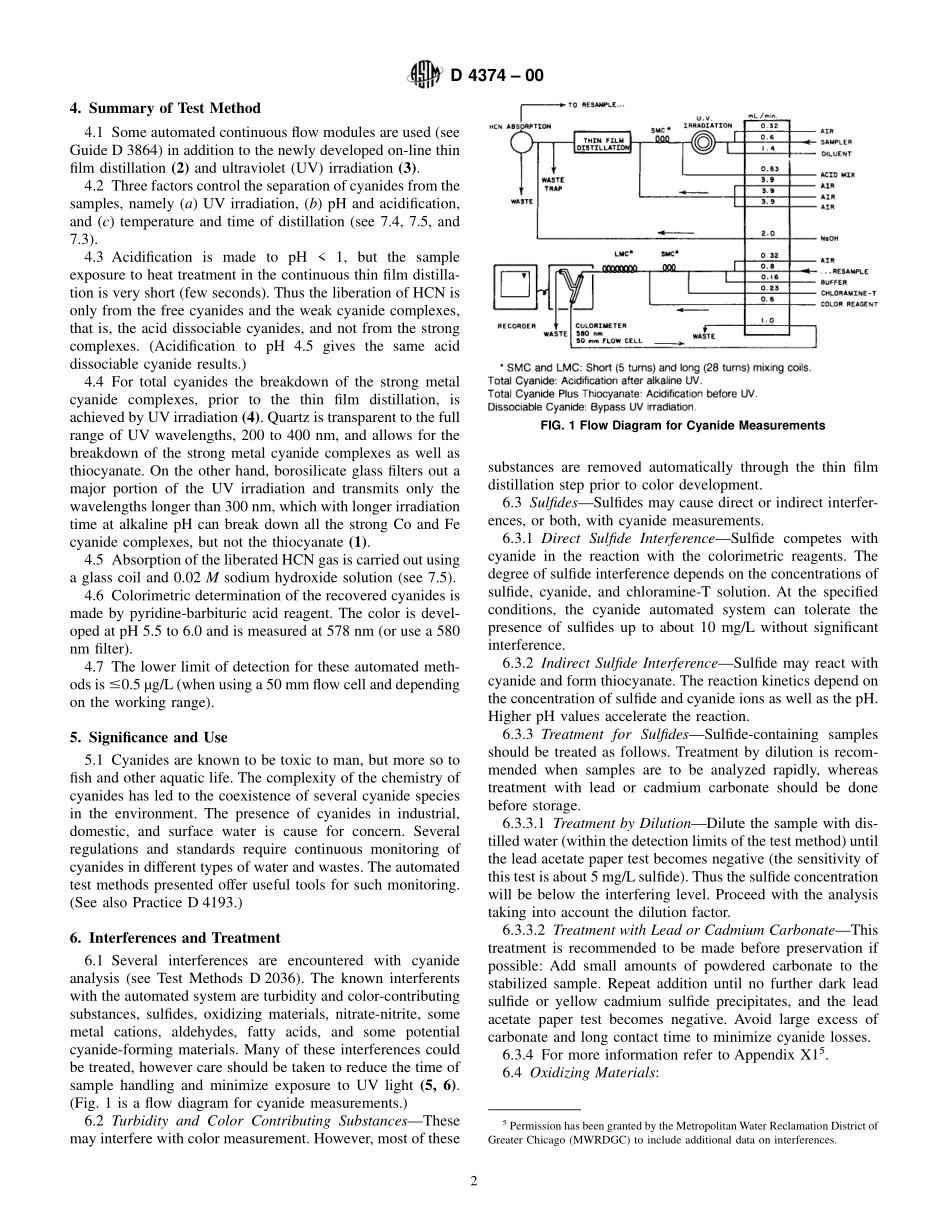
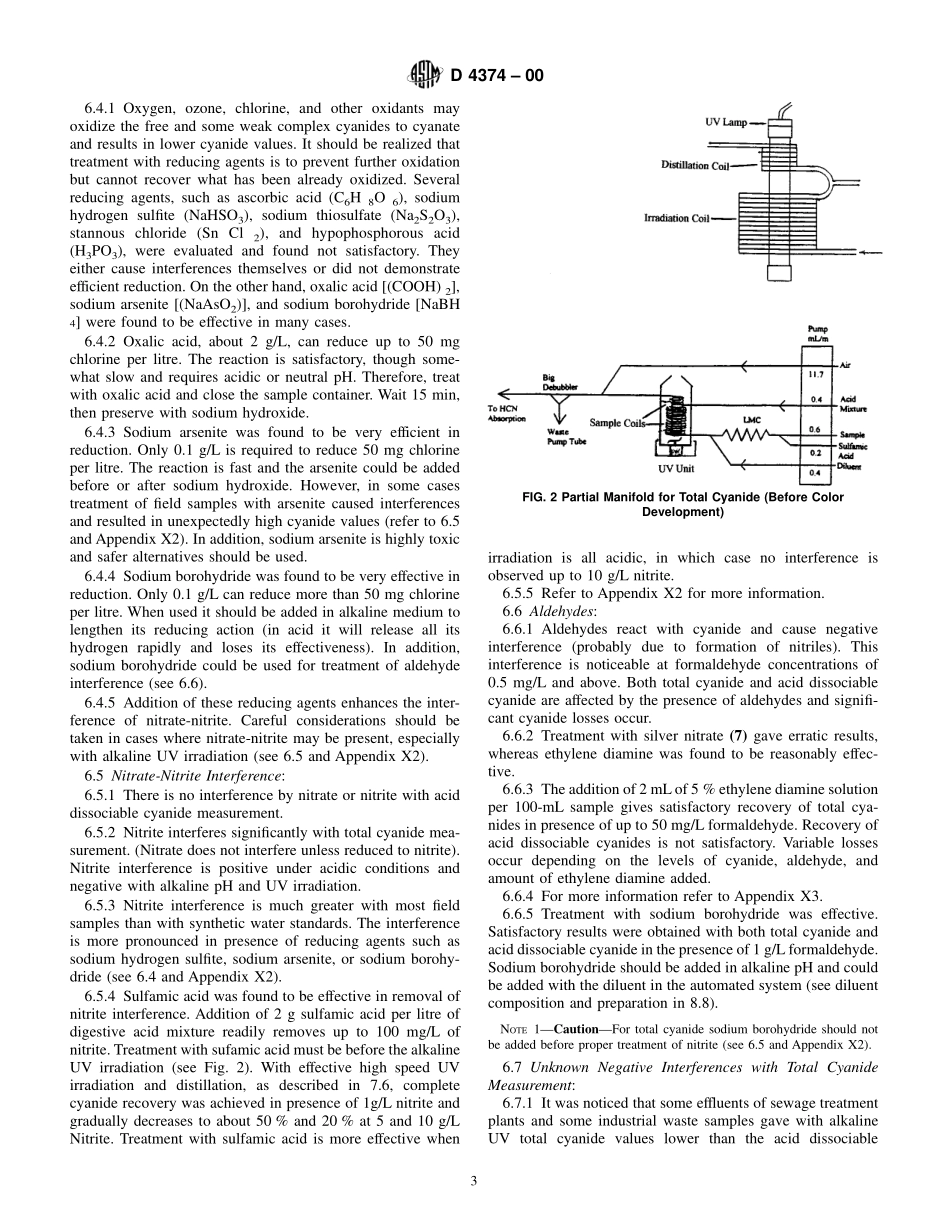
Designation:D4374–00AnAmericanNationalStandardStandardTestMethodsforCyanidesinWater—AutomatedMethodsforTotalCyanide,AciddissociableCyanide,andThiocyanate1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD4374;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thesetestmethodscoverthedeterminationofdifferentspeciesofcyanidesandthiocyanateinwaterandwastewater,namelyaciddissociablecyanide,totalcyanide,andthiocyanate(1).21.1.1TotalCyanide—Thistestmethoddeterminesalltheaciddissociablecyanidesandthestrongmetal-cyano-complexes,suchasferrocyanide[Fe(CN)6]4−,ferricyanide[Fe(CN)6]3−,hexacyanocolbaltate[Co(CN)6]3−,andthoseofgoldandplatinum.1.1.2AcidDissociableCyanide—Thistestmethodbasicallydeterminesfreecyanides,asCN−andHCN,andweakmetal-cyano-complexessuchas[Cd(CN)4]2−and[Mn(CN)6]3−.Ironcomplexesarenotincluded.1.1.3Cyanidecomplexes,strongcomplexeslikethoseofiron,cobalt,etc.,canbedeterminedbydifference,thatis,cyanidecomplexes=totalcyanides−aciddissociablecya-nides.1.1.4Thiocyanate—Thistestmethoddeterminesthethio-cyanateasthedifferencebetweenanothermeasurementthatincludestotalcyanideplusthiocyanateandthevalueoftotalcyanide,thatis,thiocyanate=totalcyanideplusthiocyanate−totalcyanide.1.2Cyanatesandcyanogenhalidesarenotdetected.Cyano-genchloridehydrolyzestocyanateatthepHofsamplepreservation($12).1.3Mostoftheorgano-cyano-complexesarenotmeasured,withtheexceptionoftheweakcyanohydrins.1.4Thesetestmethodsapplytodifferenttypesofwater,wastewater(rawsewage,sludge,andeffluent),sludge,someindustrialwaste,andsediments.Samplematrixesshouldbeevaluatedbytheuser.Thereportedprecisionandbias(seeSection16)maynotapplytoallsamples.1.5ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itisthe...