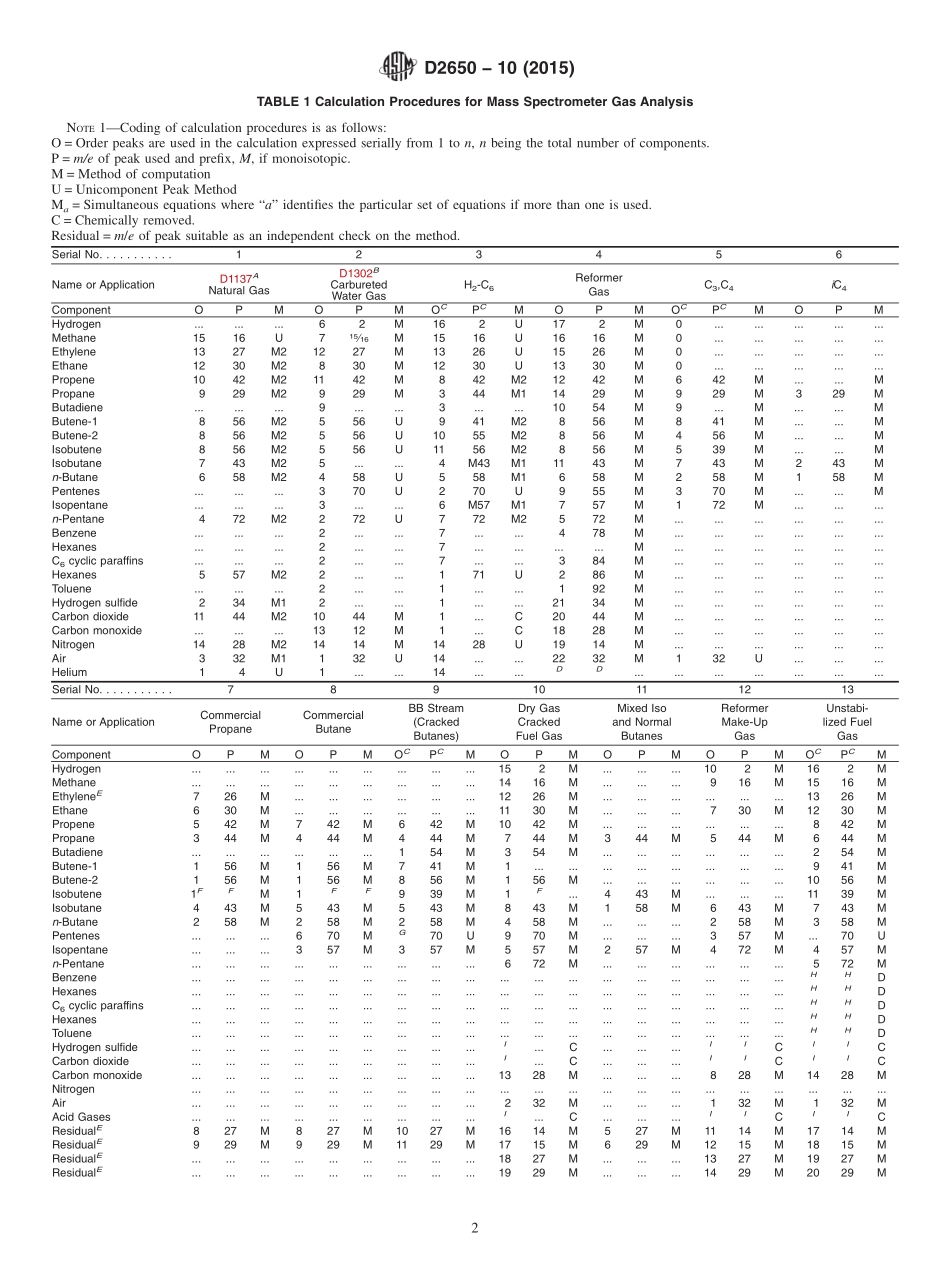
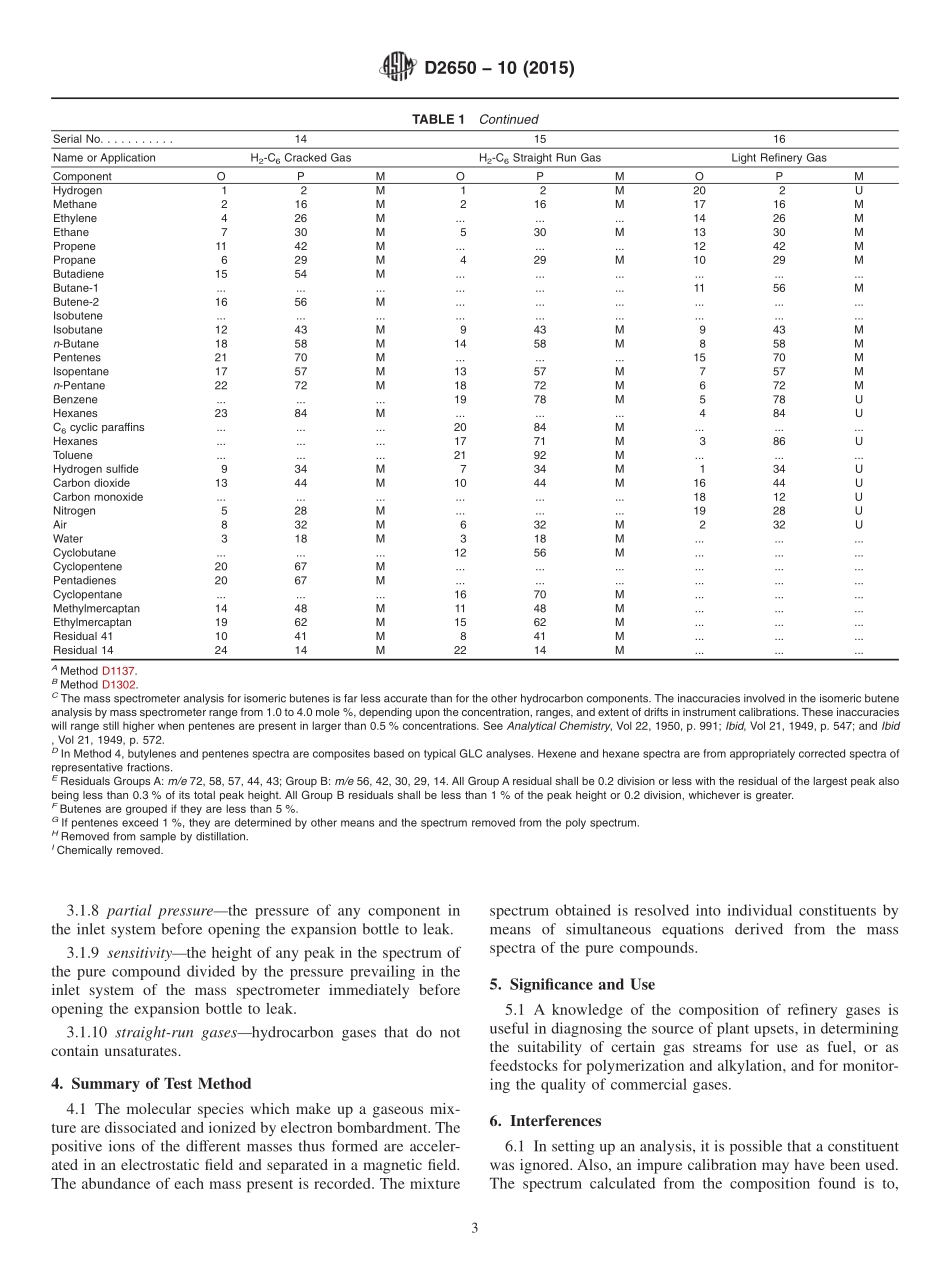
Designation:D2650−10(Reapproved2015)StandardTestMethodforChemicalCompositionofGasesbyMassSpectrometry1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD2650;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthequantitativeanalysisofgasescontainingspecificcombinationsofthefollowingcom-ponents:hydrogen;hydrocarbonswithuptosixcarbonatomspermolecule;carbonmonoxide;carbondioxide;mercaptanswithoneortwocarbonatomspermolecule;hydrogensulfide;andair(nitrogen,oxygen,andargon).Thistestmethodcannotbeusedforthedeterminationofconstituentspresentinamountslessthan0.1mole%.Dimethylbutanesareassumedabsentunlessspecificallysought.NOTE1—Althoughexperimentalproceduresdescribedhereinareuniform,calculationproceduresvarywithapplication.Thefollowinginfluencesguidetheselectionofaparticularcalculation:qualitativemixturecomposition;minimumerrorduetocomponentspresumedabsent;minimumcrossinterferencebetweenknowncomponents;maxi-mumsensitivitytoknowncomponents;lowfrequencyandcomplexityofcalibration;andtypeofcomputingmachinery.Becauseoftheseinfluences,atabulationofcalculationproceduresrecommendedforstatedapplicationsispresentedinSection12(Table1).NOTE2—ThistestmethodwasdevelopedonConsolidatedElectrody-namicsCorporationType103MassSpectrometers.Usersofotherinstrumentsmayhavetomodifyoperatingparametersandthecalibrationprocedure.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1137MethodforAnalysisofNaturalGasesandRelatedTypesofGaseousMixt...