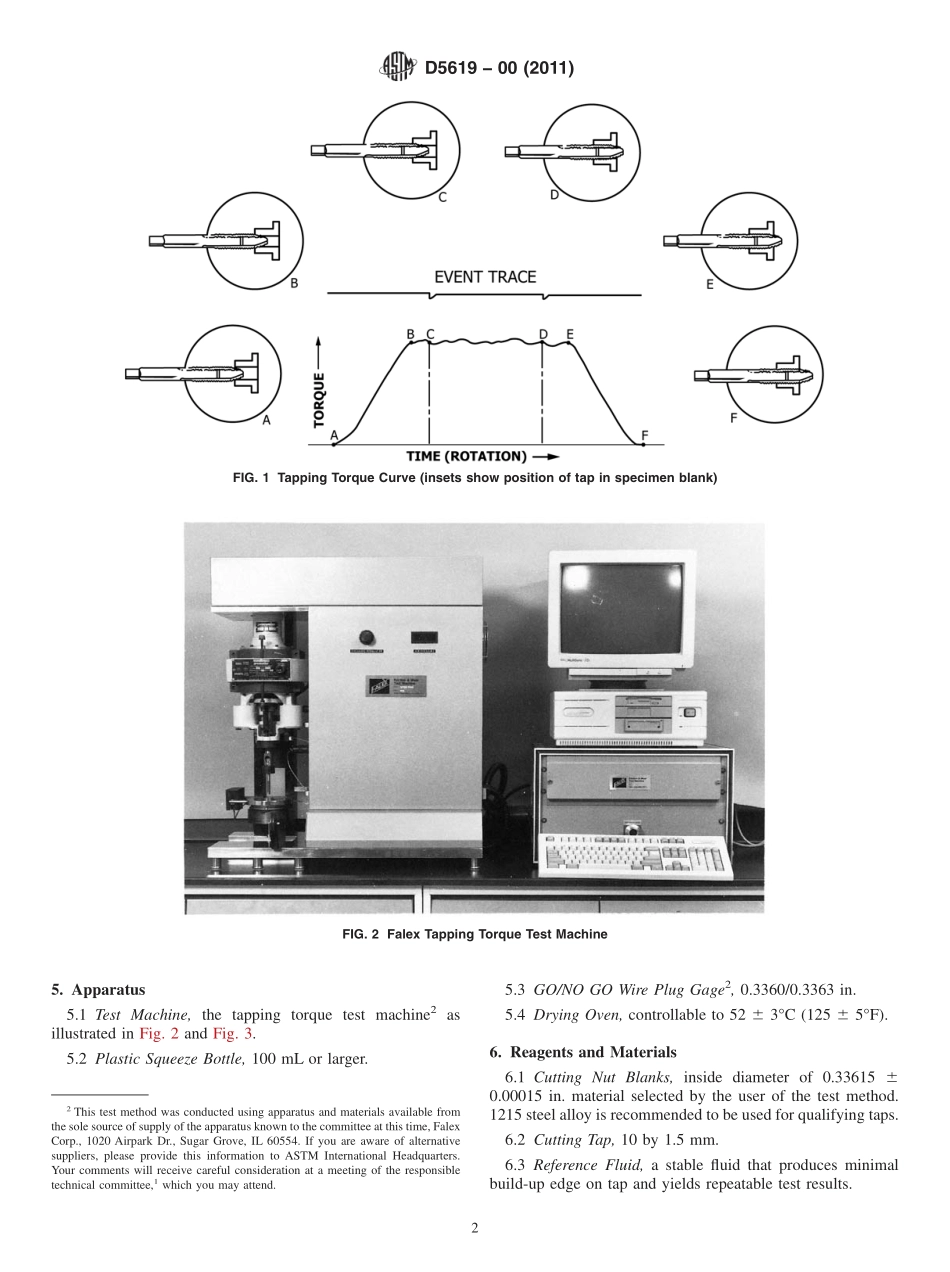
Designation:D5619−00(Reapproved2011)StandardTestMethodforComparingMetalRemovalFluidsUsingtheTappingTorqueTestMachine1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD5619;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversalaboratorytechniquetoevaluatetherelativeperformanceofmetalremovalfluidsusinganon-matrixtestprotocolusingthetappingtorquetestmachine.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.2.1Exception—Becausetheequipmentusedinthistestmethodisavailableonlyininch-poundunits,SIunitsareomittedwhenreferringtotheequipmentandthetestpieces.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.Terminology2.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:2.1.1build-upedge—atriangulardepositthatformsadja-centtothecuttingedgeonthefaceofthetoolinametalwork-ingoperation.2.1.1.1Discussion—Thehighcontactpressurebetweenthecuttingedgeofthetapandthespecimenmaterialresultsinahightemperature.Thehightemperature,theweardebris,thehighcontactpressure,andsomeoftheconstituentsofthecuttingfluidcombineatthecuttingedgeandformatriangulardeposit,referredtoasabuilt-upedge(BUE).TheBUEissustainedbythechipcurlasitispassedover,andastheBUEgrows,itisabradedbytherubbingofthechipcurl.SincetheBUEislocatedexactlywherethecurlisgenerated,itcontrib-utestothesizeofthecurl;thelargertheBUE,thelargerthediameterofthechipcurl.Asmallchipcurlwillflowsmoothlyupthefluteofthetapandwillnotaffectthetorque.However,alargecurlwilldragandjaminthefluteandwillcontributetothetappingtorque.Ifanewtapisutilized,itisnecessarytorunseveralteststorun-inth...