheguardedhotboxmethod,coversthemeasurementofthesteady-statethermaltransferpropertiesofpanels.IndistinctiontoTestMethodC177,whichisprimarilyapplicabletohomogeneoussamples,theguardedhotboxmethodprovidesfortheevaluationofthermalperformanceofbuildingassemblies.Thistestmethodissuitableforbuildingconstructionassemblies,buildingpanels,andotherapplicationsofnonohomogeneousspecimensatsimilartemperatureranges.Itmayalsobeusedforhomoge-neousspecimens.1.2Thistestmethodmaybeappliedtoanybuildingconstructionforwhichitispossibletobuildareasonablyrepresentativespecimenofsizeappropriatefortheapparatus.NOTE1—Acalibratedhotbox,TestMethodC976,mayalsobeusedforthedescribedmeasurementsandmayprovemoresatisfactoryfortestingassembliesunderdynamicconditions(nonsteady-state)andtoevaluatetheeffectsofwatermigrationandairinfiltration.Thechoicebetweenthecalibratedortheguardedhotboxshouldbemadeonlyaftercarefulconsiderationofthecontemplateduse.1.3Inapplyingthistestmethod,thegeneralprinciplesoutlinedmustbefollowed;however,thedetailsoftheappara-tusandproceduresmaybevariedasneeded.1.3.1Theintentofthistestmethodistogivetheessentialprinciplesandthegeneralarrangementoftheapparatus.Anytestusingthisapparatusmustfollowthoseprinciples.Thedetailsoftheapparatusandthesuggestedproceduresthatfollowaregivennotasmandatoryrequirementsbutasex-amplesofthistestmethodandprecautionsthathavebeenfoundusefultosatisfytheessentialprinciples.1.3....