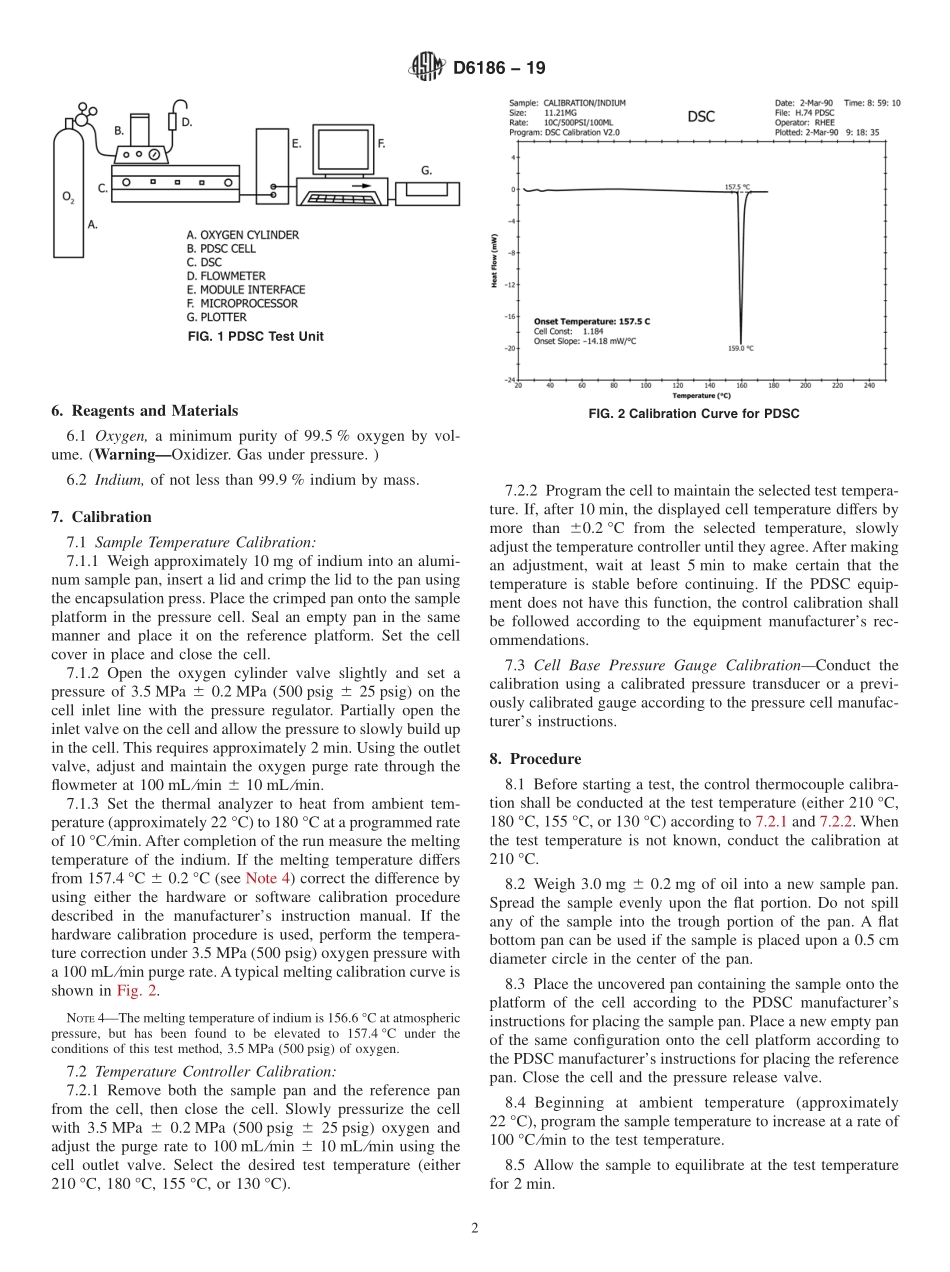
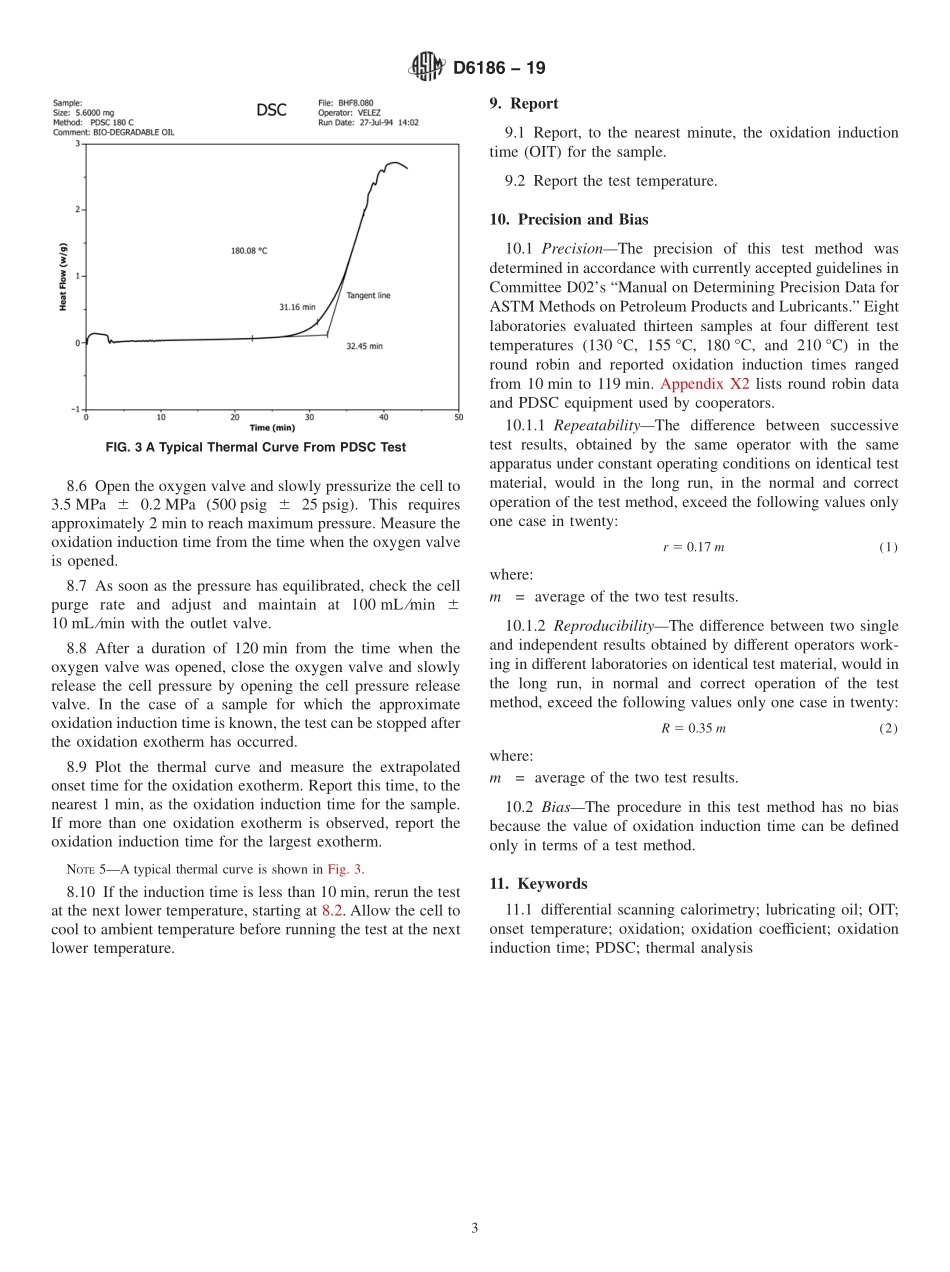
Designation:D6186−19StandardTestMethodforOxidationInductionTimeofLubricatingOilsbyPressureDifferentialScanningCalorimetry(PDSC)1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6186;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope*1.1Thistestmethodcoversthedeterminationofoxidationinductiontimeoflubricatingoilssubjectedtooxygenat3.5MPa(500psig)andtemperaturesbetween130°Cand210°C.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.2.1Exception—PressuremeasurementappearsinMPawithpsigprovidedinparenthesesforinformationonly.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafety,health,andenvironmentalpracticesanddeter-minetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.4Thisinternationalstandardwasdevelopedinaccor-dancewithinternationallyrecognizedprinciplesonstandard-izationestablishedintheDecisiononPrinciplesfortheDevelopmentofInternationalStandards,GuidesandRecom-mendationsissuedbytheWorldTradeOrganizationTechnicalBarrierstoTrade(TBT)Committee.2.Terminology2.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:2.1.1extrapolatedonsettime,n—atimedeterminedonathermalcurve,astheintersectionoftheextrapolatedbaselineandalinetangenttotheoxidationexothermconstructedatitsmaximumrate.2.1.2oxidationinductiontime,(OIT),n—aperiodoftimeduringwhichtheoxidationrateacceleratesfromzerotoamaximumandwhichcorrespondstotheextrapolatedonsettime.2.1.3thermalcurve,n—agraphofsampleheatflowversustime.3.SummaryofTestMethod3.1Asmallquantityofoilisweighedintoasamplepanandplacedinatestcell.Thecellisheatedtoaspecifiedtemperatureandthenpressurizedwithoxygen.Thecellisheldataregulatedtemperatureandpressureuntilanexothermicreactionocc...