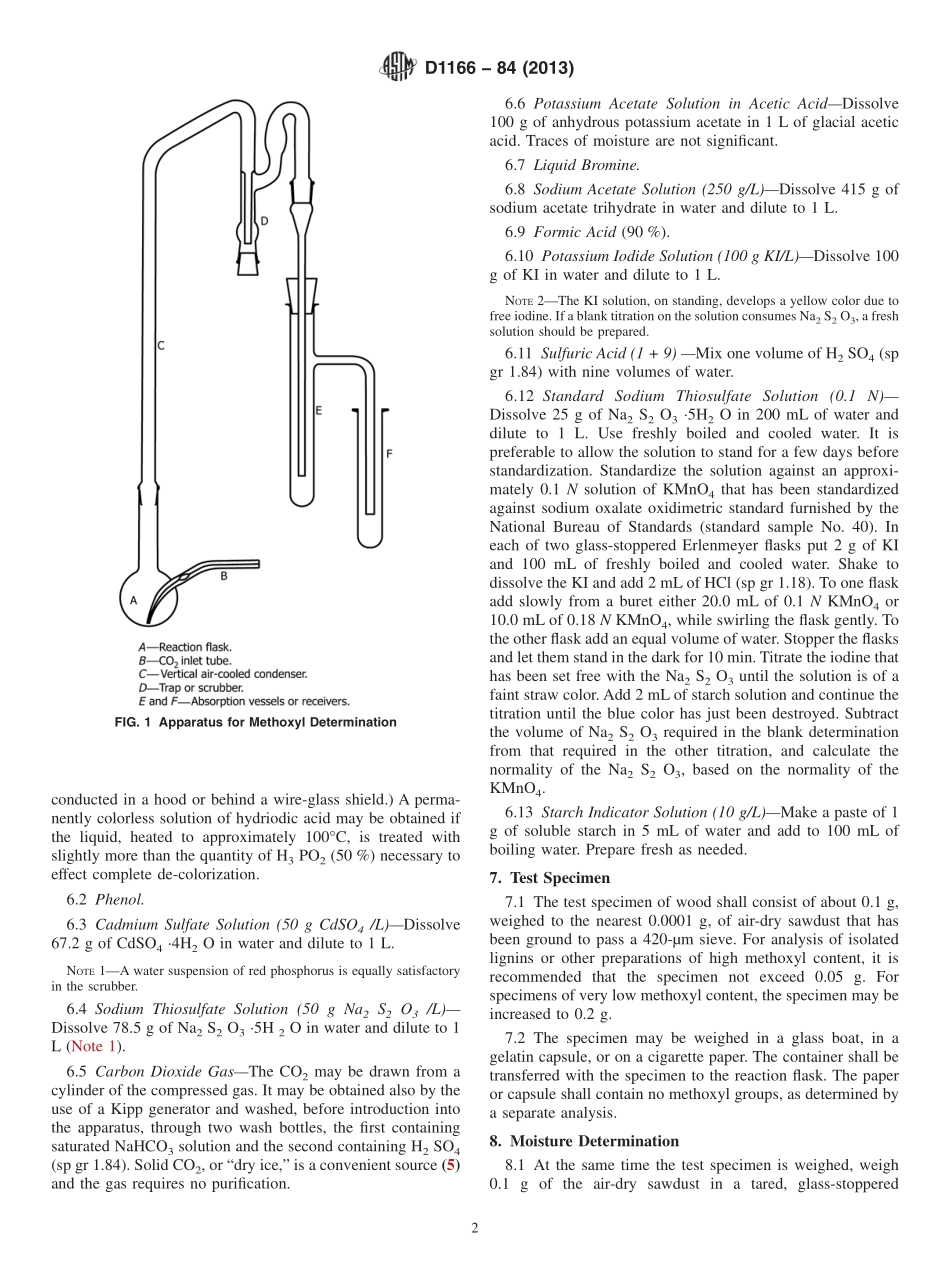
Designation:D1166−84(Reapproved2013)StandardTestMethodforMethoxylGroupsinWoodandRelatedMaterials1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD1166;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofmethoxylgroupsinwoodandrelatedmaterials(1-7).2Thetestmethodisapplicabletowoodsawdustand,bysuitableadjustmentinsizeofthetestspecimen,tofractionsisolatedfromwoodandlignin.1.2Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.Specificprecau-tionarystatementsaregiveninSection6.2.PrincipleofMethod2.1TheprincipleofthetestmethodisthesameasthatintheoriginalmethodofZeisel(1),exceptthatthemethyliodideiscollectedinanaceticacidsolutionofpotassiumacetatecontainingbromine.Thefollowingreactionsthenoccur:CH3I1Br2→CH3Br1IBr(1)IBr12Br213H2O→HIO315HBrTheiodicacidisdeterminedbytitrationofiodineliberatedbythereaction:HIO315HI→3I213H2O(2)Fromtheaboveequations,itfollowsthatonemethoxylgroup(CH3O)liberatessixatomsofiodine.3.SignificanceandUse3.1Mostofthemethoxylinwoodisattributabletothelignin.Thistestmethodisusedextensivelyinthestudyoflignin.4.Apparatus4.1TheapparatusshallbesimilartothatillustratedinFig.1andshallconsistofthefollowing:4.1.1ReactionFlask,4.1.2HeatSource—Amicroburner,providedwithacylin-dricalshieldtoeliminatetheeffectofairdrafts,4.1.3VerticalAir-CooledCondenser,4.1.4Scrubber,and4.1.5TwoAbsorptionVessels.5.PurityofReagentsandWater5.1PurityofReagents—Reagentgradechemicalsshallbeusedinalltests.Unlessotherwiseindicated,itisintendedthatallreagentsshallconformtothespecificationsoftheCommit-teeonAnalyticalReagentsoftheAmericanChemicalSociety,where...