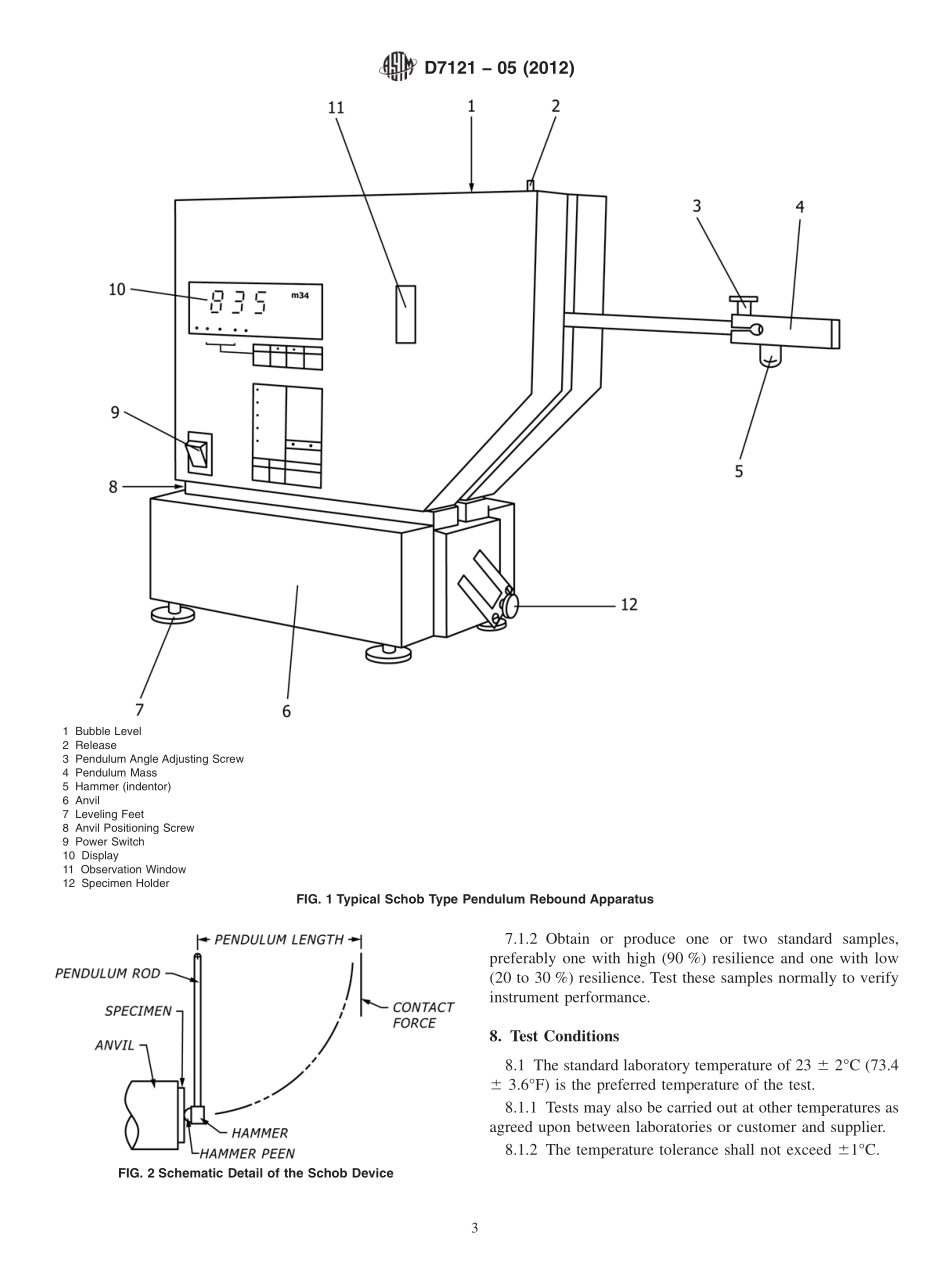
Designation:D7121−05(Reapproved2012)StandardTestMethodforRubberProperty—ResilienceUsingSchobTypeReboundPendulum1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD7121;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoversameansofdeterminingtheresilienceofrubber,withinarangeofimpactstrainandstrainrate,bymeansoftheimpactingandmeasuringapparatusconformingtotherequirementsdescribedinthistestmethod.1.2Thistestmethodisapplicabletothermosetrubbersandthermoplasticelastomers,thehardnessofwhich,atthespeci-fiedtesttemperatures,liesbetween30and85IRHD(seeTestMethodD1415)orA/30andA/85(seeTestMethodD2240).Itmayalsobeapplicabletosomepolyester,polyetherfoam,andplasticfoammaterials.1.3Allmaterials,instruments,orequipmentusedforthedeterminationofmass,force,ordimensionshallhavetrace-abilitytotheNationalInstituteforStandardsandTechnology,orotherinternationallyrecognizedorganizationparallelinnature.1.4ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.1.5Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D832PracticeforRubberConditioningForLowTempera-tureTestingD1349PracticeforRubber—StandardConditionsforTest-ingD1415TestMethodforRubberProperty—InternationalHardnessD2240TestMethodforRubberProperty—DurometerHard-nessD3182PracticeforRubber—Materials,Equipment,andPro-ceduresforMixingStandardCompoundsandPreparingStandardVulcanizedSheetsD3183PracticeforRubber—PreparationofPiecesforTestPurposesfromProductsD4483PracticeforEvaluatingPrecisionforTestMethodStandardsintheRubberandCarbonBlackManu...