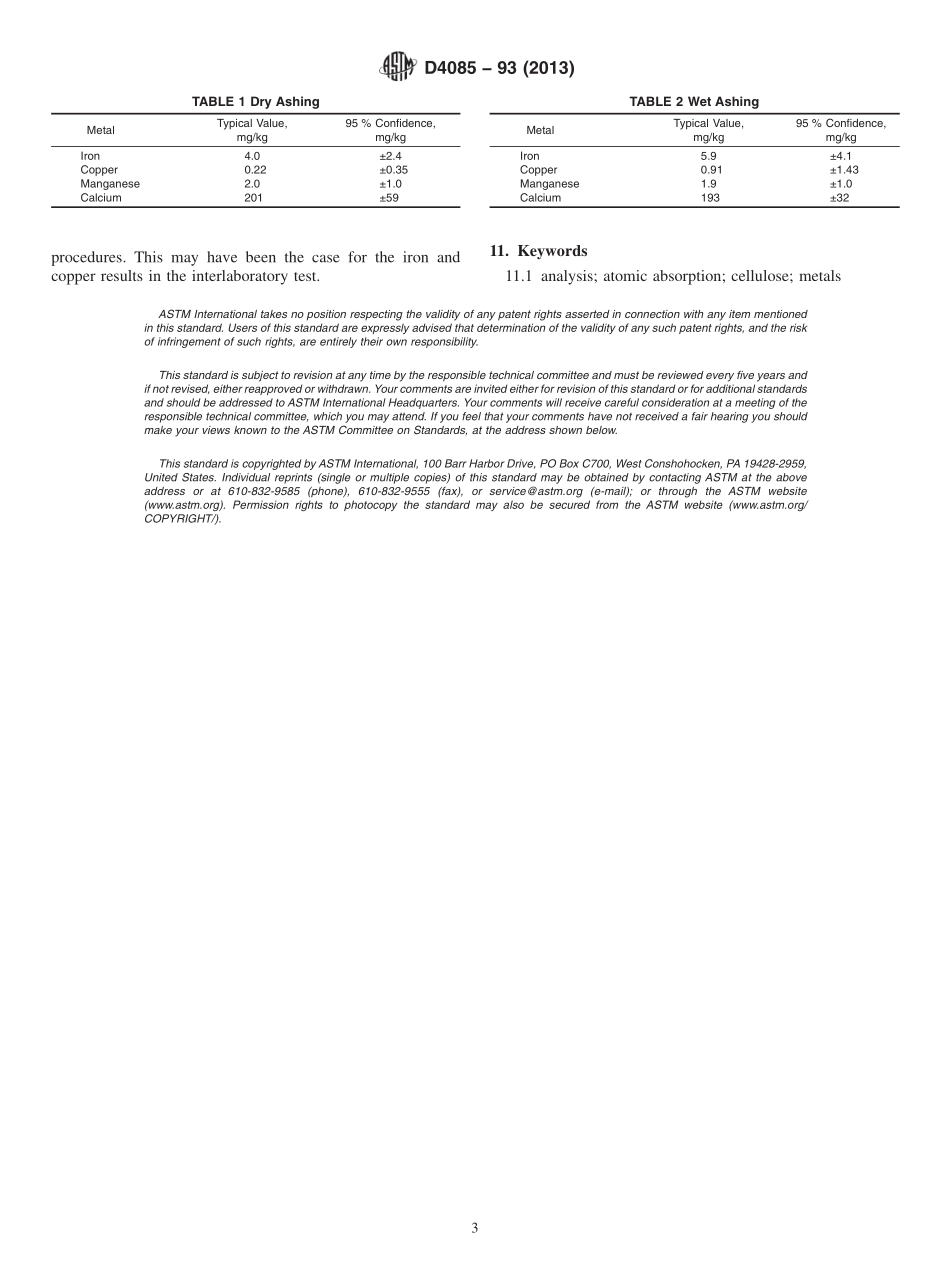
Designation:D4085−93(Reapproved2013)StandardTestMethodforMetalsinCellulosebyAtomicAbsorptionSpectrophotometry1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD4085;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationoftheiron,copper,manganese,andcalciumcontentofcellulosepulpfromwoodorcotton.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D1193SpecificationforReagentWaterD1348TestMethodsforMoistureinCelluloseD3516TestMethodsforAshingCelluloseE177PracticeforUseoftheTermsPrecisionandBiasinASTMTestMethodsE691PracticeforConductinganInterlaboratoryStudytoDeterminethePrecisionofaTestMethod3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1ThesampleisashedinaccordancewithTestMethodsD3516.3.2Thistestmethodisdependentonthefactthatmetallicelementsinthegroundstatewillabsorblightofthesamewavelengththeyemitwhenexcited.Whenradiationfromagivenexcitedelementispassedthroughaflamecontainingground-stateatomsofthatelement,theintensityofthetrans-mittedradiationwilldecreaseinproportiontotheamountoftheground-stateelementintheflame.Ahollowcathodelampwhosecathodeismadeoftheelementtobedeterminedprovidestheradiation.Themetalatomstobemeasuredareplacedinthebeamofradiationbyaspiratingthespecimenintoanoxidant-fuelflame.Amonochromatorisolatesthecharac-teristicradiationfromthehollowcathodelampandaphoto-sensitivedevicemeasurestheattenuatedtransmittedradiation.4.SignificanceandUse4.1Manganeseinpulpactsasacatalystinoxidizingcellulose.4.2Ironinpulpcanca...