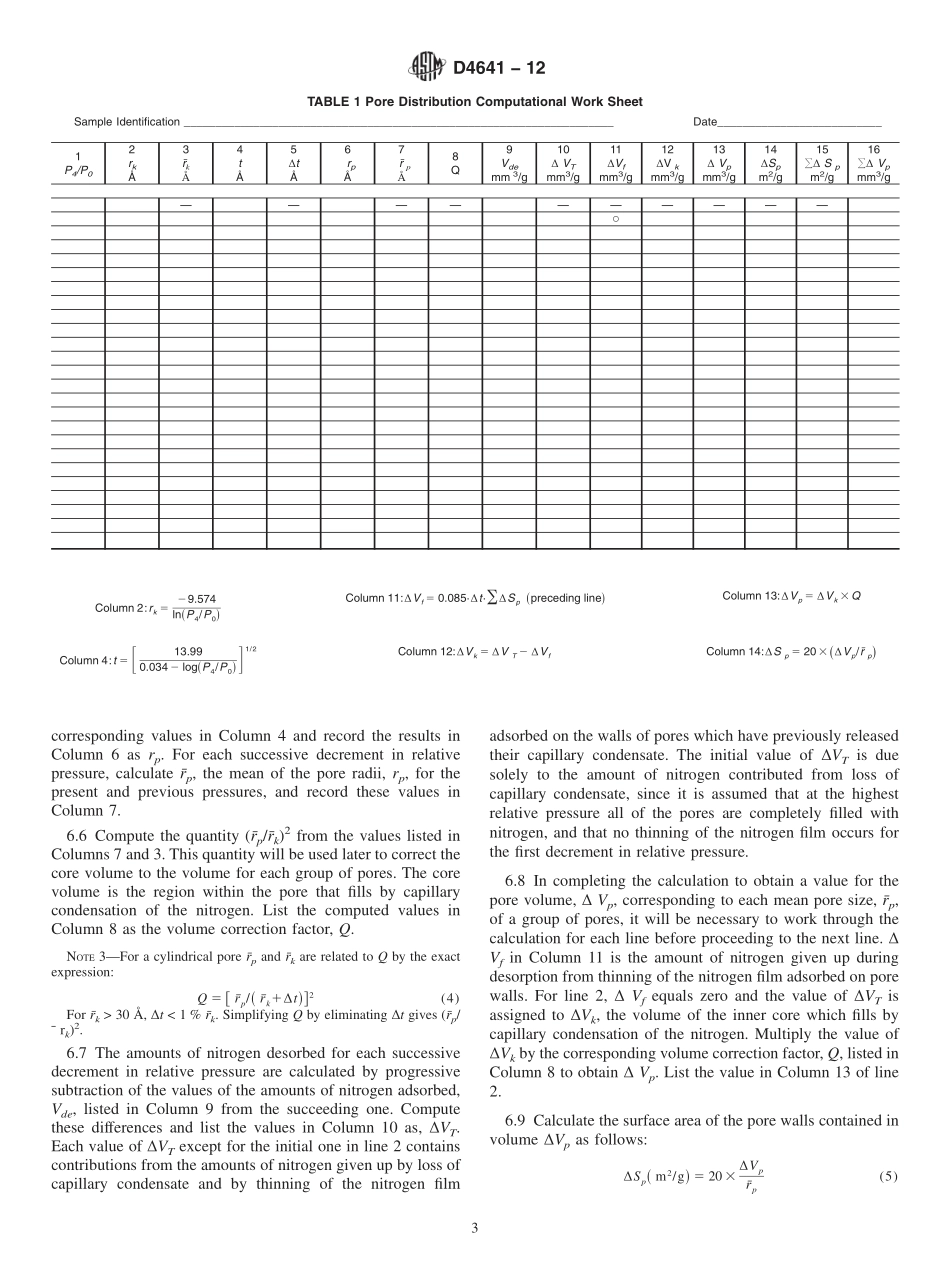
Designation:D4641−12StandardPracticeforCalculationofPoreSizeDistributionsofCatalystsandCatalystCarriersfromNitrogenDesorptionIsotherms1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD4641;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thispracticecoversthecalculationofporesizedistri-butionsforcatalystsandcatalystcarriersfromnitrogendes-orptionisotherms.Thecomputationalprocedureisparticularlyusefulfordetermininghowtheporevolumeisdistributedincatalystsamplescontainingporeswhosesizesrangefromapproximately1.5to100nm(15to1000Å)inradius.Itshouldbeusedwithcautionwhenappliedtoisothermsforsamplescontainingporesbothwithinthissizerangeandporeslargerthan100nm(1000Å)inradius.InsuchinstancestheisothermsrisesteeplynearP/Po=1andthetotalporevolumecannotbewelldefined.ThecalculationsshouldbebegunatapointontheisothermnearsaturationpreferablyinaregionnearP/Po=0.99,establishinganupperlimitontheporesizedistributionrangetobestudied.Simplificationsarenecessaryregardingporeshape.Acylindricalporemodelisassumed,andthemethodtreatstheporesasnon-intersecting,open-endedcapillarieswhichareassumedtofunctionindependentlyofeachotherduringtheadsorptionordesorptionofnitrogen.NOTE1—Thispracticeisdesignedprimarilyformanualcomputationandafewsimplificationshavebeenmadeforthispurpose.Forcomputercomputation,thesimplifiedexpressionsmaybereplacedbyexactexpres-sions.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D3766TerminologyRelatingtoCatalystsandCatalysisD4...