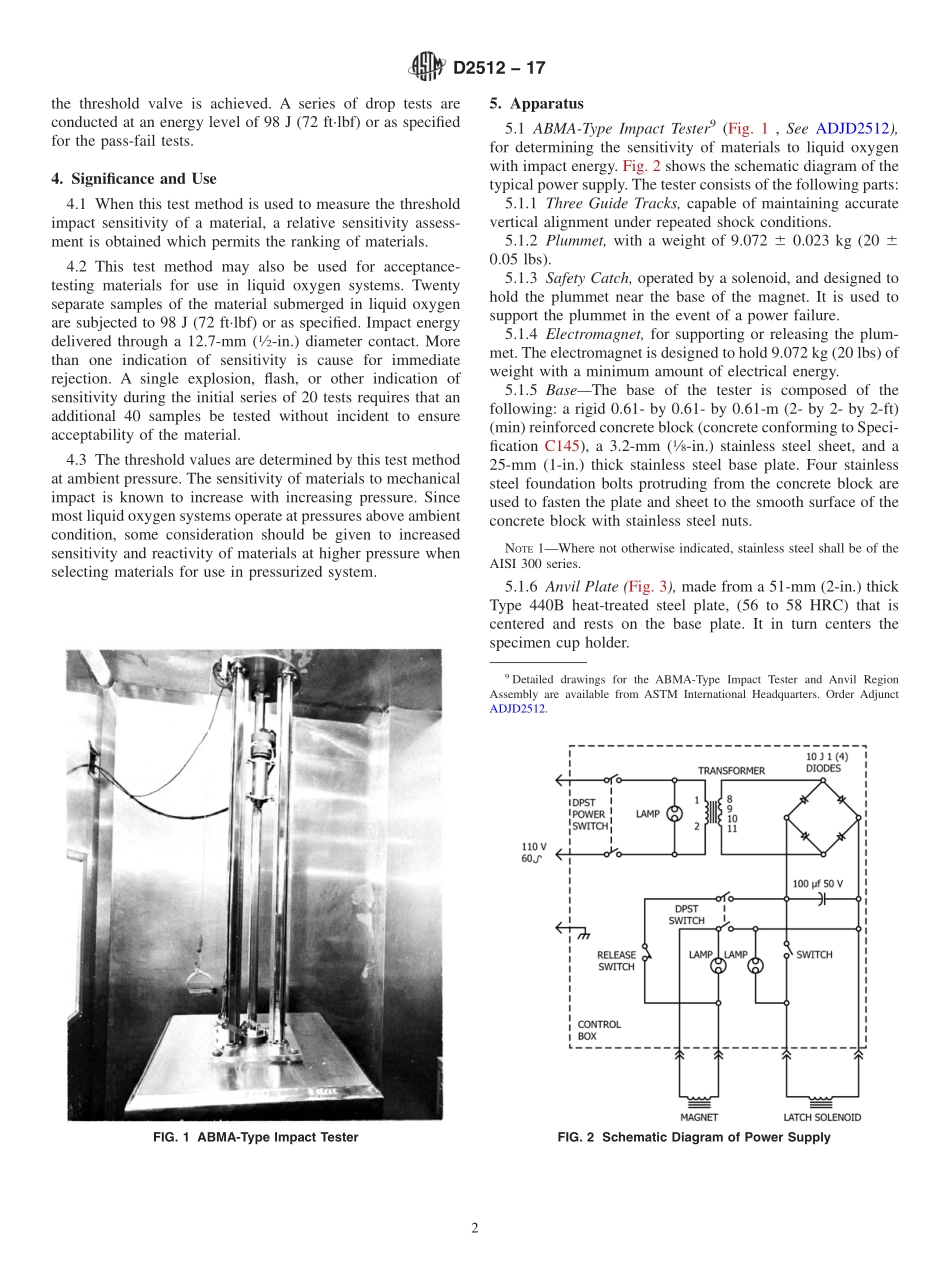
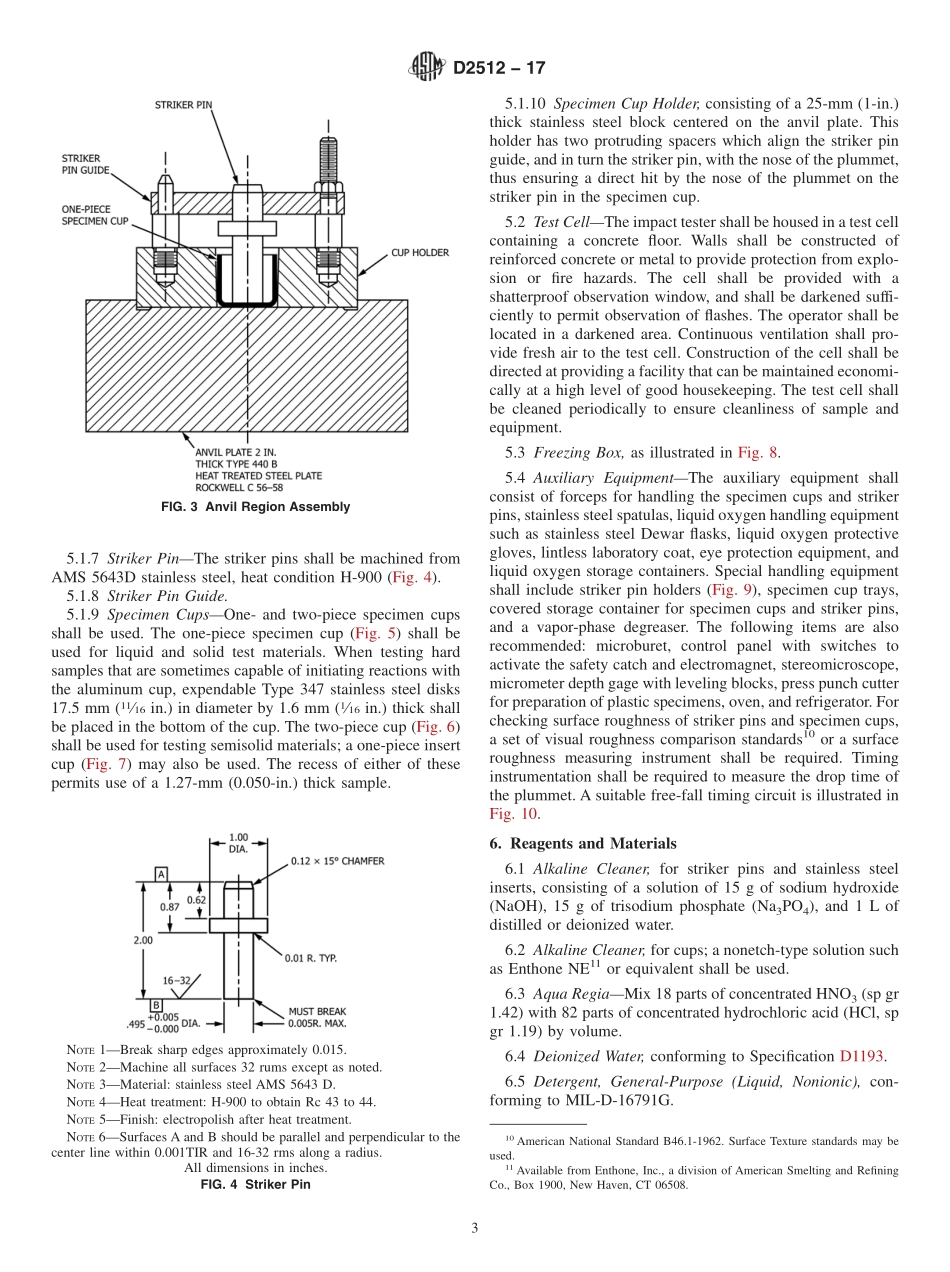
Designation:D2512−17StandardTestMethodforCompatibilityofMaterialswithLiquidOxygen(ImpactSensitivityThresholdandPass-FailTechniques)1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD2512;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.ThisstandardhasbeenapprovedforusebyagenciesoftheU.S.DepartmentofDefense.1.Scope1.1Thismethod2,3,4coversthedeterminationofcompatibil-ityandrelativesensitivityofmaterialswithliquidoxygenunderimpactenergyusingtheArmyBallisticMissileAgency(ABMA)-typeimpacttester.Materialsthatareimpact-sensitivewithliquidoxygenaregenerallyalsosensitivetoreactionbyotherformsofenergyinthepresenceofoxygen.1.2Thisstandardshouldbeusedtomeasureanddescribethepropertiesofmaterials,products,orassembliesinresponsetoheatandflameundercontrolledlaboratoryconditionsandshouldnotbeusedtodescribeorappraisethefirehazardorfireriskofmaterials,products,orassembliesunderactualfireconditions.However,resultsofthistestmaybeusedaselementsofafireriskassessmentwhichtakesintoaccountallofthefactorswhicharepertinenttoanassessmentofthefirehazardofaparticularenduse.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.4Thisinternationalstandardwasdevelopedinaccor-dancewithinternationallyrecognizedprinciplesonstandard-izationestablishedintheDecisiononPrinciplesfortheDevelopmentofInternationalStandards,GuidesandRecom-mendationsissuedbytheWorldTradeOrganizationTechnicalBarrierstoTrade(TBT)Committee.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:5C145SpecificationforSolidLoad-BearingConcreteMa-sonryUnits(Withdrawn1992)6D1193SpecificationforReagentWater2.2MilitaryStandards:MIL-D-16791GDetergent,GeneralPurpose(Liq...