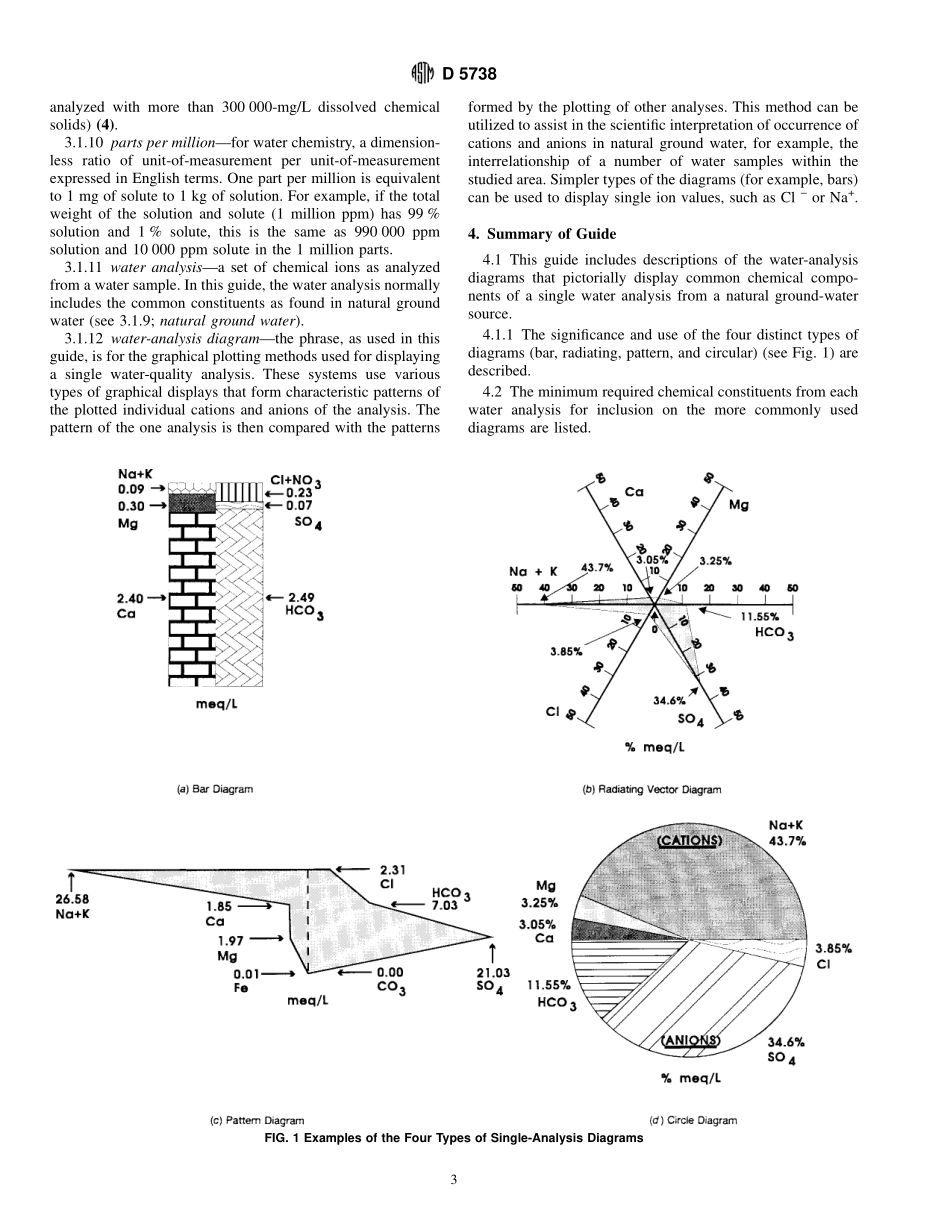
Designation:D5738–95(Reapproved2000)StandardGuideforDisplayingtheResultsofChemicalAnalysesofGroundWaterforMajorIonsandTraceElements—DiagramsforSingleAnalyses1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD5738;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(e)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thisguidecoversthecategoryofwater-analysisdia-gramsthatusepictorialorpatternmethods(forexample,bar,radiatingvectors,pattern,andcircular)asabasisfordisplayingeachoftheindividualchemicalcomponentsthatweredeter-minedfromtheanalysisofasinglesampleofnaturalgroundwater(seeTerminology).1.2Thisguideonsingle-analysisdiagramsisthesecondofseveralstandardstoinformtheprofessionalsinthefieldofhydrologywiththetraditionalgraphicalmethodsavailabletodisplayground-waterchemistry.NOTE1—Theinitialguidedescribedthecategoryofwater-analysisdiagramsthatusetwo-dimensionaltrilineargraphstodisplay,onasinglediagram,thecommonchemicalcomponentsfromtwoormorecompleteanalysesofnaturalgroundwater.1.2.1Athirdguidewillbefordiagramsbasedondataanalyticalcalculationsthatincludethosecategoriesofwateranalysisgraphswheremultipleanalysesareanalyzedstatisti-callyandtheresultsplottedonadiagram(forexample,thebox,andsoforth).1.3Numerousmethodshavebeendevelopedtodisplay,onsingle-analysesdiagrams,theionsdissolvedinwater.Thesemethodsweredevelopedbyinvestigatorstoassistintheinterpretationoftheoriginoftheionsinthewaterandtosimplifythecomparisonofanalyses,onewithanother.1.4Thisguidepresentsacompilationofdiagramsfromanumberofauthorsthatallowsfortransformationofnumericaldataintovisual,usableforms.Itisnotaguidetoselectionoruse.Thatchoiceisprogramorprojectspecific.NOTE2—UseoftradenamesinthisguideisforidentificationpurposesonlyanddoesnotconstituteendorsementbyASTM.1.5Thisguideoffersanorganizedcollectionofinformationoraseriesofoptionsanddoesnotrecommend...