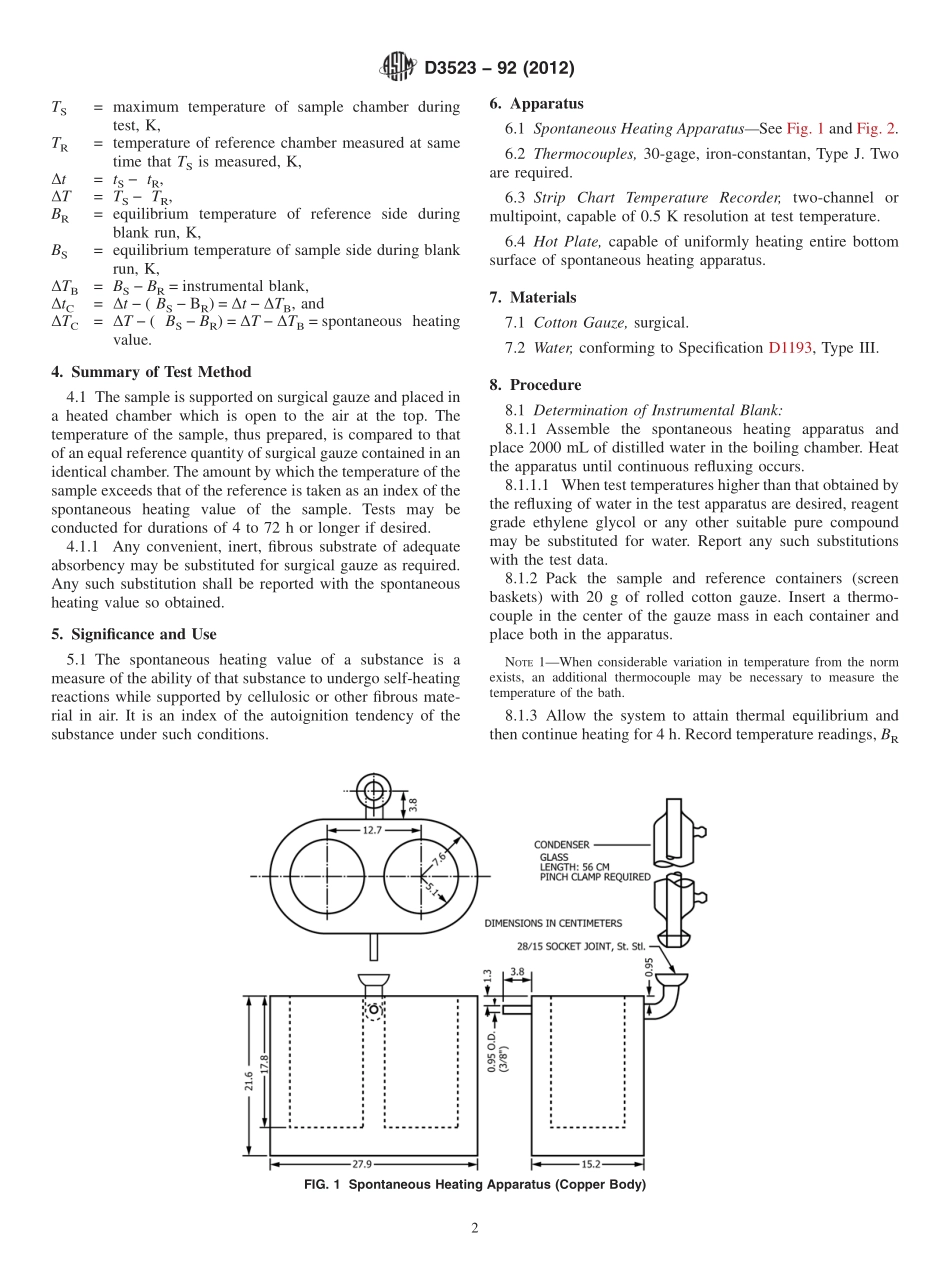
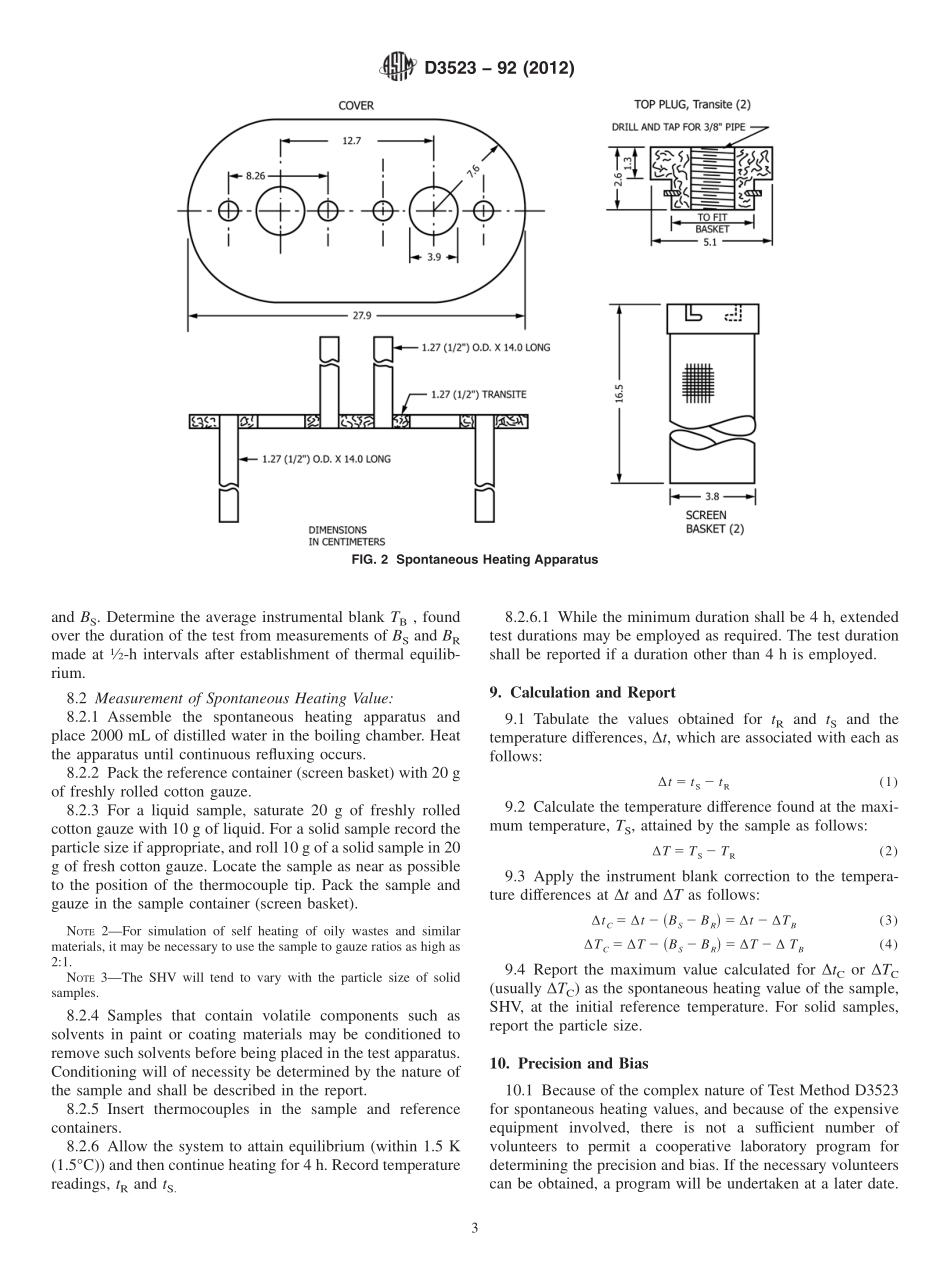
Designation:D3523−92(Reapproved2012)StandardTestMethodforSpontaneousHeatingValuesofLiquidsandSolids(DifferentialMackeyTest)1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD3523;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthenon-adiabaticdeterminationofthespontaneousheatingvalues(SHV)ofliquidsandsolids.Itisapplicabletosubstancesthatarenotcompletelyvolatileatthetesttemperature.Spontaneousheatingvaluesobtainedbythistestmethodarequalitativeindicationsofthedegreeofself-heatingthatmaybeexpectedtooccuruponexposureofthesampletoairatthetesttemperature.1.2Valuesobtainedbythismethodareapplicabletoliquidsandsolidssupportedoncellulosicsurfaces.Theyarenotapplicabletoliquidsonmetalsurfaces,oncontaminatedsurfaces,oratpressuresaboveatmospheric.1.3Spontaneousheatingvaluesdeterminedbythepresenttestmethodareregardedonlyasqualitativemeasurementsofself-heatingwhichoccursundertheconditionsofthetest.Thetestmethoddoesnotpurporttoproduceaquantitativemeasureoftheenthalpyofreactionofthesamplewithairatagiventesttemperature.Suchdatacanbeobtainedbytheuseofanadiabaticcalorimeter.Theexistence,underthetestconditions,ofapositivetemperaturedifferencebetweenthesampleandthereferenceisevidenceofathermochemicalreactioninthesample.1.4Themagnitudeofthemeasuredtemperaturedifferenceisasemiquantitativeindicationoftheenthalpyandrateofthatreaction.Sincefactorssuchasheatlossfromthesampletothebathandquenchingofthereactionduetotoorapidconsump-tionofoxygenaffecttheamountanddurationofthemeasuredheateffect,caremustbetakennottoattributetoomuchquantitativesignificancetothetestresults.Itissufficient,forthepurposeofthistest,todeterminewhetherornotthesampleiscapableofundergoingaself-heatingreactionofsufficientmagnitudeandrapiditytoproduceadetectablethermaleffect.Thespontaneousheating...