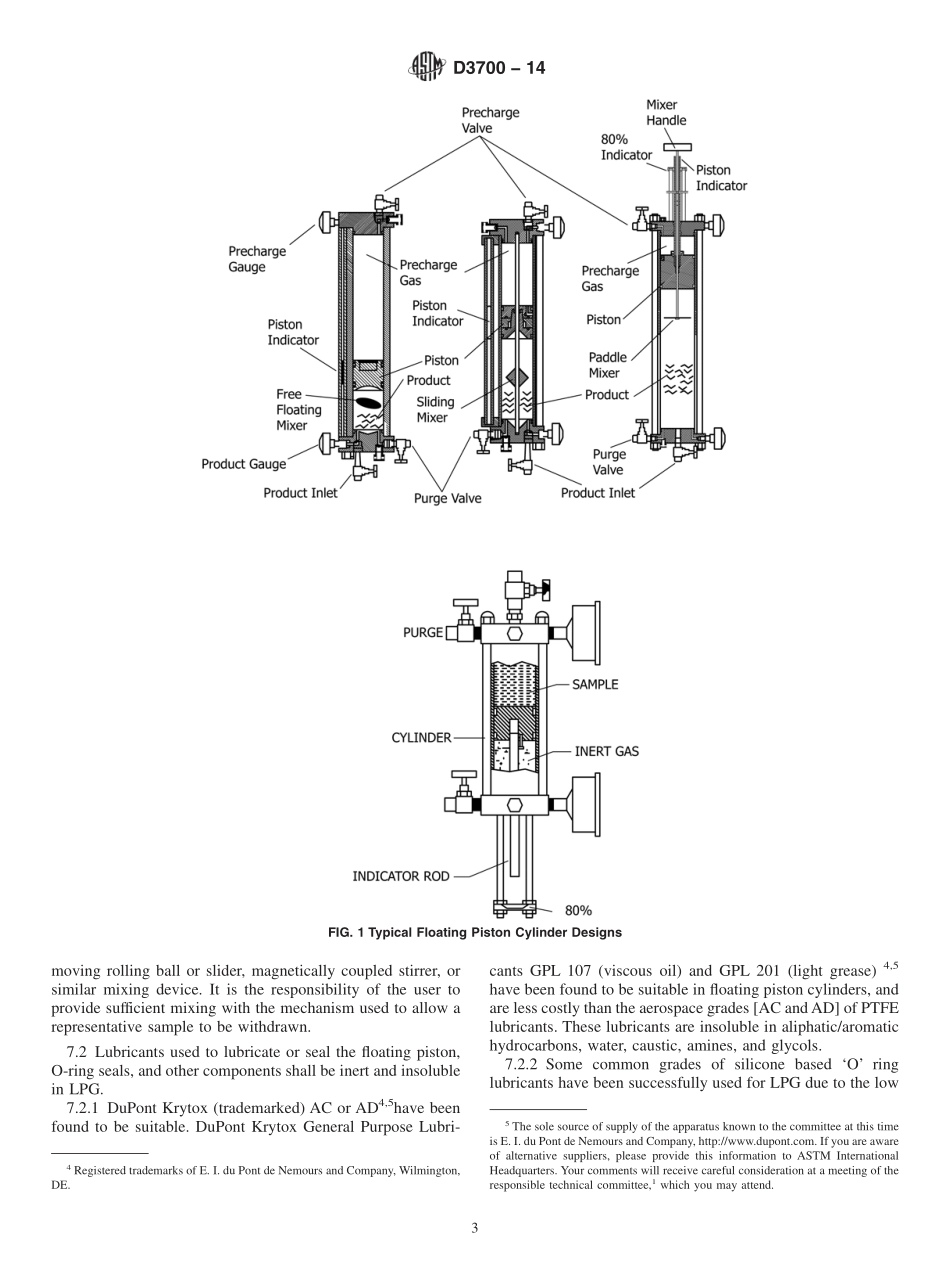
Designation:D3700−14StandardPracticeforObtainingLPGSamplesUsingaFloatingPistonCylinder1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD3700;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thispracticecoverstheequipmentandproceduresforobtainingarepresentativesampleofliquefiedpetroleumgas(LPG),suchasspecifiedinASTMSpecificationD1835,GPA2140,andcomparableinternationalstandards.Itmayalsobeusedforothernaturalgasliquid(NGL)productsthatarenormallysinglephase(forexample,NGLmix,fieldbutane,andsoforth),definedinotherindustryspecificationsorcontractualagreements,andforvolatile(highervaporpres-sure)crudeoils.1.2Thispracticeisnotintendedfornon-specificationprod-uctsthatcontainsignificantquantitiesofundissolvedgases(N2,CO2),freewaterorotherseparatedphases,suchasraworunprocessedgas/liquidsmixturesandrelatedmaterials.Thesameequipmentcanbeusedforthesepurposes,butadditionalprecautionsaregenerallyneededtoobtainrepresentativesamplesofmulti-phaseproducts(seeAppendixX1).1.3Thispracticeincludesrecommendationsforthelocationofasamplepointinalineorvessel.Itistheresponsibilityoftheusertoensurethatthesamplingpointislocatedsoastoobtainarepresentativesample.1.4ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.5Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpractices,anddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1265PracticeforSamplingLiquefiedPetroleum(LP)Gases,ManualMethodD1835SpecificationforLiquefiedPetroleum(LP)Gases2.2GPAStandards:3GPA2174ObtainingLiquidHydrocarbonSamplesforAnalysisbyGasChromatographyGPA2140LiquefiedPetroleumGasSpecificationsandTestM...