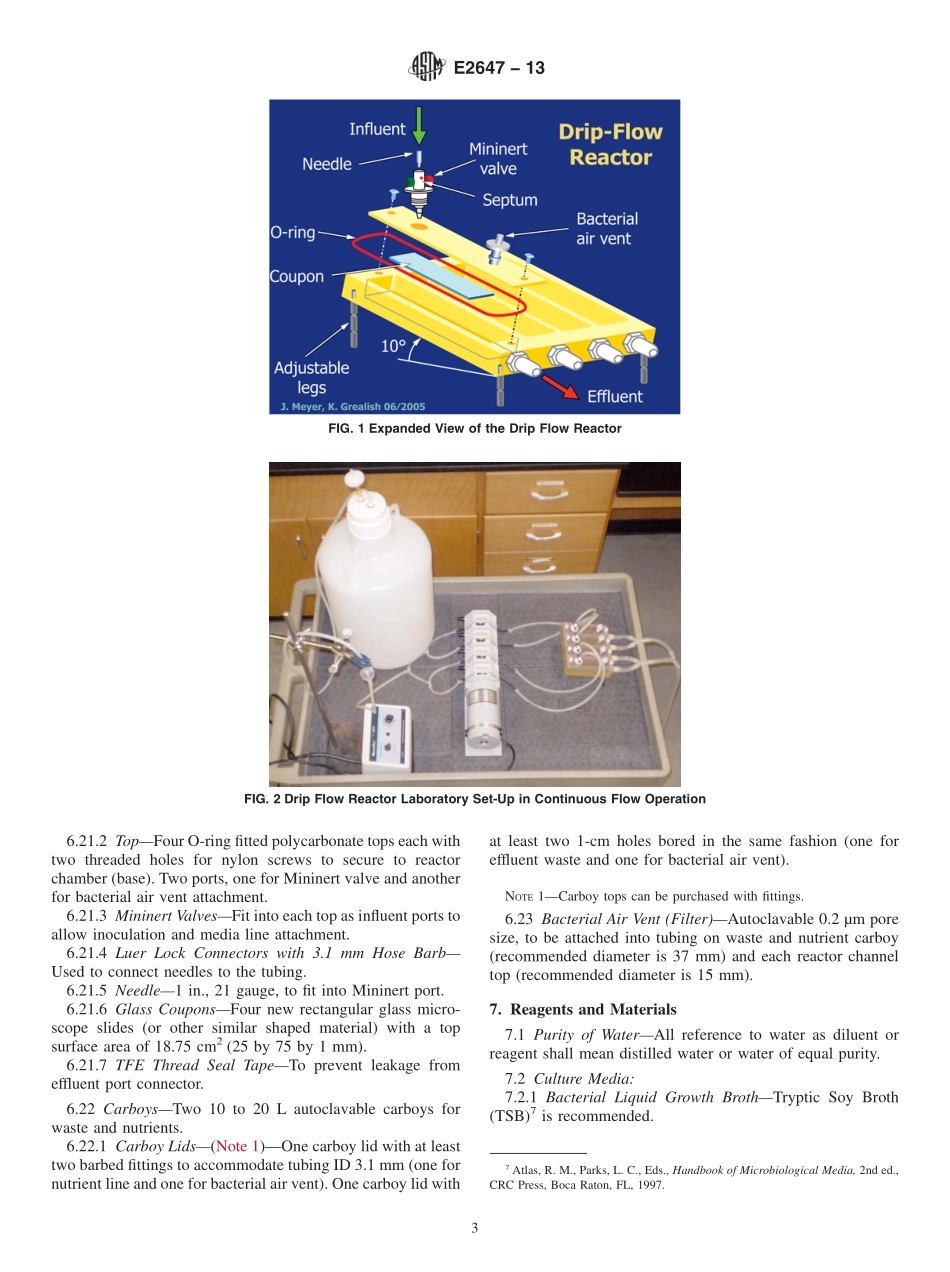
Designation:E2647−13StandardTestMethodforQuantificationofPseudomonasaeruginosaBiofilmGrownUsingDripFlowBiofilmReactorwithLowShearandContinuousFlow1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationE2647;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodspecifiestheoperationalparametersrequiredtogrowarepeatable2Pseudomonasaeruginosabio-filmclosetotheair/liquidinterfaceinareactorwithacontinuousflowofnutrientsunderlowfluidshearconditions.Theresultingbiofilmisrepresentativeofgeneralizedsituationswherebiofilmexistsattheair/liquidinterfaceunderlowfluidshearratherthanrepresentativeofoneparticularenvironment.1.2Thistestmethodusesthedripflowreactor.Thedripflowreactor(DFR)isaplugflowreactorwithlaminarflowresultinginlowfluidshear.Thereactorisversatileandmayalsobeusedforgrowingand/orcharacterizingbiofilmsofdifferentspecies,althoughthiswillrequirechangingtheoperationalparameterstooptimizethemethodbaseduponthegrowthrequirementsoftheneworganism.1.3Thistestmethoddescribeshowtosampleandanalyzebiofilmforviablecells.Biofilmpopulationdensityisrecordedaslogcolonyformingunitspersurfacearea.1.4Basicmicrobiologytrainingisrequiredtoperformthistestmethod.1.5ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.6Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:3D5465PracticeforDeterminingMicrobialColonyCountsfromWatersAnalyzedbyPlatingMethods2.2OtherStandard:Method9050C.1.aBufferedDilutionWaterPreparation,accordingtoEatonetal43.Terminology3.1Definitions:3.1.1biofilm,n—microorganismslivinginaself...