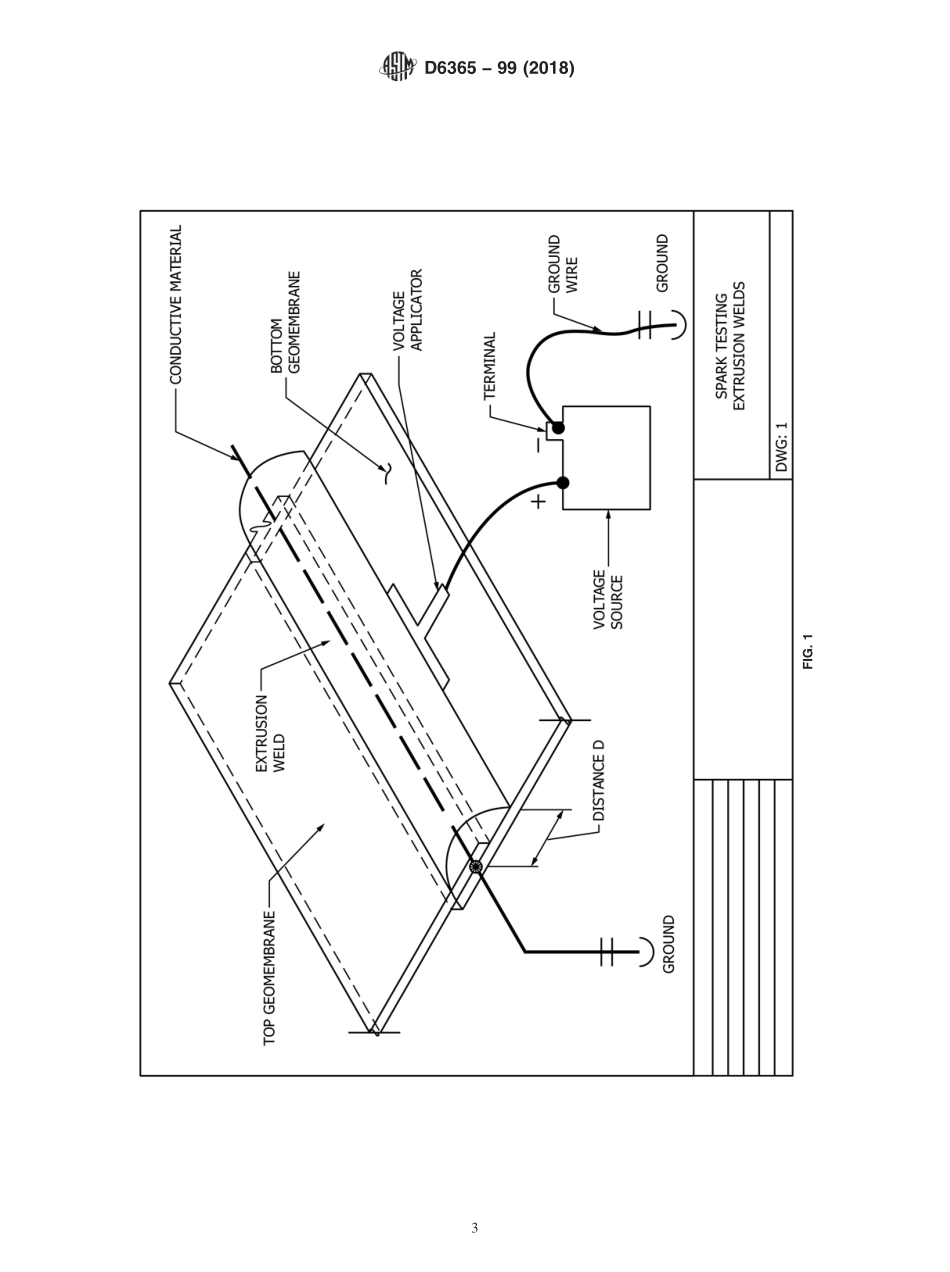
Designation:D6365−99(Reapproved2018)StandardPracticeforNondestructiveTestingofGeomembraneSeamsUsingtheSparkTest1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD6365;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thispracticecoversthenondestructivetestingoffieldseamsingeomembranesusingthesparktest.Asuspectareaisindicatedbythegenerationofaspark.Thetestisapplicabletoseamsmadebytheextrusionmethod,seamsmadebyusingweldingtape(astripofthesametypeofmaterialasthegeomembrane,thatisweldedoveradjacentsectionsofgeomembranetocreateaseam),orseamswhereitispracticaltoinsertaconductivematerialintheseamjustpriortoorduringfabrication.1.2Thesparktestmayproduceanelectricalsparkandthereforecanonlybeusedwhereanelectricalsparkwouldnotcreateahazard.1.3Unlessthevoltagesanddistancesprescribedarecare-fullyadheredto,a“falsepositive”indicationmayresult.Thisfalsepositiveoccurswhenthearcdistanceistoolargeforthevoltageappliedatthetimeandconditionsoftesting.1.4ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.5Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafety,health,andenvironmentalpracticesanddeter-minetheapplicabilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.1.6Thisinternationalstandardwasdevelopedinaccor-dancewithinternationallyrecognizedprinciplesonstandard-izationestablishedintheDecisiononPrinciplesfortheDevelopmentofInternationalStandards,GuidesandRecom-mendationsissuedbytheWorldTradeOrganizationTechnicalBarrierstoTrade(TBT)Committee.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D4439TerminologyforGeosyntheticsD4491/D4491MTestMethodsforWaterPermeabilityofGeotextilesbyPermittivity3.Terminology3.1Definitions:3.1.1geomembrane,n—anessen...