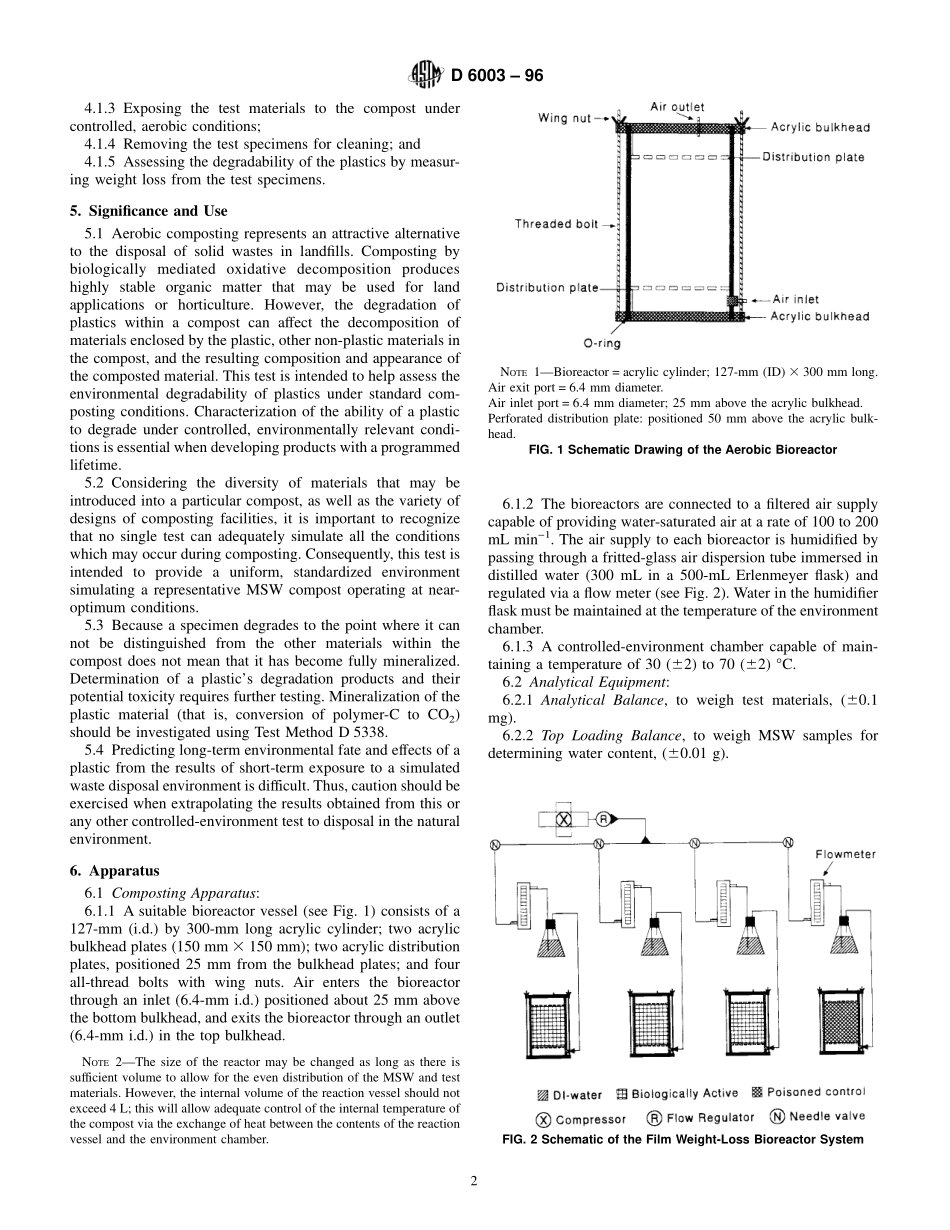
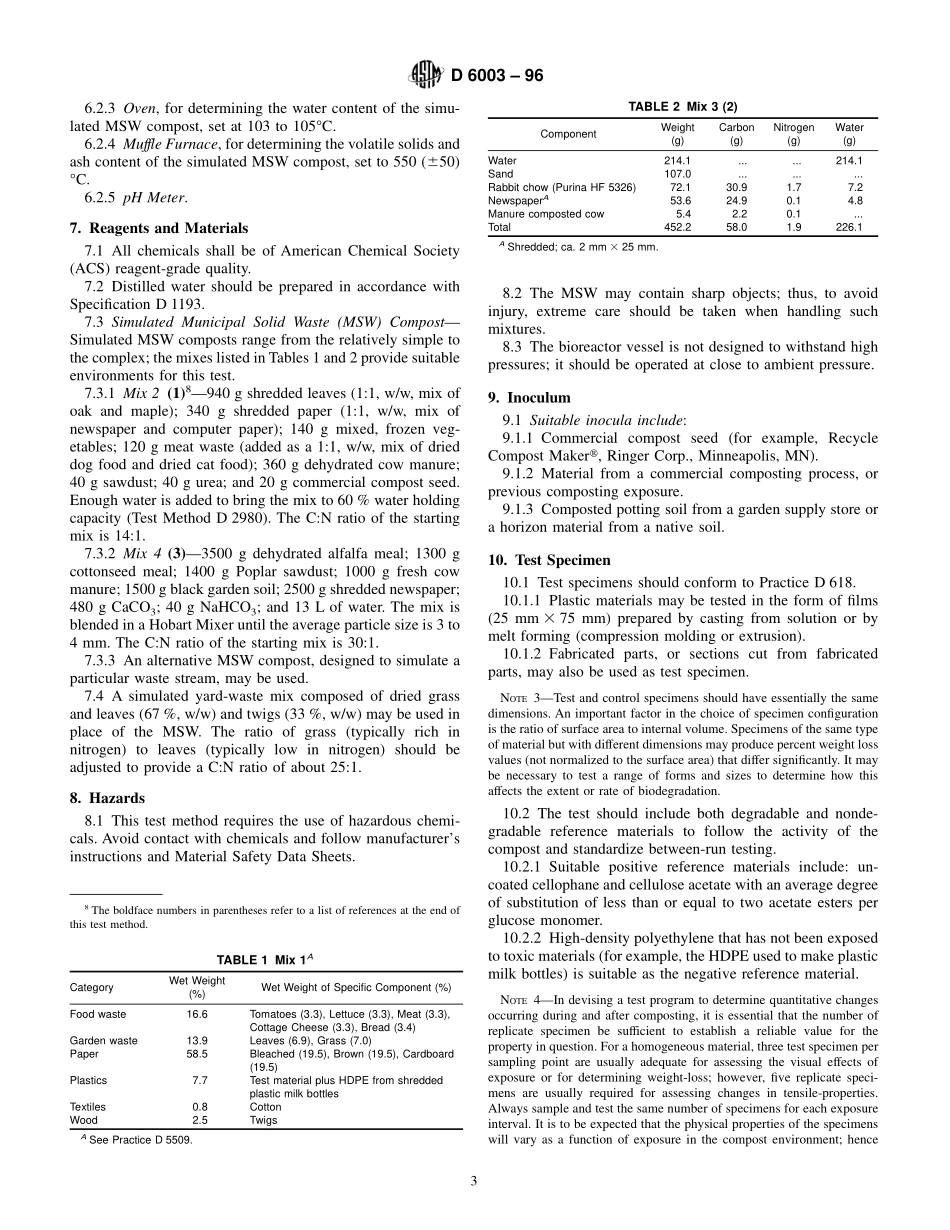
Designation:D6003–96StandardTestMethodforDeterminingWeightLossFromPlasticMaterialsExposedtoSimulatedMunicipalSolid-Waste(MSW)AerobicCompostEnvironment1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6003;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodisusedtodeterminethedegreeandrateofaerobicbiodegradationofplasticmaterialsexposedtoacontrolledcompostingenvironment.Aerobiccompostingtakesplaceinanenvironmentwheretemperature,aeration,andhumidityarecloselymonitoredandcontrolled.1.2Thetestisdesignedtodeterminethebiodegradabilityofplasticmaterials,relativetothatofastandardmaterial,inanaerobicenvironment.Aerationofthetestreactorsismaintainedataconstantratethroughoutthetestandreactorvesselsofasizenogreaterthan4-Lvolumeareusedtoensurethatthetemperatureofthevesselsisapproximatelythesameasthatofthecontrolledenvironmentchamber.1.3Biodegradabilityoftheplasticisassessedbydetermin-ingtheamountofweightlossfromsamplesexposedtoabiologicallyactivecompostrelativetotheweightlossfromsamplesexposedtoa“poisoned”control.1.4ThetestisdesignedtobeapplicabletoallplasticmaterialsthatarenotinhibitorytothebacteriaandfungipresentinthesimulatedMunicipalSolidWaste(MSW).1.5ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.NOTE1—ThereisnosimilarorequivalentISOmethod.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:D618PracticeforConditioningofPlasticsandElectricalInsulatingMaterialsforTesting2D883TerminologyRelatingtoPlastics2D1193SpecificationforReagentWater3D1898PracticeforSamplingofPlastics2D2973TestMethodforTotalNitrogeninPeatMaterials4...