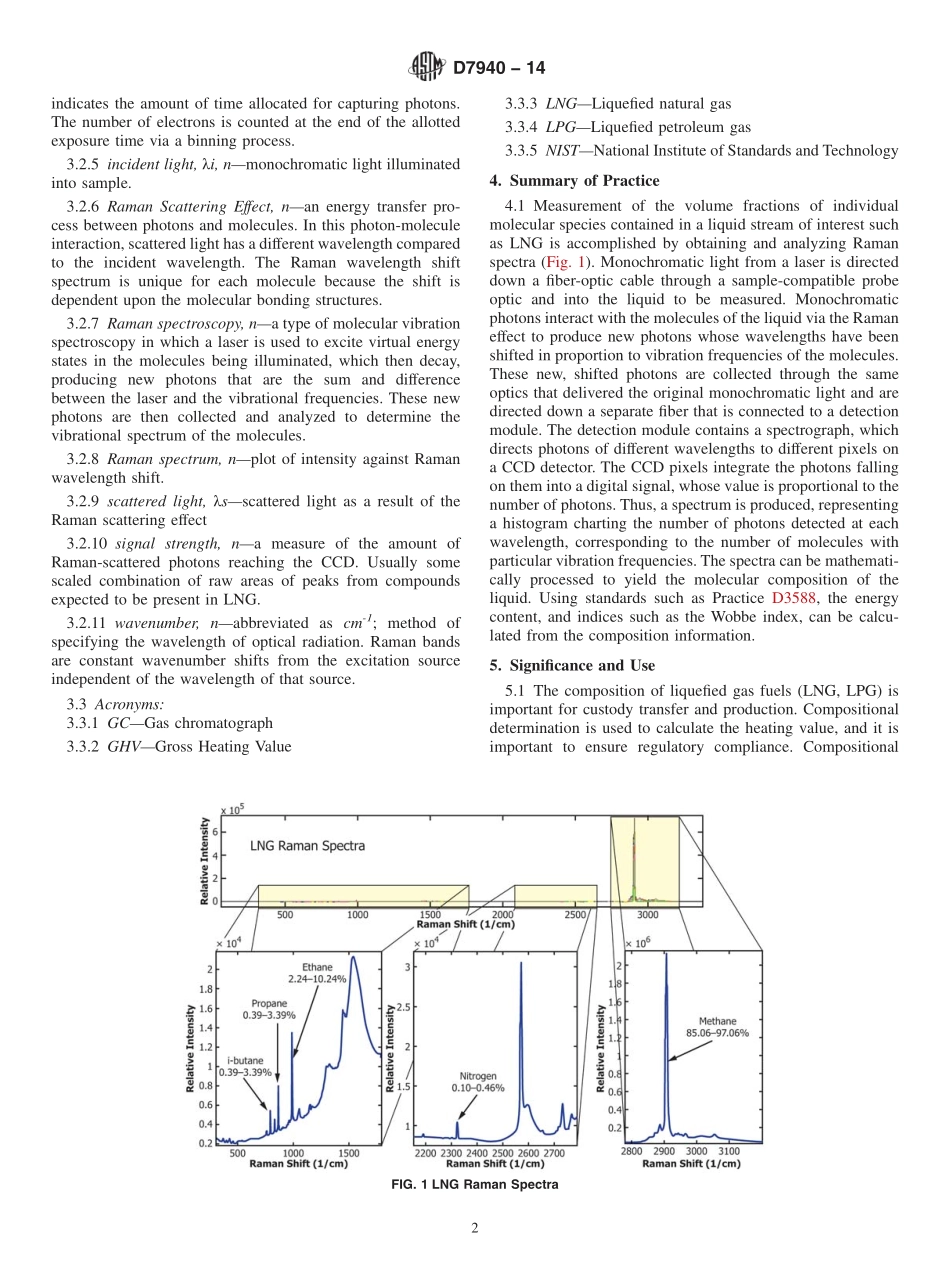
Designation:D7940−14StandardPracticeforAnalysisofLiquefiedNaturalGas(LNG)byFiber-CoupledRamanSpectroscopy1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD7940;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thisstandardpracticeisforbothon-lineandlaboratoryinstrument-baseddeterminationofcompositionforliquefiednaturalgas(LNG)usingRamanspectroscopy.Thebasicmethodologycanalsobeappliedtootherlighthydrocarbonmixturesineitherliquidorgaseousstates,iftheneedsoftheapplicationaremet,althoughtherestofthispracticerefersspecificallytoliquids.Fromthecomposition,gaspropertiessuchasheatingvalueandtheWobbeindexmaybecalculated.ThecomponentscommonlydeterminedaccordingtothistestmethodareCH4,C2H6,C3H8,i-C4H10,n-C4H10,iC5H12,n-C5H12,neo-C5H12,N2,O2.Theapplicablerangeofthisstandardis200ppmvto100mol%.ComponentsheavierthanC5arenotmeasuredaspartofthispractice.NOTE1—Ramanspectroscopydoesnotdirectlyquantifythecomponentpercentagesofnoblegases,however,inertscanbecalculatedindirectlybysubtractingthesumoftheotherspeciesfrom100%.1.2ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Nootherunitsofmeasurementareincludedinthisstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D3588PracticeforCalculatingHeatValue,CompressibilityFactor,andRelativeDensityofGaseousFuelsD4150TerminologyRelatingtoGaseousFuelsE691PracticeforConductinganInterlaboratoryStudytoDeterminethePrecisionofaTestMethodD1945TestMethodforAnalysisofNaturalGasbyGasChromatographyD1946PracticeforAnalysisofReformedGasbyGasChromatographyD7833TestMethodforDeterminationofHydrocarbonsandNon-Hydroc...