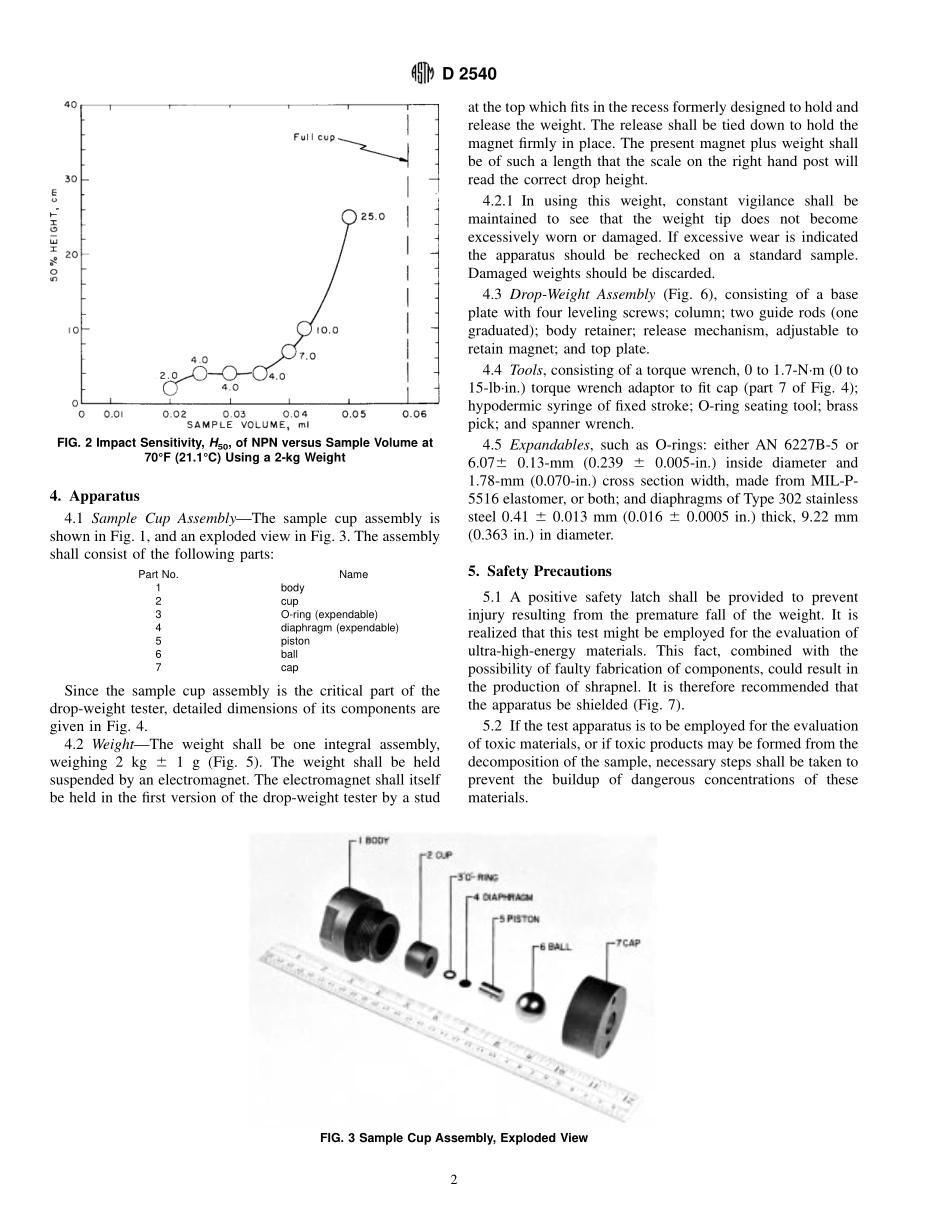
Designation:D2540–93StandardTestMethodforDrop-WeightSensitivityofLiquidMonopropellants1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD2540;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethod2coversthedeterminationofthesensitivityofliquidmonopropellantstotheimpactofadropweight.1.2Thisstandardshouldbeusedtomeasureanddescribethepropertiesofmaterials,products,orassembliesinresponsetoheatandflameundercontrolledlaboratoryconditionsandshouldnotbeusedtodescribeorappraisethefirehazardorfireriskofmaterials,products,orassembliesunderactualfireconditions.However,resultsofthistestmaybeusedaselementsofafireriskassessmentwhichtakesintoaccountallofthefactorswhicharepertinenttoanassessmentofthefirehazardofaparticularenduse.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyproblems,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.4ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.2.SummaryofTestMethod2.1Asmallsampleoftheliquid(0.03mL)tobetestedisenclosedinacavity(0.06mL)formedbyasteelcup,anelasticring,andasteeldiaphragm(seeFig.1).Apistonrestsonthediaphragmandcarriesaventholewhichisblockedbythesteeldiaphragm.Aweightisdroppedontothepiston.Apositiveresultisindicatedbypunctureofthesteeldiaphragmaccom-paniedbyaloudnoiseorseveredeformationofthediaphragmandevidencethatthesamplewascompletelyconsumed.Thesensitivityvalueforagivensampleshallbeexpressedastheheightfromwhichthespecifiedweightisdroppedfortheprobabilityofexplosiontobe50%.3.SignificanceandUse3.1Indrop-weighttestingofliquids,explosionsareiniti-atedinacomplexcompressionprocessinvolvingthedegreeandrateofpressurization,thether...