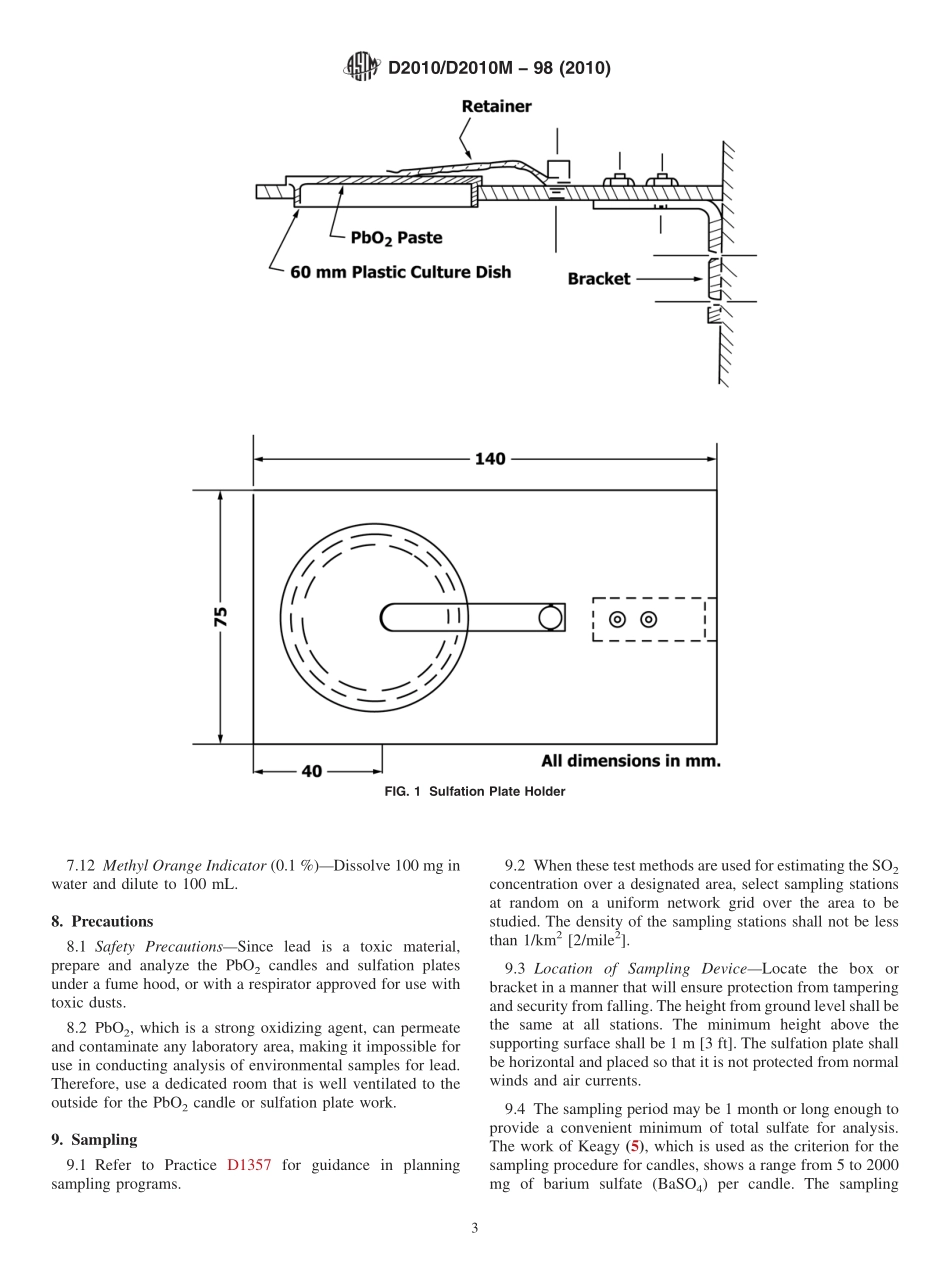
Designation:D2010/D2010M−98(Reapproved2010)StandardTestMethodsforEvaluationofTotalSulfationActivityintheAtmospherebytheLeadDioxideTechnique1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD2010/D2010M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.ThisstandardhasbeenapprovedforusebyagenciesoftheU.S.DepartmentofDefense.1.Scope1.1Thesetestmethodsdescribetheevaluationofthetotalsulfationactivityintheatmosphere.Becauseofitsoxidizingpower,leaddioxide(PbO2)convertsnotonlysulfurdioxide(SO2),butothercompounds,suchasmercaptansandhydrogensulfide,intosulfate.Itfixessulfurtrioxideandsulfuricacidmistpresentintheatmosphere(seeNote1).1.2TestMethodAdescribestheuseofaPbO2candle,andTestMethodBdescribesthatofaPbO2sulfationplate.21.3ThesetestmethodsprovideaweightedaverageeffectiveSO2levelfora30-dayinterval.1.4Theresultsofthesetestmethodscorrelateapproxi-matelywithvolumetricSO2concentrations,althoughthepresenceofdeworcondensedmoisturetendstoenhancethecaptureofSO2ontothecandleorplate.1.5ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsshallberegardedasthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninbracketsareforinformationonlyandmaybeapproximate.NOTE1—IthasbeenshownthattherateconstantofthechemicalreactionbetweenSO2andPbO2isindependentoftheconcentrationofSO2uptolevelsof1000ppm(v),if15%orlessofthePbO2hasbeenreduced(1).315%ofthePbO2isequivalentto11to12mgofSO2/cm2perday.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.Forspecificprecautionarystatements,seeSection8.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:4D516TestMethodforSulfateIoninWaterD1193SpecificationforReagentWaterD1356TerminologyRelatingtoSamplingandAnalysisofAtmospheresD1357Practicef...