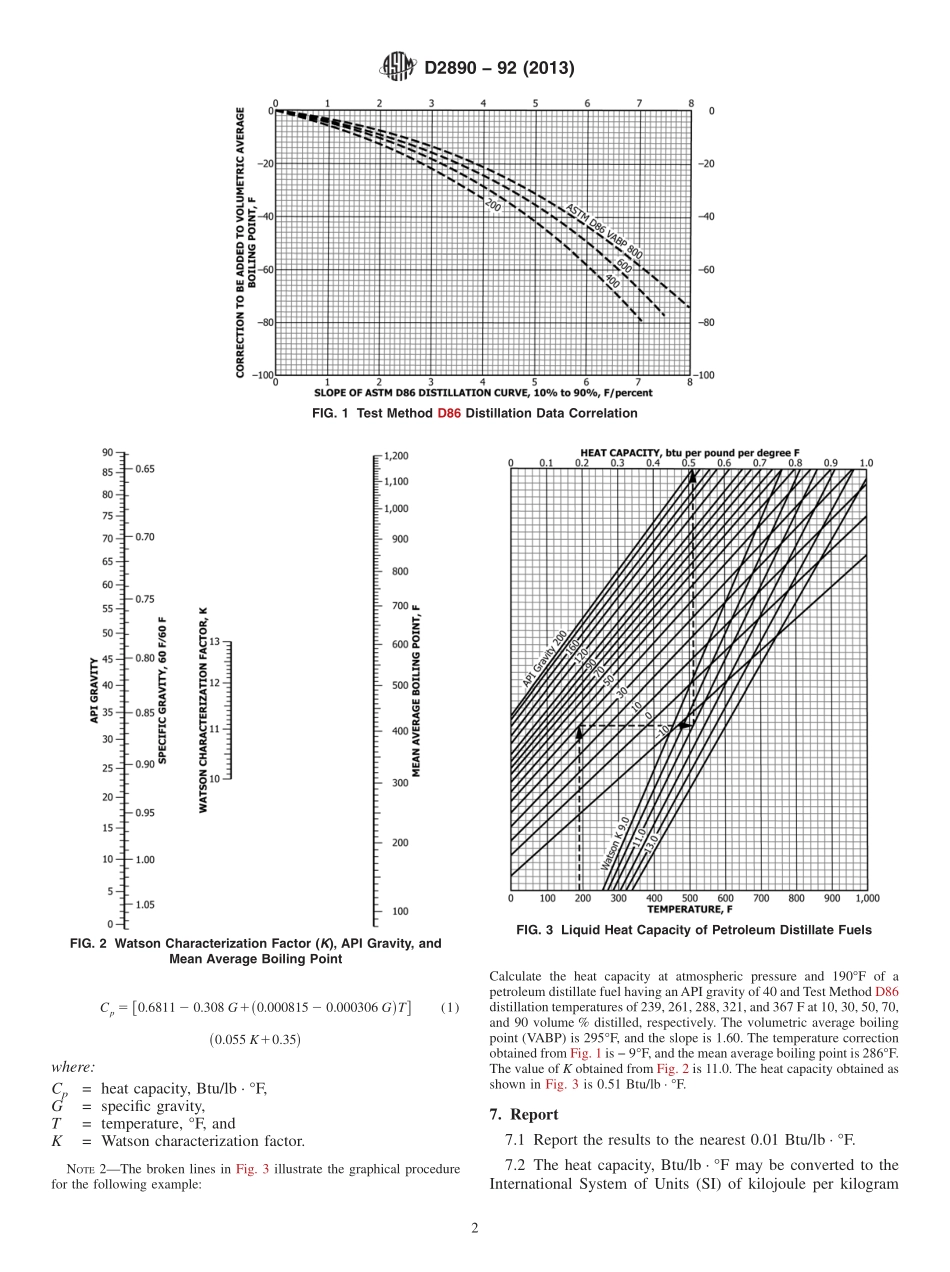
Designation:D2890−92(Reapproved2013)StandardTestMethodforCalculationofLiquidHeatCapacityofPetroleumDistillateFuels1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD2890;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthecalculationofliquidheatcapacity,Btu/lb·°F(kJ/kg·K),atatmosphericpressure,ofpetroleumfuelsforwhichdistillationdatamaybeobtainedinaccordancewithTestMethodD86withoutreachingadecom-positionpointpriortoobtaining90volume%distilled.1.2Thistestmethodisnotapplicableattemperatureslessthan0°F(−18°C)andgreaterthan60°F(16°C)abovethevolumetricaverageboilingpointofthefuel.1.3Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.ThevaluesgiveninparenthesesaremathematicalconversionstoSIunitsthatareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.1.4Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D86TestMethodforDistillationofPetroleumProductsatAtmosphericPressureD287TestMethodforAPIGravityofCrudePetroleumandPetroleumProducts(HydrometerMethod)3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1TheWatsoncharacterizationfactor,K,isobtainedfromagraphicalcorrelationrelatingdeterminedTestMethodD86distillationdataandK.Theliquidheatcapacityisobtained,eithergraphicallyormathematically,fromcorrelationsrelatingcalculatedheatcapacity,temperatureatwhichheatcapacityisbeingcalculated,determinedAPIgravity,andK.NOTE1—Detailsofthemethodhavebeenpublished.34.SignificanceandUse4.1Heatcapacitiesobtainedbythismethodarethoseatatmosphericpressure.However,becausethetemperaturerangeislow,thecalculatedvaluesaresimilartosaturatedliquidheatcapaci...