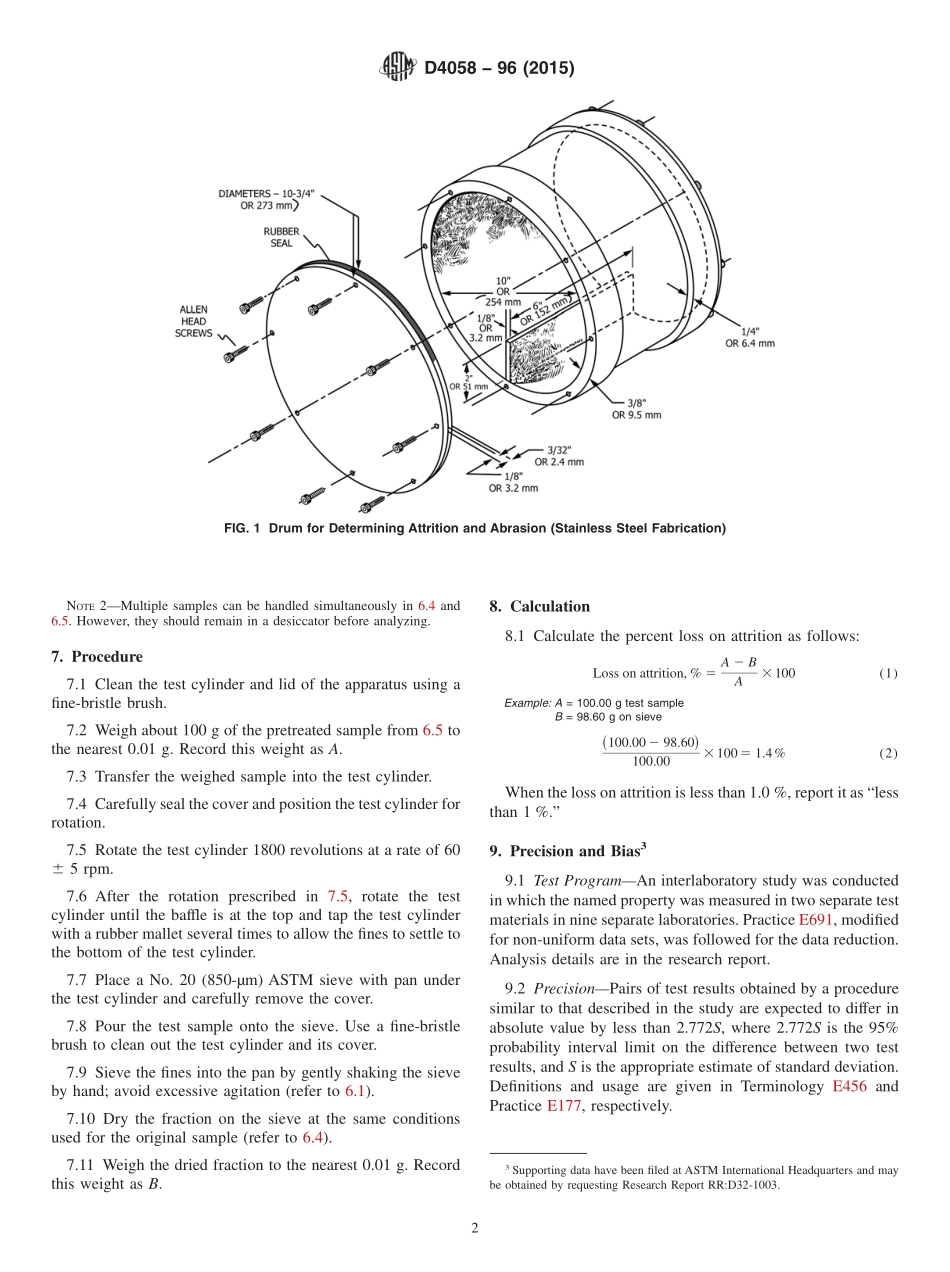
Designation:D4058−96(Reapproved2015)StandardTestMethodforAttritionandAbrasionofCatalystsandCatalystCarriers1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD4058;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationoftheattri-tionandabrasionresistanceofcatalystsandcatalystcarriers.Itisapplicabletotablets,extrudate,spheres,andirregularlyshapedparticleslargerthanabout1⁄16in.(1.6mm)andsmallerthanabout3⁄4in.(19mm).Thematerialsusedindevelopingthemethodexhibitedlossesonattritionlessthan7%;however,themethodshouldbeapplicabletomaterialsgivingmuchhigherattritions.1.2Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.ThevaluesgiveninparenthesesaremathematicalconversionstoSIunitsthatareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2E177PracticeforUseoftheTermsPrecisionandBiasinASTMTestMethodsE456TerminologyRelatingtoQualityandStatisticsE691PracticeforConductinganInterlaboratoryStudytoDeterminethePrecisionofaTestMethod3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1Asampleofcatalystorcatalystcarrierisrotatedforafixednumberofrevolutionsinacylindricaldrumhavingasinglebaffle.Finesproducedbyattritionandabrasioninthetestaredeterminedbysievingthroughastandardsieve.4.SignificanceandUse4.1Thistestmethodisconsideredtobeameasureofthepropensityofacatalysttoproducefinesinthecourseoftransportation,handling,anduse.However,thereisnoabso-lutelevelofacceptability.Thevaluesobtainedaresignificantprincipallyinrelationtovaluesforothermaterials(orothersamplesofthesamematerial)ofcomparab...