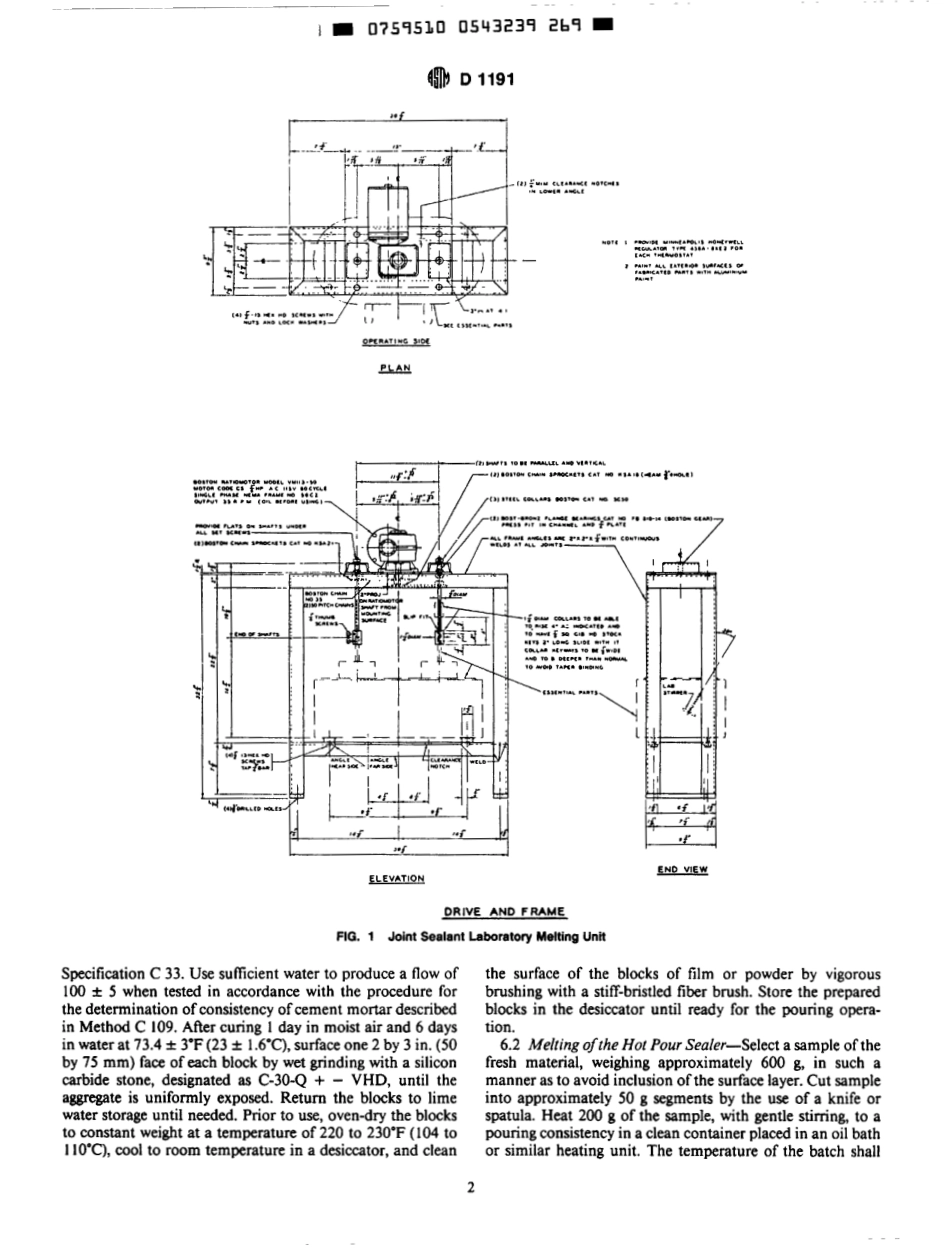
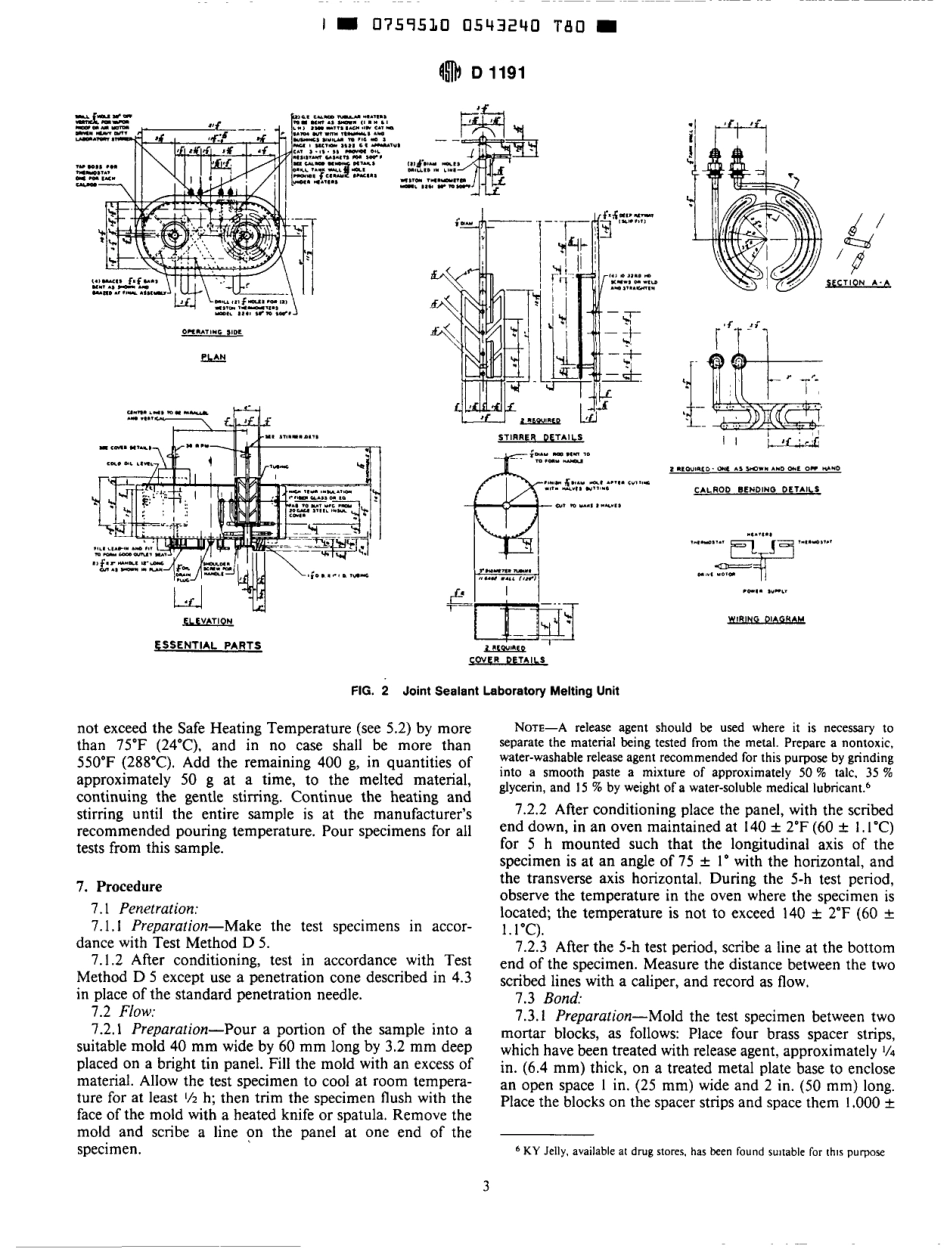
AMERICANSOCIETYFORTESTINGANDMATERIALS1916RaceStPhiladelphia,Pa19103ReprintedfromtheAnnualBookoiASTMStandards.CoDvriahtASTM[[TbDesignation:D1191-84(Reapproved1994)''If&tlistedinthecurrentcombinedrndeqwillappearinthénkedltionStandardTestMethodsforConcreteJointSealers'ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationDI191;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearofonginaladoptionor,inthecase.ofrevision.theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(6)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.fiNOTE-KevwordswereaddededitonallvinJune1994.1.Scopejointsealersofthehotpouredelastictype.1.1Thesetestmethodscovertestsforevaluatingconcrete1.2Testprocedurescanbethefollowing:TestParagraphBondFlowPenetration7.I1.27.31.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:C33SpecificationforConcreteAggregates'C109TestMethodforCompressiveStrengthofHydraulicCementMortars(Using2-in.or50-mmCubeSpeci-men~)~SpecimensintheLaboratory'Grease5C150SpecificationforPortlandCement3C192PracticeforMakingandCuringConcreteTestD5TestMethodforPenetrationofBituminousMaterials4D217TestMethodforConePenetrationofLubricating3.SignificanceandUse3.1Thesetestmethodsestablishtestproceduresforlabo-ratoryevaluationofmaterialsthatwillformaresilientandadhesivecompoundcapableofeffectivelysealingjointsagainsttheinfiltrationofmoistureandforeignmaterialthroughoutrepeatedcyclesofexpansionandcontractionwithtemperaturechanges.theoilbathandmaterialinthemeltingvat.Theheatsourcefortheoilbathshallbethermostaticallycontrolledandcapableofmaintainingtemperaturesupto550°F(288'C).Mechanicalagitatorspeedofapproximately30&5rpmisrecommended.SeeFig.1andFig.2fortypicallaboratorymelters.4.2Penetrometer-AsdescribedinTestMethodD5.4.3Cone...