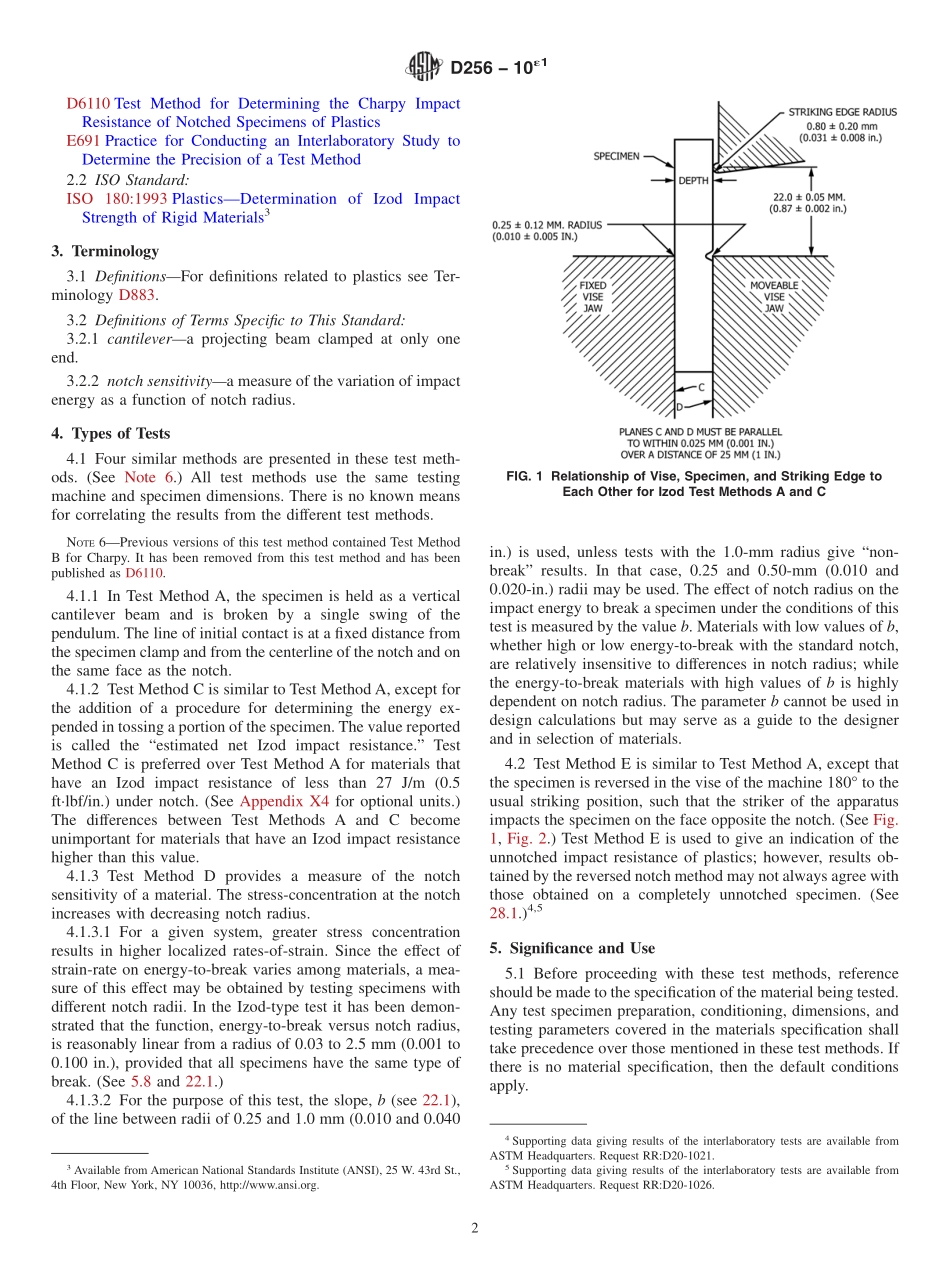
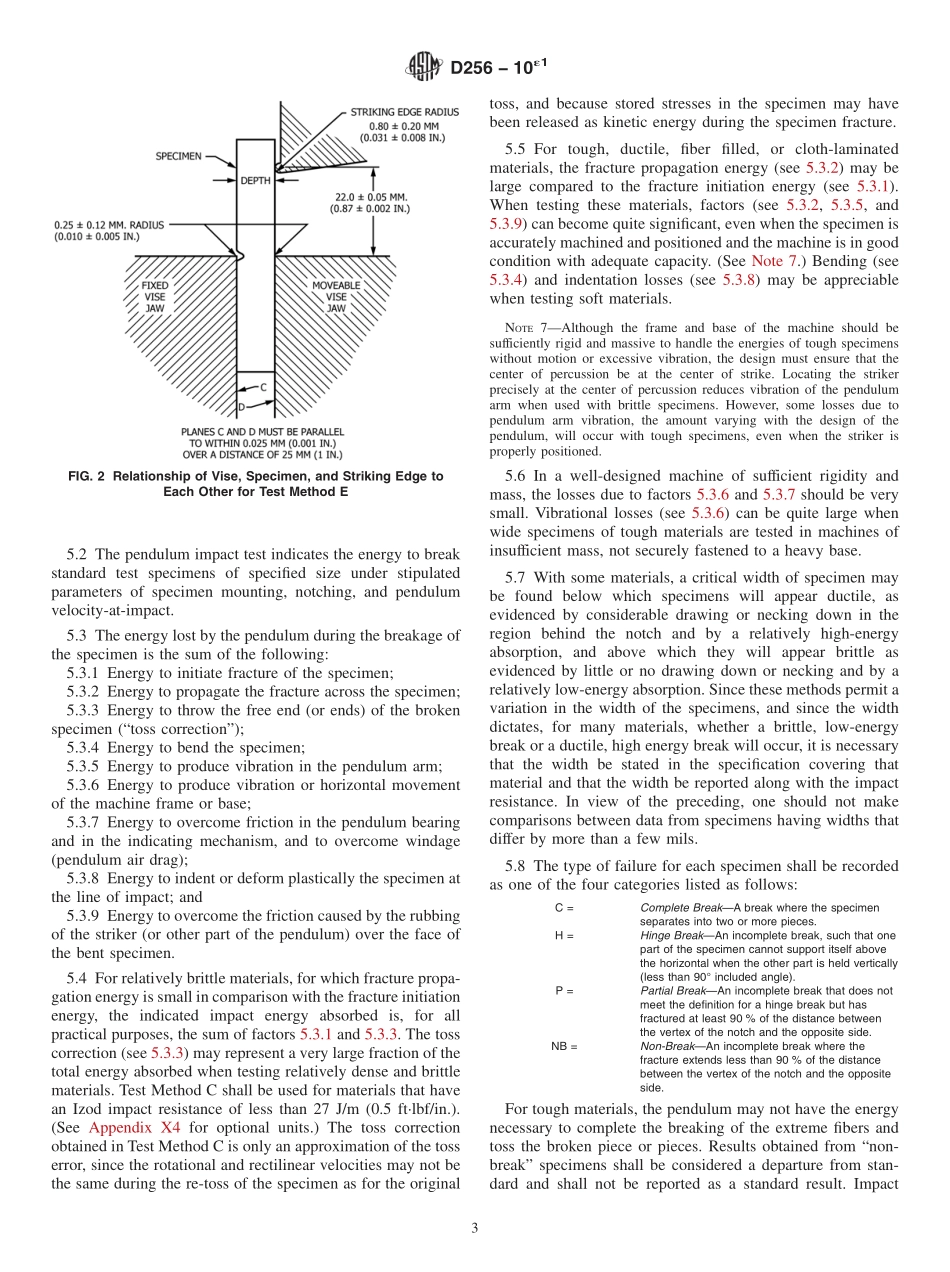
Designation:D256−10´1StandardTestMethodsforDeterminingtheIzodPendulumImpactResistanceofPlastics1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD256;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.ThisstandardhasbeenapprovedforusebyagenciesoftheU.S.DepartmentofDefense.ε1NOTE—EditoriallycorrectedFigure2inOctober2015.1.Scope*1.1Thesetestmethodscoverthedeterminationoftheresistanceofplasticsto“standardized”(seeNote1)pendulum-typehammers,mountedin“standardized”machines,inbreak-ingstandardspecimenswithonependulumswing(seeNote2).Thestandardtestsforthesetestmethodsrequirespecimensmadewithamillednotch(seeNote3).InTestMethodsA,C,andD,thenotchproducesastressconcentrationthatincreasestheprobabilityofabrittle,ratherthanaductile,fracture.InTestMethodE,theimpactresistanceisobtainedbyreversingthenotchedspecimen180°intheclampingvise.Theresultsofalltestmethodsarereportedintermsofenergyabsorbedperunitofspecimenwidthorperunitofcross-sectionalareaunderthenotch.(SeeNote4.)NOTE1—Themachineswiththeirpendulum-typehammershavebeen“standardized”inthattheymustcomplywithcertainrequirements,includingafixedheightofhammerfallthatresultsinasubstantiallyfixedvelocityofthehammeratthemomentofimpact.However,hammersofdifferentinitialenergies(producedbyvaryingtheireffectiveweights)arerecommendedforusewithspecimensofdifferentimpactresistance.Moreover,manufacturersoftheequipmentarepermittedtousedifferentlengthsandconstructionsofpendulumswithpossibledifferencesinpendulumrigiditiesresulting.(SeeSection5.)Beawarethatotherdifferencesinmachinedesignmayexist.Thespecimensare“standard-ized”inthattheyarerequiredtohaveonefixedlength,onefixeddepth,andoneparticulardesignofmillednotch.Thewidthofthespecimensispermittedtovarybetweenlimits.NOTE2—Resultsgeneratedusingpendulumsthatutilizealoadcelltorecordt...